Introduction
In this serial of articles, I will share some knowledge I learnt recently in using WebSocket in .NET 4.5.
Protocol Overview
The WebSocket protocol was standardized by IETF as
RFC 6455. We could find introductions and more information on
Wikipedia and W3C.
A WebSocket connection is established by a HTTP handshake (prefixed by "ws://" or "wss://") between the client and the server. For example (from Wikipedia),
the client sends a request:
GET /mychat HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Key: x3JJHMbDL1EzLkh9GBhXDw==
Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
Origin: http://example.com
Then the server sends a response to accept the connection:
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Accept: HSmrc0sMlYUkAGmm5OPpG2HaGWk=
Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat
"Sec-WebSocket-Key" and "Sec-WebSocket-Accept" are used for confirming the connection between the client and the server through an algorithm of key validation.
"Sec-WebSocket-Version" is used by the client to tell the server which version of the protocol is supported on the client side. No backward compatibility is required in the standard. The server could send a version list
through this header if the client specified version is not supported by the server. "13" (1.3) is a milestone version of WebSocket.
"Sec-WebSocket-Protocol" is used to confirm the customized sub-protocol of the connection. This enables both selecting a sub-protocol from the client side and being sure that the server agreed to serve that sub-protocol.
For more details about the protocol, please refer to
RFC 6455.
WebSocket in .NET
Microsoft .NET 4.5 provides several ways in using WebSocket.
On the server side, we can host our WebSocket server through any one of the ways below:
- Using
HttpContext.AcceptWebSocketRequest - Creating a WCF service with
CallbackContract and the new netHttpBinding - Using
WebSocketHandler or
WebSocketHost provided in Microsoft.WebSockets.dll
On the client web side, HTML 5 provides WebSocket APIs and jQuery
wraps those APIs for easier usage.
If we want to create a client side application, we can do that through either of the ways below:
- Using the
ClientWebSocket class (System.Net.WebSockets). - Creating a WCF client and referencing the WCF service which supports WebSocket connection.
NOTE: We can only use .NET WebSocket on Windows 8, Windows Server
2012 and above, including both server-side and client-side applications. And the
web server must be IIS 8 and above.
IIS 8 Express which is also packaged in Visual Studio 2012 does NOT support
WebSocket at present. I hope Microsoft will add support in future. <o:p>
HTML 5 WebSocket API has no limitation on OS platform. The
only limitation is the browser versions. Internet Explorer started supporting HTML 5 WebSocket since IE 10.
Preparation
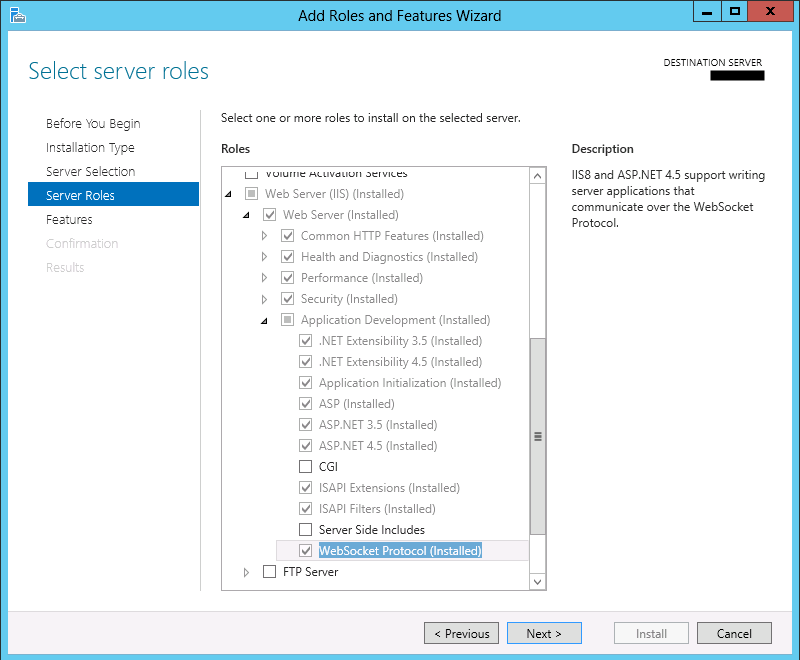
To enable WebSocket on the server side, you need to install WebSocket Protocol for IIS 8. On Windows Server 2012, you could do that through Server Manager -> Manage -> Add Roles and Features. Expand the Web Server (IIS) role and check Web Server -> Application Development -> WebSocket Protocol. You may be asked to install dependencies and just allow them. Then install all your selections. Windows 8 should be similar.
You might meet an exception when you test your WebSocket applications. The exception says:
"Could not load type ‘System.ServiceModel.Activation.HttpModule’
from assembly 'System.ServiceModel, Version=3.0.0.0, Culture=neutral,
PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089'"
Please refer to this article for solutions.
Summary
Next in Part 2, I will demonstrate how to use HttpContext.AcceptWebSocketRequest in a traditional ASP.NET or MVC 4 web application.
Related Links
Using WebSocket in .NET 4.5:
