Automate the process of set value to the Excel cells, assigning a cell
name that match the query result column name, leaving the end user the
possibility to change the layout template.
Introduction
For
work activity, I need to create a report like in the figure below:
The
template can be modified from the user, changing the cell's position, removing cells
and adding new cells that will get the value from the query result.
Desiderata
I want to
have the possibility to define a cell name equal to the column name returned
from a query result, so I will be able to get the cell matching its name with
the column name in query result. In this way I can loop over every column in
the query result and get the Excel cells, independently by its position:
foreach (DataRow dataRow in dataTable.Rows)
{
foreach (DataColumn dataColumn in dataTable.Columns)
{
Excel.Range cell = ws.Cells[dataColumn.ColumnName];
cell.Value = dataRow[dataColumn.ColumnName];
}
} The above code, unfortunately, does not work.
Solution
To get the desired result, we must use the Evaluate() method,
defined in the WorkSheet Excel object. This method takes a string and start looking for a cell (or a range of cells) that match that string.
When evaluate positively, it returns an instance of an Excel.Range object, that is the requested cell:
foreach (DataRow dataRow in dataTable.Rows)
{
foreach (DataColumn dataColumn in dataTable.Columns)
{
Excel.Range cell = ws.Evaluate(dataColumn.ColumnName);
if (cell != null) cell.Value = dataRow[dataColumn.ColumnName];
}
} Define cell name
To correctly run the above code, we must specify the cell names.
To do that, right click on the cell and choose the Define Name item menu, like show below:

This will open a popup window where you can define the cell name:

The Scope option, give you the possibility to choose the name visibility: this name must be unique in the chosen scope: unique per entire
Excel document (Workbook) or unique per sheet (worksheet). Once you have assigned the cell name, you can see it in the left up corner:

After you have set the cell name, it can still be get using the classic mode that is use the coordinates, like show below:
Excel.Worksheet workSheet = workbookReport.Worksheets[1];
Excel.Range cell = workSheet.Cells[1, 2];
Delete or change the cell name
To remove a cell name or simply change it, you must use the Name Manager menu item under the Formulas tab:

This will open the following page that reports all the cell’s names allowing you to delete or change their names:

Choosing a name in the list, you can modify it simply clicking on the Edit or Delete button.
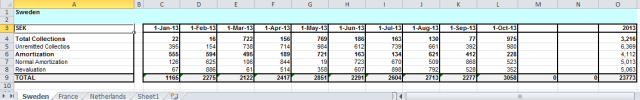
Create tabular report
Starting from a query result, loaded within a DataTable:

We want to create an Excel tabular report like:

As you can see, we need a sort of Pivot table, because we have the records organized row by row. We can easily solve it, applying a cell name that is related
to the month: so, for every cell we can assign a name that is identic to the DataTable column’s name plus the month number:

Now, we can simply use the following code to get the automatic set for every cell matching the datatable’s columns name:
foreach (DataRow dataRow in dataTable.Rows)
{
DateTime period = Convert.ToDateTime(dataRow["PERIOD_START_DATE"]);
foreach (DataColumn dataColumn in dataTable.Columns)
{
string cellName = dataColumn.ColumnName + "_" + period.Month.ToString("d2"));
Excel.Range cell = workSheet.Evaluate(cellName) as Excel.Range;
if (cell != null) cell.Value = value;
}
}
Attached project
The attached project in this article, include an Excel file used like template. In this template I have defined the cell names, according to the DataTable’s
column name: using this template I create a new Excel report on which I set the cell's values.
Requirements
The project must reference Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.
