The Project on GitHub MCIplayer
(If you can't extract the files, just change the extension from .zip to .rar.)
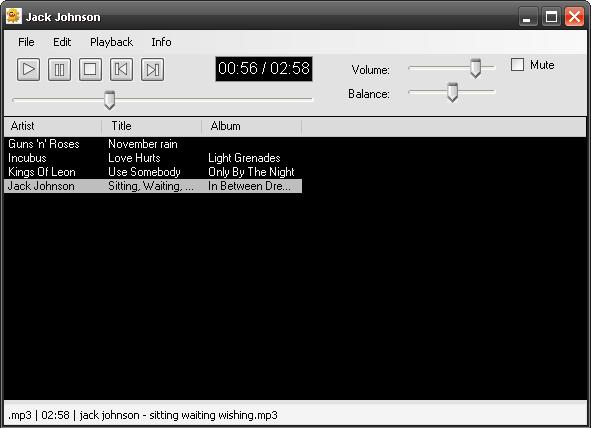
Introduction
This is a very simple music player that uses the MCI multimedia command string to interact with the device. The MCI interface is fairly powerful, and can be very useful. You can play almost any audio file (video files too, but I haven't covered this part in my player) including MP3, Wave, MIDI, ASF, and more.
Background
This link helped me a lot. It was very useful to get started with MCI.
You can find the commands used in this application here.
Using the code
The application has a player class that handles all the interactions with the MCI device. A tag reader class reads specific information about the sound file (title, artist, album, and so on). And, the environment file handles the main form.
Player class
Declaration of variables used in the Player class:
Random randomNumber;
private StringBuilder msg;
private StringBuilder returnData;
private int error;
private string Pcommand;
private ListView playlist;
public int NowPlaying { get; set; }
public bool Paused { get; set; }
public bool Loop { get; set; }
public bool Shuffle { get; set; }
First, there is an object of type Random that returns a random number that I'm using for the shuffle mode. Two StringBuilders are used by the MCI device: the first (msg) is used by mciGetErrorString to get the message for the given int value that mciSendString returns (mciSendString returns an integer value, 0 for a successful operation and a number for a failed operation). returnData is used when I'm expecting a return message (when trying to get the status: "playing", "paused", and so on). Pcommand is just a string that holds the command that I'm sending via mciSendString. The ListView playlist is a very important variable because it holds a list of all file paths in the playlist and I access all file paths via the index (0 for the first song, 1 for the second, and so on). NowPlaying holds the index of the ListView playlist that represents the song that's playing. The boolean variables are just used to watch the status of the player.
DllImport
[DllImport("winmm.dll")]
private static extern int mciSendString(string strCommand,
StringBuilder strReturn, int iReturnLength, IntPtr hwndCallback);
[DllImport("winmm.dll")]
public static extern int mciGetErrorString(int errCode,
StringBuilder errMsg, int buflen);
You must import the MCI methods.
Class constructor
public Player(ListView pl)
{
randomNumber = new Random();
playlist = pl;
NowPlaying = 0;
Loop = false;
Shuffle = true;
Paused= false;
msg = new StringBuilder(128);
returnData = new StringBuilder(128);
}
You must pass a reference to a ListView when creating a new player class, and this is the connection between the form and the class. All other variables are set appropriate for the needs.
Close and Open methods
public void Close()
{
Pcommand = "close MediaFile";
mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
}
public bool Open(string sFileName)
{
Close();
Pcommand = "open \"" + sFileName +
"\" type mpegvideo alias MediaFile";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
if (error != 0)
{
Pcommand = "open \"" + sFileName +
"\" alias MediaFile";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
if (error == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
else
return true;
}
The Close method does nothing special, it just closes the device that's open. Even if trying to close an already closed device, nothing bad will happen.
The Open method takes a string as input (argument), and it will try to open the given file path. But first, it closes the device just to be sure that there won't be two songs running at the same time. In the next step, it tries to open the file as type mpegvideo. The mciSendString method will return 0 for a successful operation, and a non-zero value for a failed operation. When an operation fails, in the next step, the MCI device decides which type the file is. Even if this operation fails, it returns false. For all other solutions, it returns true.
Play method
public bool Play(int track)
{
if (Open(playlist.Items[track].SubItems[1].Text))
{
Pcommand = "play MediaFile";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
if (error == 0)
{
NowPlaying = track;
return true;
}
else
{
Close();
return false;
}
}
else
return false;
}
The Play method takes an integer value as argument that represents the song in the playlist. It passes the file path of the song to the Open method. If it returns true, then the operation was successful and the song was loaded into the MCI device, else it failed to load the song and it will return false and won't play the song. In the next step, it sends the play command and tries to play the song. If MCI returns 0, the operation was successful, it sets the NowPlaying variable to the index of the track that is now playing, and returns 0, else if it doesn't return 0, it closes the device that was successfully opened but couldn't be played, and returns false.
Pause, Stop, Resume methods
public void Pause()
{
if (Paused)
{
Resume();
Paused = false;
}
else if(IsPlaying())
{
Pcommand = "pause MediaFile";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
Paused = true;
}
}
public void Stop()
{
Pcommand = "stop MediaFile";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
Paused = false;
Close();
}
public void Resume()
{
Pcommand = "resume MediaFile";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
}
The Pause method first checks if the paused variable is true (if it's true, then the player is paused). Then, it calls the Resume method and sets the paused variable to false (because the player isn't paused anymore). If the player isn't paused, then it checks if the player is playing (I'll explain this method in just a moment). If it's playing, then it pauses the player and sets the paused variable to true.
The Stop method just stops the device, sets the paused variable to false, and closes the open MCI device.
The Resume method just continues with playing when the player is paused, and is called only from the Pause method.
IsPlaying method
public bool IsPlaying()
{
Pcommand = "status MediaFile mode";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, returnData, 128, IntPtr.Zero);
if (returnData.Length == 7 &&
returnData.ToString().Substring(0, 7) == "playing")
return true;
else
return false;
}
This method sends the status mode command to the MCI device. The return value is set in the returnData variable. The value in the returnData variable can be playing, paused, open ... and so on, but I only need information whether the device is playing or not. So, it checks if the string length is equal to 7 and if the value in the string is "playing". If so, then it returns true; for all other situations, it returns false.
Song length and current position
public int GetCurentMilisecond()
{
Pcommand = "status MediaFile position";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, returnData,
returnData.Capacity, IntPtr.Zero);
return int.Parse(returnData.ToString());
}
public void SetPosition(int miliseconds)
{
if (IsPlaying())
{
Pcommand = "play MediaFile from " + miliseconds.ToString();
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
}
else
{
Pcommand = "seek MediaFile to " + miliseconds.ToString();
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
}
}
public int GetSongLenght()
{
if (IsPlaying())
{
Pcommand = "status MediaFile length";
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, returnData, returnData.Capacity, IntPtr.Zero);
return int.Parse(returnData.ToString());
}
else
return 0;
}
GetCurrentMilisecond returns the position of the song in milliseconds. It sends the status position command and sets the return message in the returnData variable. The message is a string, so it must be parsed into an integer.
The SetPosition method takes an integer argument that represents the position in milliseconds to that the song should be set. It first checks if the song is playing. If it's playing, then it sends the play from command with the value in milliseconds. Else, it sends the seek command that just moves the position of the song to the given value, but it won't play from there (this is useful if the song is paused or something like that).
The GetSongLength method returns the length of the song in milliseconds. First, it checks if the song is playing; if it's playing, then it sends the status length command and sets the return value into the returnData variable. Then, it must be parsed into an integer.
Volume and Balance
public bool SetVolume(int volume)
{
if (volume >= 0 && volume <= 1000)
{
Pcommand = "setaudio MediaFile volume to " + volume.ToString();
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public bool SetBalance(int balance)
{
if (balance >= 0 && balance <= 1000)
{
Pcommand = "setaudio MediaFile left volume to " + (1000 - balance).ToString();
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
Pcommand = "setaudio MediaFile right volume to " + balance.ToString();
error = mciSendString(Pcommand, null, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
Both methods take an integer value as argument that represents the volume/balance to that the player should be set. The value can be between 0 and 1000. If the value is in between these values, then the method sends the command and returns true; else it returns false.
GetSong method
public int GetSong(bool previous)
{
if (Shuffle)
{
int i;
if (playlist.Items.Count == 1)
return 0;
while (true)
{
i = randomNumber.Next(playlist.Items.Count);
if (i != NowPlaying)
return i;
}
}
else if (Loop && !previous)
{
if (NowPlaying == playlist.Items.Count - 1)
return 0;
else
return NowPlaying + 1;
}
else if (Loop && previous)
{
if (NowPlaying == 0)
return playlist.Items.Count - 1;
else
return NowPlaying - 1;
}
else
{
if (previous)
{
if (NowPlaying != 0)
return NowPlaying - 1;
else
return 0;
}
else
{
if (NowPlaying != playlist.Items.Count - 1)
return NowPlaying + 1;
else
return 0;
}
}
}
The method takes a bool argument: true if the player should go backwards, and false if it should go forwards. If shuffle is on, then it first checks if there is only one song in the playlist and returns this one if it's so. If there is more than one song, it returns a random value in between 0 and playlist.Items.Count. But I've butted it all into a while loop to avoid the situation that it returns the same song twice. The rest of the method returns the appropriate values for the situation (if it's set to loop, if it goes forward or backward ...)
mciGetErrorString
I haven't used this method in this class to avoid messages popping up. This would be just annoying to the user. But if you're interested in the error messages:
bool a = mciGetErrorString(error, returnData, 128);
error is the int value that the MCI method returns, and returnData is a StringBuilder that will hold the error message.
Bugs
If you run into any kind of bug, for a swift resolution please log an issue on the GitHub page and I'll try to provide a fix. Here the Link to the Issue section MCIplayer/Issues
