Define some functions in native DLL (let say it “Win32Native.dll”) as shown below. this function receives array of char pointers (string).
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) void ModifyStringArrayValues( int nCount, char* ppStrArray[] )
Implementing Functions
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) void ModifyStringArrayValues( int nCount, char* ppStrArray[] )
{
size_t cchDest = 40;
const size_t alloc_size = sizeof(char) * 40;
for ( int nI = 0; nI < nCount; nI++ )
{
char *pszFormat = "<<from DLL>> [Modified String %2d]";
STRSAFE_LPSTR temp = (STRSAFE_LPSTR)CoTaskMemAlloc( alloc_size );
StringCchPrintfA(temp, cchDest, pszFormat, nI);
CoTaskMemFree( ppStrArray[nI] );
ppStrArray[nI] = (char *) temp;
}
}
Point of Interest
- CoTaskMemAlloc is used to allocated the memory required.
CoTaskMemFree is used to free any previously allocated buffer, if null is passed then, CoTaskMemFree is not called.StringCchPrintfA printf used to print a formatted output to a string buffer.
If you want to use a heap that is shared between native and managed, it is more common to use the COM heap.
Writing the client code (the managed part)
We can simple create a console base application which can use this DLL. Let’s name it MarshallingTest.
See the code snippet below.
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
namespace MarshallingTest
{
class Program
{
[DllImport("Win32Native.dll")]
public static extern double ModifyStringArrayValues(int nSize, [In, Out] String[] strArr);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int nSize = 5;
string[] arrStr = new string[nSize];
for (int nI = 0; nI < nSize; nI++) arrStr[nI] = "String " + (nI + 1).ToString();
Console.WriteLine("String Values in Array, before calling function");
for (int i = 0; i < nSize; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Array[{0:D2}] : {1}", i, arrStr[i]));
}
ModifyStringArrayValues(nSize, arrStr);
Console.WriteLine("String Values in Array, after calling function");
for (int i = 0; i < nSize; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Array[{0:D2}] : {1}", i, arrStr[i]));
}
}
}
}
Point of Interest
namespace System.Runtime.InteropServices; defines the declarations necessary for Interop operations, like DllImport.DllImport defines the DLL entry point.
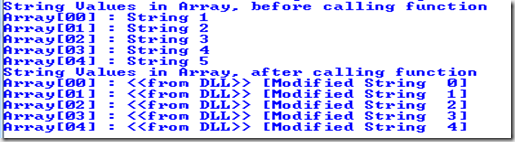
Compile and execute and you will get following output.