Introduction
The Hello World Application is the first application for everybody that opens the program world. Here, we describe the secrets inside the Hello World application. And this will help you to understand the Java programming in depth.
The Hello World Application
Here is an example of Hello World application that comes from The Java Tutorials:
class HelloWorldApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
Here is the analysis result of the corresponding class file HelloWorldApp.class:
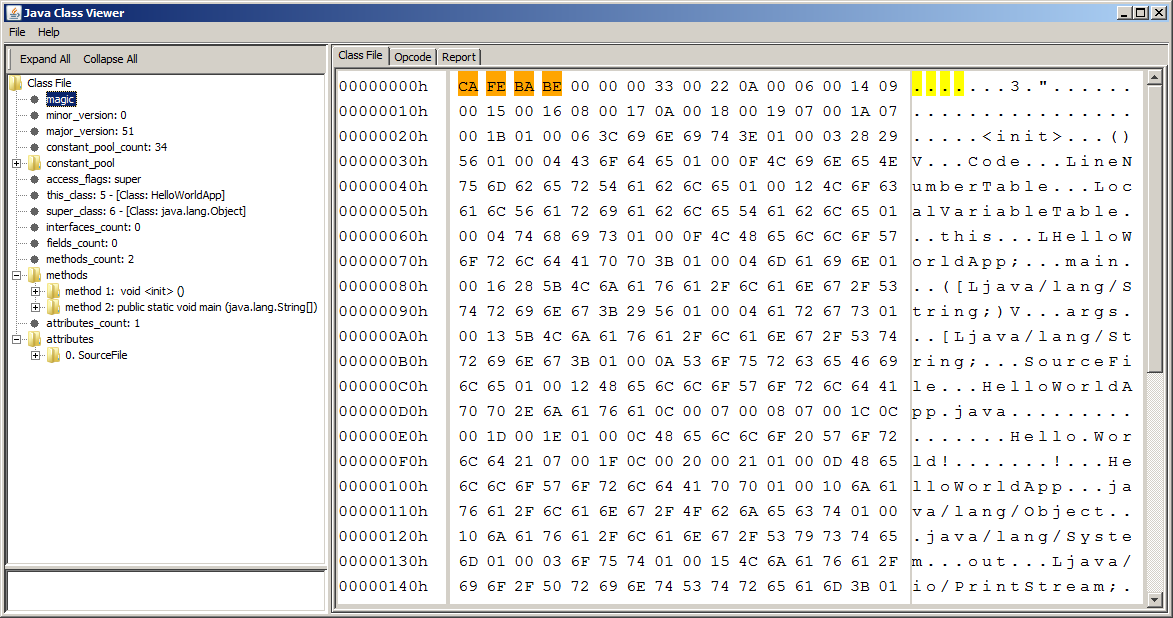
Inside the Hello World Application
The Constant Pool
The constant pool is a table of structures representing various components in the class file, like string constants, class and interface names, field names, etc. It includes:
ClassFieldrefMethodrefInterfaceMethodrefStringIntegerFloatLongDoubleNameAndTypeUtf8MethodHandleMethodTypeInvokeDynamic
Although the 'Hello World' application is so simple to contain only 1 line of code, the constant pool of this class contains 34 items, as the following screen shot shows:

The following screen shows the extracted data (human readable) of the constant pool:

- The first part shows the 'tag', it is the type of the constant pool object
- The rest shows the value of the constant pool object
Where is the Text of 'Hello World!'?
The 'Hello World!' string is contained in constant pool item 3 (tag/type: String), and item 3 is redirected to item 23 (tag/type: Utf8):

The Methods
Although there is only one main method that is defined in the HelloWorldApp.java source code, 2 methods exist in the class file:
void <init> ()public static void main (java.lang.String[])
When compiled, the javac tool generated one method named <init> .

The Method: <init>
This method is used to initialize the object. If no constructor is defined in the class source code, the method <init> will also be generated. By default, the method will call the java.lang.Object.<init> method directly.
Here is the source code of the method in binary format, it has 5 bytes:
2A B7 00 01 B1

Here is the extracted source code (technically readable) of the <init> method. The code is in opcode format, and the Java Class Viewer adds the description of the binary code:

There are 3 commands in the opcode:
-
Load the 0th variable local variable table, it is a reference to a Java Object Instance. In our case, it loads the this object from the local variable.
There are similar opcode instructions to aload_n:
| aaload | Load reference from array |
| aload | Load reference from local variable |
| aload_n | Load reference from local variable, The n must be an index into the local variable array of the current frame |
| baload | Load byte or boolean from array |
| caload | Load char from array |
| daload | Load double from array |
| dload | Load double from local variable |
| dload_n | Load double from local variable |
| faload | Load float from array |
| fload | Load float from local variable |
| fload_n | Load float from local variable |
| iaload | Load int from array |
| iload | Load int from local variable |
| iload_n | Load int from local variable |
| laload | Load long from array |
| lload | Load long from local variable |
| lload_n | Load long from local variable |
| saload | Load short from array |
-
Call the instance method <init> of super class java.lang.Object.
-
Return void from current method.
The Method: main
This is the main() method compiled from the source code.
Here is the source code of the method in binary format, it has 9 bytes:
B2 00 02 12 03 B6 00 04 B1

Here is the extracted source code (technically readable) of the main() method. The code is in opcode format, and the Java Class Viewer adds the description of the binary code:

There are 4 commands in the opcode:
-
Get the static field out from class java.lang.System.
-
Push item 3 from run-time constant pool; the tag (type) of item 3 is CONSTANT_String_info, and it refers to item 23, whose type is CONSTANT_Utf8_info.
As described above, the value of item 23 is 'Hello World!'.
-
Invoke the instance method java.io.PrintStream.println.
-
Return void from current method.
The Attribute of the Class
Attributes are used in the Class, Field, Method, and Code objects of the class file in JVM.
In our case, there is a SourceFile attribute of the HelloWorldApp class.
This attribute refers to item 19 of constant pool, and its value is 'HelloWorldApp.java', specifying the source code file name of current class.

History
- 2014-04-22 - Created this article
- 2014-04-24 - First version of this article
