Introduction
Designing apps in Win32 Console Mode is pretty boring. There exist no User interface libraries. But this simple app demonstrates how to create an object oriented application in a Win32 console. But before we begin, let's talk about a header file called cExampleTextMode.h.
The C Header File cExampleTextMode.h contains the functions that are of outmost importance for the game to be able to position the cursor and text characters in the correct x and y location. Also included in the file textmode.h are the functions to draw simple dialogs, draw lines, plot points and of course set a text character's color.
Functions in cExampleTextMode.h:
delay() delays x milliseconds
gotoxy() Goes to position on 80x25 console screen
setcolor() Changes text and background color
clrbox() draws colored box without frames
box() draws framed box
gotoxy() only works with printf(), cprintf() and not cout<
The gotoxy(int x, int y) Method
The gotoxy(int x, int y) event is called upon to set the cursor at a specific x and y location.
void gotoxy(int x, int y)
{
COORD coord;
coord.X = x; coord.Y = y;
SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord);
return;
}
The setcolor(WORD Color) Method
The setcolor(WORD color) event is called upon to set the color of text characters.
void setcolor(WORD color)
{
SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE),color);
return;
}
The clrscr() Method
The clrscr() event is called upon to clear the screen or to fill the screen with specific color.
void clrscr()
{
COORD coordScreen = { 0, 0 };
DWORD cCharsWritten;
CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO csbi;
DWORD dwConSize;
HANDLE hConsole = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hConsole, &csbi);
dwConSize = csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y;
FillConsoleOutputCharacter(hConsole, TEXT(' '),
dwConSize, coordScreen, &cCharsWritten);
GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hConsole, &csbi);
FillConsoleOutputAttribute(hConsole, csbi.wAttributes,
dwConSize, coordScreen, &cCharsWritten);
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hConsole, coordScreen);
return;
}
The Class Header File cExample.h
And now the application itself. We begin by declaring a class header file and then we continue with defining the class member functions in the file cExample.h.
Our class cExample will inherit some function methods from the class cExampleTextMode which is done by using this syntax:
class cExample: public cExampleTextMode
We choose not to define and embody our member functions in the header file, we will just put the prototypes in cExample.h. We will define the function and method bodies in Example.cpp.
#ifndef CExample_H
#define CExample_H
#include "cExampleTextMode.h"
class cExample: public cExampleTextMode {
public:
cExample();
cExample( int i); ~cExample();
void ExampleInfo(void);
void ExampleMethod(void);
};
#endif CExample_H
The Class Definition File cExample.cpp
In cExample.cpp, we will define and embody our member functions with function calls, syntaxes and statements. Our class cExample inherits function methods from the class cExampleTextMode so we need to include this syntax:
cExample::cExample( int i) : cExampleTextMode()
Now the function methods in cExampleTextMode.h have become "one" with the function methods in our class cExample. We have also placed function calls we want to be initialized at start up in the constructor so that when our class is being instantiated, those function methods get called and executed.
#include "cExample.h"
cExample::cExample( int i) : cExampleTextMode() {
ExampleInfo();
ExampleMethod();
}
void cExample::ExampleInfo(void)
{
setcolor(15);
clrscr();
clrbox(2,2,78,6,224);
gotoxy(3,2);printf(" %s ",ver);
gotoxy(3,3);printf(" %s ",prgdate);
gotoxy(3,4);printf(" %s ",author);
gotoxy(3,5);printf(" %s ",website);
setcolor(15);gotoxy(1,23);
}
void cExample::ExampleMethod(void)
{
clrbox(20,10,60,16,31);
box(20,10,60,16,15,15,"ExampleMethod Title");
gotoxy(22,12);printf("ExampleMethod Text out ");
setcolor(15);gotoxy(1,23);
}
The Constructor
We have placed function calls we want to be initialized at start up in the constructor so that when our class is being instantiated, those function methods get called and executed.
cExample::cExample( int i) : cExampleTextMode() {
ExampleInfo();
ExampleMethod();
}
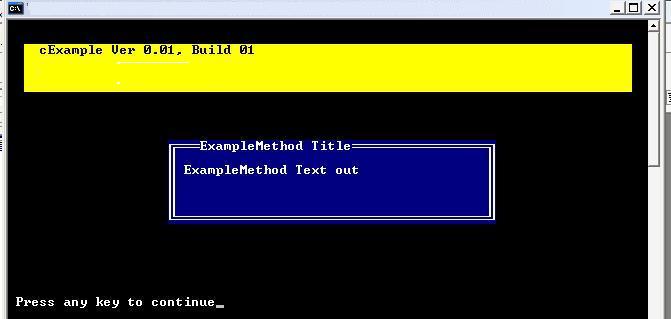
The cExample::ExampleMethod(void) Method
The method cExample::ExampleMethod(void) is executed when an instance for our class is created and since we placed a call to it in the constructor, it will proceed to draw a dialog box in text mode titled "ExampleMethod Title" and print the text "ExampleMethod Text out " in the center of the dialog box.
void cExample::ExampleMethod(void)
{
clrbox(20,10,60,16,31);
box(20,10,60,16,15,15,"ExampleMethod Title");
gotoxy(22,12);printf("ExampleMethod Text out ");
setcolor(15);gotoxy(1,23);
}
The Main File
The file cExample_main.cpp is where we create an instance for our class and run our application:
#include "cExample.h"
int main()
{
cExample *Example = new cExample(1);
return 0;
}
And that is how easy it is to create a simple object oriented Win32 console application.
Thanks for reading.
History
