Introduction, Quick Start
- Prerequisites:
- A Kinect v2 sensor
- The Microsoft Kinect V2 SDK version 2.0 installed
- Visual Studio 2012 or higher
- Start the program KinectPointCloud.exe
- Check the checkbox "Save if depth frame ..."
- Click on „Capture“ – see below

- Hold still in front of the sensor while scanning.
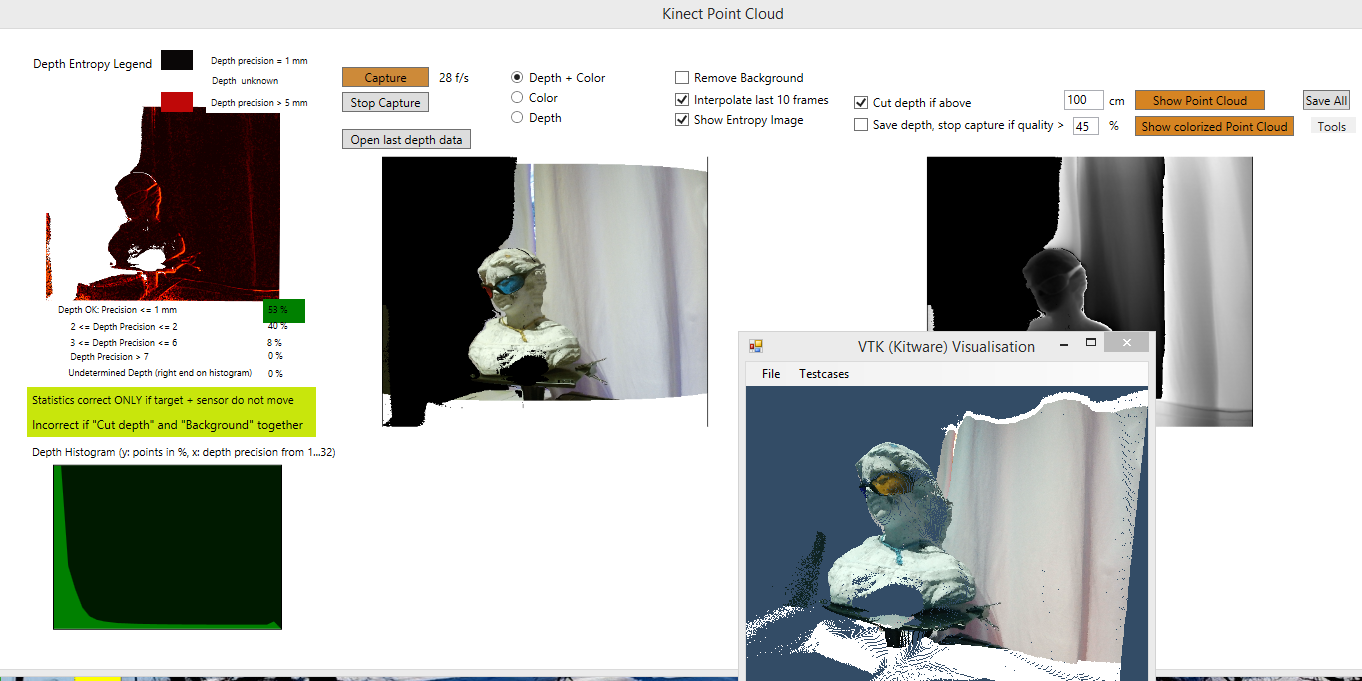
Capture will stop when the image quality is high – „Depth OK…“ is over 45% - see below

- Click on „Show Point Cloud“ to open the point cloud
- View the point cloud with or without color info

- Open the point cloud for further editing in external tools like MeshLab (either the .ply file -contains color info - or the .xyz file)

Other Source Code Used
Different open source code is used within the project:
- Parts of the Microsoft samples contained within the Kinect SDK
- The VTK library by means of the C# wrapper Activiz:
- Parts of the code of Vangos Pternas from his Codeproject article:
Coding
Grabbing the Data with Kinect
Extracting a point cloud from the Kinect by using the standard Microsoft sample code gives quite poor results – e.g. up to 30% of the depth frame points miss depth information. Either the depth is zero or there are artefacts on the depth image which occur from low depth precision.
Improve depth quality
The method to improve the depth quality used is Frame Interpolation.
A number of 10 frames are captured, the „interpolated“ image is the average of the depths.
For quality check of the grabbed image, I also calculate an "entropy“ image, which consists of the difference between maximum and minimum depth, i.e., the pixel quality is best if the pixel is zero (all measurements show the same depth), and the pixel quality is worse if the entropy is higher. For instance, if a head is scanned in the range of 0,5 to 1 m, the camera and the scanned target are still, the ambient light is OK (scan with daylight), the depth precision should be between 0 and 5 for > 95% of the pixels. This means a maximum of 5 millimeters depth uncertainty for the points scanned.

A depth histogram is calculated:
The x axis shows the depth precision from 0 to 32. All depth precisions above 32 are ignored, since they are less than 1% of the total scanned points.
On the y axis, the number of points are plotted.
Fort the example below, you see that more than 50% of the points have a precision of 1 mm or less and 34 % of the points a depth precision of 2, etc.

If you scan an image like in the example below, only about 16% of the points have a good precision, then you better do not use the result. You will have a lot of artefacts, see the entropy image below.

Code Sample
The Main Window used is MainWindow.xaml, the class doing all the Kinect work is KinectUC.
Start Capture:
private void buttonConnect_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
KinectConnect();
}
Save point cloud:
private void buttonSave_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
SaveDepthPoints();
SaveDepthBitmap();
SaveDepthPointsInterpolated();
SaveImageInterpolated();
SaveColorBitmap();
SaveColorInfoForDepth_FileAndImage();
}
Show the Point cloud with:
private void buttonShowPointCloud_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
this.OpenSavedDepthData();
ShowDepthScreenshot();
FormVTK vtkForm = new FormVTK();
vtkForm.ShowPointCloud
(this.DepthMetaData.FrameData, DepthMetaData.XResDefault, DepthMetaData.YResDefault);
}
There are utils for Kinect data handling like:
namespace KinectUtils
{
public class DepthMetaData : MetaDataBase
{
...
public WriteableBitmap DepthBitmap
{
get
{
if (depthBitmap == null)
{
this.pixels = ImageUtil.ConvertUshortToByte(this.FrameData);
depthBitmap = ImageUtil.ByteArrayToWriteableBitmap_Gray
(pixels, DepthMetaData.XResDefault, DepthMetaData.YResDefault);
}
return depthBitmap;
}
}
or VTK handling, like public class ColorUtils.
The code can be best understood if you debug the main usecases: Capture, save data and show in VTK window.
Remarks
The depth statistics is only valid if the target and the scanner do not move.
If large movements occur, the percentage values may not add to 100% total. The reason is that the depth points cut out of the image are different if the sensor or the scan target move.
Conclusion
A point cloud can be scanned with acceptable quality using the Microsoft Kinect v2 camera if one uses the procedures described in this article like image interpolation and saving the point cloud only if the depth precision is high.
Code Usage
The code and all information of this article may be used in any application as long as you cite this article in the acknowledgements.
I am happy for any comments or ideas for code improvements.
Points of Interest
I am interested in stitching point clouds scanned from different angles together and then put them together to get a better point cloud, e.g. using some ICP algorithm. Any tip or even better - C# code which fits with the architecture used here is highly appreciated.
See Also
"Kinect-Point-Cloud-using-OpenGL" - this article shows the UI in an OpenGL Control. For my further work with the Kinect, I'll use the OpenGl control. However, I keep the code of the VTK, for people interested in this, and for later usage of other VTK samples.
History
- Version 0.9.0.1 of code on 9/30/2014
- 0.9.0.2 on 12/26/2014
- Replaced Kinect version 2.0
- Minor code fix for opening point clouds
