
Introduction
A single-page application (SPA) is defined as a web application that fits on a single web page with the goal of providing a more pleasant user experience similar to a desktop application.
The following sample application code is an alternative to using libraries such AngularJS, Knockout, etc. Only established libraries jQuery and boostrap are used in conjunction with JavaScript, HTML and CSS.
A very simple approach is used in overlaying iframes or objects and jQuery Post routines & JSON, to read and update the database, without any postback.
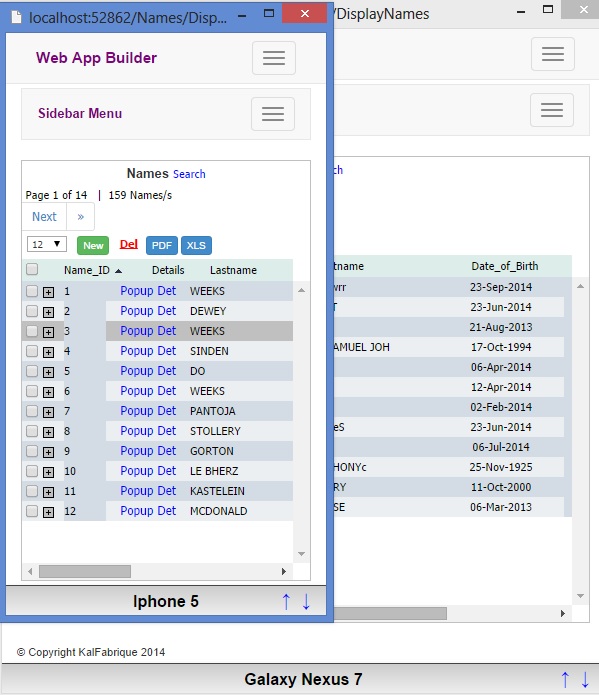
The Grid and Detail forms included in this application also contain simple CSS, to make them automatically resize to any mobile device, down to iPhone, etc. Using horizontal and vertical scrolling or swiping allows the user to quickly read all data columns and rows in a Grid.
The included demo application can be opened from Visual Studio 2012/2013 and Express versions. Just follow the provided readme.txt file for instructions in defining the SQL Server database.
Grid Record Persistence on Edit/Add
This application can maintain and freeze updated or added record in large databases, by keeping the updated record instantly available, even if sorted column has been modified. Record kept currently available, until ready to do another search, and increases performance dramatically.
The sample application is written in ASP.NET C# Framework 4.0, with Razor pages and Entity Framework - Entity SQL database manipulation.
Using the Code, to Make it Look Like a Desktop Application
The main logic to make it a SPA application is expanding DIVs and overlaying iframes/objects and then returning, by erasing the overlayed iframe.
The iframes are secured by including iframe busting code and a line entry in the web.config file.
iframe busting code
function IframeCSSCheck() {
if (top.location.hostname != self.location.hostname) {
top.location.href = self.location.href;
alert('iframe trying to be busted, please wait...');
}
}
web.config
add name="X-Frame-Options" value="SAMEORIGIN"
JavaScript code to overlay iframe and hide again
function OpenDetails(PKID, row_ID, arrayname) {
var iframeid = "iframeNamesdetail";
var iframdiv = document.getElementById(iframeid);
document.getElementById('Name_ID').value = PKID;
var pagesrc = '(Url.Action("NamesShow","Names"))';
var frameHeight = document.getElementById('NamesForm').offsetHeight;
var frameWidth = document.getElementById('NamesForm').offsetWidth;
var ifrm = "iframeupdDetailNames" + row_ID;
var iframdivsrc = "<iframe id=" + ifrm + " style='overflow: no;
border: 0px' width=" + frameWidth + " height=" + frameHeight + " frameborder='0'" +
"scrolling='no' src=" + pagesrc + "></iframe>";
iframdiv.innerHTML = iframdivsrc;
var topset = document.getElementById('NamesForm').offsetTop;
var topsetchr = topset + "px";
var leftset = document.getElementById('NamesForm').offsetLeft;
var leftsetchr = leftset + "px";
document.getElementById(iframeid).style.display = "block";
document.getElementById(iframeid).style.position = "absolute";
document.getElementById(iframeid).style.top = topsetchr;
document.getElementById(iframeid).style.left = leftsetchr;
}
function MinimDetail() {
var realparentrowid = parent.document.getElementById('CurrentRowNumber').value;
var iframerowid = "iframeupdDetailNames" + realparentrowid;
if (parent.document.getElementById(iframerowid) != null) {
parent.document.getElementById(iframerowid).src = "about:blank";
parent.document.getElementById(iframerowid).style.display = "none";
}
}
Walking through Sample Application
Master Grid to Child Logic and Code

As from diagram above, the initial start off point is from NamesGrid.cshtml page, which is invoked from the menu layout page and the controller NamesController.cs (DisplayNames). The NamesGrid.cshtml then renders 2 other pages (i.e., Names.cshtml & NamesResults.cshtml). The Names.cshtml automatically reads the Names table from the database, via a jQuery Post call, and then the resultant JSON data is rendered onto the NamesResults.cshtml page.
NamesController
public ActionResult DisplayNames()
{
Models.NamesViewModel ThisViewModel = new Models.NamesViewModel();
ThisViewModel.TotalPages = 0;
ThisViewModel.TotalRows = 0;
ThisViewModel.CurrentPageNumber = 0;
ThisViewModel.SortAscendingDescending = "DESC";
ViewData.Model = ThisViewModel;
return View("NamesGrid");
}
public PartialViewResult NamesSearch()
{
long totalRows;
long totalPages;
bool returnStatus;
string returnErrorMessage;
NamesBLL ThisBLL = new NamesBLL();
Models.NamesViewModel ThisViewModel = new Models.NamesViewModel();
this.TryUpdateModel(ThisViewModel);
List<names> scripts = ThisBLL.NamesSearch(
ThisViewModel,
ThisViewModel.CurrentPageNumber,
ThisViewModel.PageSize,
ThisViewModel.SortBy,
ThisViewModel.SortAscendingDescending,
out totalRows,
out totalPages,
out returnStatus,
out returnErrorMessage);
ViewData["scripts"] = scripts;
ThisViewModel.TotalPages = totalPages;
ThisViewModel.TotalRows = totalRows;
ViewData.Model = ThisViewModel;
return PartialView("NamesResults");
}
To show the subsequent child Grid that is linked to the each Master record, another page is overlayed on top of the Master Grid page, by expanding a DIV and using a jQuery Post call to display the NamesShowDetail.cshtml page and its linked Child Grid records as shown in the above diagram.
Detail JavaScript
function OpenDetails(PKID, row_ID, arrayname) {
NamesShowProgressBar();
resetablebg();
HideChildALL();
rowhighlight(row_ID);
var iframeid = "iframeNamesdetail";
var iframdiv = document.getElementById(iframeid);
document.getElementById('Name_ID').value = PKID;
var pagesrc = '@(@Url.Action("NamesShow","Names"))';
var frameHeight = document.getElementById('NamesForm').offsetHeight;
var frameWidth = document.getElementById('NamesForm').offsetWidth;
var ifrm = "iframeupdDetailNames" + row_ID;
var iframdivsrc = "<iframe id=" + ifrm + " style='overflow: no;
border: 0px' width=" + frameWidth + " height=" + frameHeight + " frameborder='0'" +
"scrolling='no' src=" + pagesrc + "></iframe>";
iframdiv.innerHTML = iframdivsrc;
var topset = document.getElementById('NamesForm').offsetTop;
var topsetchr = topset + "px";
var leftset = document.getElementById('NamesForm').offsetLeft;
var leftsetchr = leftset + "px";
document.getElementById(iframeid).style.display = "block";
document.getElementById(iframeid).style.position = "absolute";
document.getElementById(iframeid).style.top = topsetchr;
document.getElementById(iframeid).style.left = leftsetchr;
}
function MinimDetail() {
var realparentrowid = parent.document.getElementById('CurrentRowNumber').value;
var iframerowid = "iframeupdDetailNames" + realparentrowid;
if (parent.document.getElementById(iframerowid) != null) {
parent.document.getElementById(iframerowid).src = "about:blank";
parent.document.getElementById(iframerowid).style.display = "none";
}
$("#iframeNamesdetail").html("");
if (document.getElementById('Name_ID').value != 0) {
newrowhighlight();
}
return;
}
}

From the Names Master Grid, a Popup Detail page is initiated from a link on each Grid record, via a jQuery dialog call.
Popup JavaScript
function PopDialog(PKID, row_ID) {
$("#NamesForm #Name_ID").val(PKID);
var putTitle = "";
if (PKID == -1) {
putTitle = "Add Names";
}
else {
putTitle = "Edit Names";
resetablebg();
rowhighlight(row_ID);
}
var strAction = "NamesDetail";
var strController = "Names";
var pagesrc = '@(@Url.Action("NamesDetail7","Names7"))';
pagesrc = pagesrc.replace("NamesDetail7", strAction);
pagesrc = pagesrc.replace("Names7", strController);
var dialogWidth = 0;
var topform = top.document.forms[0].id;
dialogWidth = document.getElementById(topform).offsetWidth;
$("#modalIframeId").attr("src", pagesrc);
$("#divId").dialog({
autoOpen: true,
modal: true,
title: "",
width: dialogWidth,
height: 400,
position: "center",
resizable: false,
draggable: true
});
$("#divId").dialog("option", "title", putTitle);
}
Child to GrandChild Logic and Code

As from the diagram above, the Master and Child Grid page NamesShowDetail.cshtml is now overlaying on top of the Master page NamesGrid.cshtml. The Child Grid (i.e., Client_CareGrid.cshtml) is under the Names details.
All Child and GrandChild Grid program code are the same, and only differ from the Master Grid, in that
the foreign linked database key is not used in the Master code.
The architecture of the application is setup, so that you can easily add more GreatGrandChilds, etc.
Grid auto resizing for mobile devices

HTML and CSS code
<div id="idDivNamesTBody" style="width: auto;
height: auto; overflow: scroll; -webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch;"
onscroll="myTimer();" >
<table id="NamesTable" style="width: 100%; min-width: 700px; height: auto;">
Grid rows & columns ..........................
</table>
</div>
A DIV is enclosed around a Table, which has a min-width, thus causing the horizontal & vertically
scrolling to appear. The min-width can be modified to suit the Grid columns used.
Grid record persistence on Edit/Add

Entity SQL code
var customers = from c in customerQuery
select new { c.Name_ID, c.Firstname, c.Lastname, c.Date_of_Birth, c.Update_Date };
int numberOfRows = customers.Count();
var customersunion = from c in customerQuery
select new { c.Name_ID, c.Firstname, c.Lastname, c.Date_of_Birth, c.Update_Date };
if (SearchValues.Name_ID != 0) //Update or Add
{
customerQueryADD = customerQueryADD.Where(c => c.Name_ID == SearchValues.Name_ID);
customersunion = from c in customerQueryADD
select new { c.Name_ID, c.Firstname, c.Lastname, c.Date_of_Birth, c.Update_Date };
}
//if PageSize = -1, then creating PDF Report or Spreadsheet instead, so get all records.
var customerList = customers;
if (pageSize == -1)
{
customerList = customers;
}
else
{
if (SearchValues.Name_ID != 0) //doing Update or Add a record
{
if (numberOfRows == 0) //always set record count to at least 1
{
numberOfRows = 1;
}
customerList = customersunion.Union(customers.Skip((Convert.ToInt32
(currentPageNumber) - 1) * Convert.ToInt32(pageSize)).Take(Convert.ToInt32(pageSize)));
}
else
{
customerList = customers.Skip((Convert.ToInt32(currentPageNumber) - 1) *
Convert.ToInt32(pageSize)).Take(Convert.ToInt32(pageSize));
}
}
If the Grid record is being Updated or Added, then the record is always included in the final selected records
by doing a union. This ensures that the record will always be shown on the existing page that the user is on.
http://youtu.be/q2XpEvzcYqY - Grid record persistence on Edit/Add
Demo Videos
Below are demo YouTube videos, showing the main features of this application in action.
Points of Interest
I have gone out on a limb with this approach to creating a SPA application, in that I use the tag <iframe>, which have some detractors. But it is part of HTML5 specs, and they are used by Google and You Tube. The HTML5 tag <object> can be used instead of iframe, and I have code for this option. But, I do create all iframes from internal JavaScript, and I also use iframe busting JavaScript as well as domain control code in the web.config, to prevent any iframe XSS external attack. I have also used a very simple method, in resizing all screens for all devices, especially the Grids, which show horizontal and vertical scroll bars, via CSS.
History
- 10th October, 2014: Initial version
