Introduction
This article is intended for beginners and would introduce you to the world of Internet of things. This article covers broadly the introduction, platforms and examples of Internet of Things and do not focus on any of the development environments or tools yet.
Below are the quick links for the Topics:
What is Internet of things ?
As we all know that the global network of computers that are interconnected through TCP/IP is called internet. Internet changed the way long distance communication was conducted, it created new ways to share and acquire knowledge; it changed the way awareness was spread across communities and so on. Internet also changed the entertainment and media industry. It was a great leap when people from different parts of the world were able to connect with each other through internet to share, learn and care.
Today, an average household has more devices at home which are connected to internet than the number of people at home. Each device that is on the internet is identifiable with a unique ID; that is the IP address. The IP address is string of characters and numbers which help identify a device, locate the device on the network and route the internet traffic. However, IPv4, which was the version 4 of Internet protocol had an addressing system of 32 bits/4 bytes. The addresses were separated at each byte or 8 bits. And since 8 bits can only be used to represent a number upto 255 [11111111], the range of each byte was 0 to 255. Below is a representation of an IPv4 address.
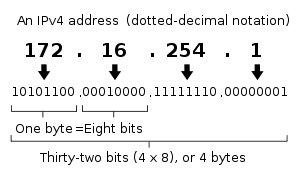
Image Source: Wikipedia
As you can see the number of devices that can be identified by a IPv4 address are limited to 232, which is approximately 4.3 billion addresses. According to various sources number of internet connected devices crossed 8 billion in 2012, to identify all the devices uniquely IPv4 was not enough and hence IPv6 was introduced/formulated in 1998 by the IETF [Internet Engineering Task Force].
IPv6 uses a 128 bit address instead of a 32 bit address in IPv4, this allows 2128 addresses. This is almost 7.9×1028 times as many as IPv4 can support. However, the two versions of addressing is not interoperable and hence the old IPv4 address needs to be replaced with the new IPv6 address. It was expected that all IPv4 addresses will be replaced with IPv6 address by May 2014. Below is a representation of an IPv4 address.

Image Source: Wikipedia
During the 1970’s Theodore G. Paraskevakos conceptualized and patented the idea of a device which combined both telephony and computing capabilities and these are now known as smart phones [no prizes for guessing]. With smart phones taking over the conventional landlines and cellphones with no data capability, the number of devices connected to internet surpassed the number of people very quickly. Today we have many other devices apart from smart phones and computers which have the capability to connect and communicate through internet. Below are few devices
- Garage door openers – There are garage door openers which have the ability to connect to internet and let you know if your door is opened/closed with details about timings and duration.
- Internet connected sprinkler systems: These sprinklers connect to the internet to get the weather forecast to decide whether to water your lawn or not.
- Water quality sensors: Test and communicate the water quality in the streams which will help authorities to preserve and help grow natural habitats for animals.
- ATM machines: Lets the bank know if there are checks deposited that needs to be retrieved or if the cash is running out so the bank could send a personnel to add more cash
- Vending machines: Lets the vendor know when to refill the machine and collect cash
- Electricity and utility meters: Lets the Utility Company know about the usage and eliminates the need for a human visit to the site.
- Cars and other vehicles: Vehicles can now be connected to a central monitoring station to relay details about the condition of your car, if it needs servicing, emergency communication, remote door unlock & engine starting when you lose your keys and so on.
- Medical and Heath Monitoring devices: Devices that can be wore to monitor your vitals and communicate the same to your health care provider for timely response treatment. These devices could be anything from a Blood pressure monitor to a pace maker.
These are only a few examples of what capability a device can acquire by connecting to internet.
All the interconnection of these uniquely identifiable computing devices within the existing internet infrastructure can be termed as Internet of Things or in short IoT.
The IoT is expected to offer an unprecedented connectivity of all the things including but not limited to devices, systems and services. This kind of interconnected would create a platform to automate and connect for almost all the fields and industry. According some statistics and researches published by companies like Gartner Inc.and Cisco there would be around 50 Billion devices that will be interconnected by end of 2020, while the population forecast for 2020 is 7.6 Billion. That makes it 6.6 devices for each person on the planet.
However, many of these devices do only one thing and may not need a full computing power of a typical computer. Hence, Low cost computing platforms could be used which specialize in doing only one thing and also consume less power. Use of this kind of computing platforms will also help reduce carbon footprints on the environment and save energy.
Why did Internet of Things evolve?
While internet may not solve all the problems and challenges we have today, it certainly is the one technology that can help solve many of the challenges. We as individuals have taken the internet advantage to help our businesses and careers. Now we could use the same technology to help improve the accessibility to education, resources and help for communities and countries that haven’t yet had the opportunity. Internet of Things is sometimes defined as bringing together people, process, data and devices to make the connections more relevant and valuable.
Most of the IoT devices shown as example above were only transmitting information, but innovation is bring devices into existence that can convert this information into actions which will add a completely new capability to the devices and provide richer experience to the consumers.
The Internet of Things also brings a new economic opportunity for Individuals, countries, organization and businesses.
The power of Internet grows exponentially as we get more and more devices, data and people to interconnect. Robert Metcalfe, founder of 3Com said that the value of a network increases proportionately to the square of the number of users. With the billions of users [people and devices] getting connected the value becomes incredibly huge.
By having the ability to put the Process, People, Data and devices together we have the ability to create the exponential responses to the exceptional challenges the businesses, individuals and countries face today. Hence the need for Internet of Things has become more relevant than ever.
What are the real world devices and applications of IoT available today?
Before diving into the technical details of the operating systems and micro controllers let us look at some of the interesting applications and devices that are currently in market that implements the concept of Internet of Things.
Embedded Platform:
NEST:
The Nest is a thermostat that when installed in place of your current thermostat will allow you to control and track your home heating from anywhere. This also has some learning capabilities that can program itself to adjust the heating based on how you have used it before. This thermostat also senses that you are not at home and automatically adjusts the temperature to avoid heating or cooling an empty home. The product connects to internet using Wifi and also has a mobile app and web app through which you can interface.
https://nest.com/
Belkin WeMo Home automation:
Wemo is a collection of products that can be controlled using your mobile or any internet enabled browser. The products aim at automating your home. For example, Wemo switches replace the traditional switches and can be turned on and off via internet, similarly there are other products like smart slow cooker, netcam for remote viewing etc:
http://www.belkin.com/us/Products/home-automation/c/wemo-home-automation/
Korner:
Korner is a Home security product that can be used at home or an apartment to secure the doors and windows.
It uses a combination of sensors that stick to your window or door and communicate to a Fob on your router. Once armed it would send an alert to your app and also sound a siren from the Fob when a Door or Window is opened.
https://www.indiegogo.com/projects/korner-home-security-anyone-can-use-and-everyone-can-afford
Below are two of the most used embedded Platforms for IoT smart devices.
Arduino:
Arduino is a microcontroller with a board to build hardware projects which don’t need multitasking. Arduino is a open-source project and has a board designed based on a Atmel AVR microcontroller. The latest models have USB interface along with the analog and digital I/O ports.
Arduino was introduced in 2005 aiming at designers that need easy and cost effective way to create and test devices that interact with sensors and actuators. It has its own Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that can be setup on computers and the programs for Arduino can be writer in C or C++.
There are quite a few official Arduino boards and I have tried listing most of them below:
- Arduino Diecimila in Stoicheia
- Arduino Duemilanove
- Arduino UNO
- Arduino Leonardo
- Arduino Mega
- Arduino MEGA 2560 R3
- Arduino Nano
- Arduino Due
- LilyPad Arduino

ArdOS operating system for Arduino:
ArdOS was introduced recently as an Operating system for Arduino boards which was based on the ATmega 168 and ATmega328. With ArdOS, Arduino now has:
- Multitasking [in true sense]
- Priority scheduler for hard real-time applications
- Round-Robin scheduler with configurable time quanta for the soft-real-time applications
- Sleep function
- Idle hook to make use of idle time by other processes
- Task coordination mechanisms
- Task communication mechanisms
Raspberry Pi and its Operating Systems:
Raspberry Pi is another single board computer that was developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in UK for teaching basic of computer science in schools.
The Raspberry Pi is as powerful as an Iphone 3Gs roughly, it operates at 700 MHz by default and can be overclocked up to 800 MHz, it also has some minimal graphic capabilities equivalent to that of a 2001 Xbox. Because of this low config the board seldom has heat sync issues.
Newer versions of the firmware offers 5 turbo presets to choose from, the overclocking or the turbo mode will try to get the max performance of the SoC without frying the board, this is achieved by monitoring the core temperature of the chip. Below are the five presets:
| Preset
| Description
|
| None
| 700 MHz ARM, 250 MHz core, 400 MHz SDRAM, 0 overvolt,
|
| Modest
| 800 MHz ARM, 250 MHz core, 400 MHz SDRAM, 0 overvolt,
|
| Medium
| 900 MHz ARM, 250 MHz core, 450 MHz SDRAM, 2 overvolt,
|
| High
| 950 MHz ARM, 250 MHz core, 450 MHz SDRAM, 6 overvolt,
|
| Turbo
| 1000 MHz ARM, 500 MHz core, 600 MHz SDRAM, 6 overvolt.
|
The Raspberry B model has 128MB allocated to the GPU by default which leave another 128 for the CPU. It can be attached with a Ethernet adapter to connect to the network and also have the generic Keyboards and mouse connected with the ports.
Below are some of the OS available for the Pi:
| OS
| Description
|
| Raspbian OS
| Raspbian OS is a Debian[Linux] based operating system for the Raspberry Pi developed and maintained independent of the Foundation.
|
| Risc OS
| This was an OS designed in Cambridge, England by Acorn in 1987. The team who developed the ARM microprocessor were part of the team building the Risc OS. The OS is now owned by Castle Technology Ltd and the source is managed by Risc OS Open Limited [ROOL]
Source: RISCOS
|
| Plan 9
| Plan 9 OS comes as a bundle of Operating system and softwares. The software is written for Plan 9 and are not ported from Unix or Linux. Most of the services like the window system, compiler, file server and network services were freshly written for the Plan 9 Operating system
|
| Android
| The popular mobile OS android can also be run on the Raspberry Pi.
|
The above embedded systems can be used in conjunction with Sensors/Actuators , connectivity and People/process to create a full-fledged IoT experience.
Sensors and actuators:
The embedded systems can be connected to different sensors such as below for collecting the information:
- Humidity sensor
- Level/tilt sensor
- Pressure sensor
- Temperature sensor
- Motion Sensors
- Proximity Sensors
- Optical Sensors
- Acceleration sensors
- Load sensors
- Vibration sensors
- Chemical sensors
- Flow sensors
They can also be connected to actuators to translate the collected or received information into actions, below are some of the actuators:
- Light emitting Diodes [LED]
- Relays
- Motors
- Linear actuators
- Lasers
- Solenoids
- Speakers
- LCD or Plasma displays

Image Source: Postscapes
Connectivity:
The embedded systems can use a range of connectivity to connect with other devices or the internet.
Some examples are as below:
- WiFi
- Bluetooth
- RFID
- ZIGBEE
- NFC
- Ethernet
- LTE
- 3G
- GSM
- CDMA

Image Source: Postscapes
People and Process:
The information transmitted via the chose connectivity can be used by people and processes to take action or re-transmit the info to a different embedded system to be used to perform an action using actuators, below are some examples:
- A gas leak/ smoke is detected by a chemical sensor and the info is transmitted to a monitoring center. Help is dispatched immediately and the affected are informed
- A home security system detects intrusion, a call is placed to the authorities and owners alerted. Help dispatched
- Load sensor can initiate a communication to the supplier to send more stock enabling the supply chain management automation
- Car can send the diagnostics to the service center and the service center schedules a repair.
- Your IoT thermostat sends the information to the cloud which can then be analysed by to manage your energy expenditure.

Image Source: Postscapes
Wearable Platform:
The other platform for IoT is the wearable platform. According to a recent study by Rackspace there is already nearly 20% of the population in the US and UK wearing some sort of wearable technology.
These wearable primarily provide real-time data about their health or an augmented view of the world. But these wearable might become an integral part if IoT soon which will be enabled by the BigData and cloud technologies. However, wearables also have one of the biggest concerns among users which is privacy.
Below are some of the wearables that are already/soon to be in market:
- Pebble
- Apple watch
- Samsung Gear
- Fitbit
These use different OS like modified IoS, android, tizen .
Development environments:
There are several IDE’s available for Arduino and Raspberry Pi development. Below are some of them
IDE’s for Arduino :
- Arduino IDE for Visual Studio/ Atmel Studio
- Atmel Studio is a visual studio inspired development environment. This is developed by the makers of the Microcontroller that are used in Arduino.
- It has the compilers baked in that can compile for Arduino.
- The libraries used in Arduino IDE can also be used in the Atmel Studio
- Arduino Eclipse IDE
- Mario Mole
- An alternative development environment create as a easy to use IDE.
- Includes modern features like multiple projects integration, color themes, linker options etc.
- Light weight and open source
- Universal Embedded Computing IDE (UECIDE)
- Xcode on OS X
The IoT opens up a new window of opportunity for innovation for developers and businesses alike. This is a new shift in focus for business just like the DotNet shift.
IoT also creates opportunities which are equally beneficial for both Hardware and Software developers. Most importantly IoT has started a new wave which is still in the initial stages and a long way to go.
