This is a new post in a series of beginners' articles on how to do things in Azure. This series will be for absolute beginners, and if you are not one of those, this will not be for you.
You can find the complete set of posts that make up this series here:
This time, we will look at how to use Azure blob storage for uploading things like files (images, Word documents, whatever you like really).
Introduction To Blob Storage
What exactly is Blob Storage? Well, it is actually very simple, it is Azure hosted storage that allows you to upload large amounts of unstructured data (typically binary data, so bytes) that may be shared publicly using http/https.
Typical usage may be:
- Storing images
- Storing documents
- Storing videos
- Storing music
A typical Azure blob service would make use of these components
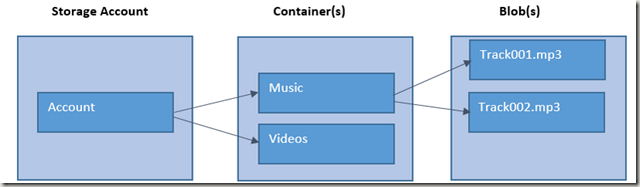
Account
This would be your Azure storage account. You must create a storage account using the Azure portal, which you would do through the portal: https://manage.windowsazure.com (we will see more on this in just a minute).
Container(s)
These belong to Account, and are using two group blob(s). Each account can have unlimited number of containers, and each container may contain an unlimited number of blobs.
Blob(s)
Blobs represent the Azure hosted data that represent the originally uploaded binary data. It is the blobs that you would eventual end up loading when you share an Azure blob storage URL.
There are 2 types of blob storage available.
Block Blobs
These are binary blocks of up to 200GB, where you can upload 64MB at one time. Typically for a larger block, you would spit things up and upload them in chunks using multiple threads, and Azure will reassemble them making them available as a single blob.
Page Blobs
These can be up to 1TB and consist of a collection of 512 pages. You would set a maximum size when creating the page blob. I have not used these so much, and personally I think these are here to support other Azure features like Virtual Hard Drives (VHDs) which are stored as page blobs in Azure Storage.
Url Syntax
The actual blob URL format is as shown below:
http://<storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container>/<blob>
How To Get An Azure Storage Account
The first thing you will need to do is create a storage account, this is easily achieved by using the portal. Go to the portal : https://manage.windowsazure.com, and then click new.

Then pick storage, and go through creating a new Storage Account.

Then once you have that, you can open the newly created storage account, and click the dashboard, and that will show you the relevant connection strings which you may use in your application.

Using the Storage Emulator
NOTE: If you just want to try things out without going through the process of creating a Storage Account, you can actually use the Storage Emulator, which you can do using an account connection string something like this:
<!--
<add key="azureStorageConnectionString" value="UseDevelopmentStorage=true;" />
Since I am writing the bulk of these posts on a train without any internet connectivity, I will be using the storage emulator in any demos in this post.
If you want to use the emulator, ensure that is running, and that you have enabled the storage emulator.


Getting the Right NuGet Package
You will need to install this NuGet Package to work with Azure Blob Storage “WindowsAzure.Storage”.
Creating a Container
This is done using the following sort of code:
CloudStorageAccount storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount
.Parse("UseDevelopmentStorage=true");
CloudBlobClient blobClient = storageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
CloudBlobContainer container = blobClient.GetContainerReference("sachasContainer");
container.CreateIfNotExists();
container.SetPermissions(
new BlobContainerPermissions
{
PublicAccess = BlobContainerPublicAccessType.Blob
});
Uploading a File to Azure Blob Storage
This is done using the following code:
CloudBlockBlob cloudBlockBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(
"mandrillBlobUploaedToAzure.jpg");
cloudBlockBlob.Metadata["TypeOfImage"] = "Animal";
using (var fileStream = System.IO.File.OpenRead(@"C:\Users\User\Pictures\mandrill.jpg"))
{
cloudBlockBlob.UploadFromStream(fileStream);
Console.WriteLine("Blob Url : {0}", cloudBlockBlob.Uri);
}
Listing All Blobs in a Container
This is done using the following code:
container = blobClient.GetContainerReference("sachasContainer");
foreach (IListBlobItem item in container.ListBlobs(null, false))
{
if (item.GetType() == typeof(CloudBlockBlob))
{
CloudBlockBlob blob = (CloudBlockBlob)item;
Console.WriteLine("Block blob of length {0}: {1}", blob.Properties.Length, blob.Uri);
}
}
Download Blobs
This is done using this sort of code:
CloudBlockBlob blockBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference("mandrillBlobUploaedToAzure.jpg");
using (var fileStream = System.IO.File.OpenWrite(@"C:\Users\User\Pictures\XXX.jpg"))
{
blockBlob.DownloadToStream(fileStream);
}
Blob Metadata
Blobs supports metadata via a dictionary which is available using the Metadata property which is a simple key/value pair.
How to Add Descriptive Metadata to a Blob
This is actually very easy, you just store more data in either a SQL Azure or SQL Azure table storage where you would include the blobs URL. Job done!
Deleting a Blob from a Container
This is done using this sort of code:
blockBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference("mandrillBlobUploaedToAzure.jpg");
blockBlob.Delete();
