Introduction
With Internet and the variety of mobile messaging app available, nowadays people can communicate through many channels, be it through email, WhatsApp, LINE, WeChat, Facebook Messenger, Skype, Telegram and many others. However, SMS is still relevant due to its reliability. In this article, we will turn an Android phone into an SMS gateway by installing a free app and start sending and receiving SMS through C# or any other programming languages that you prefer.
Background
I developed this solution to bundle it with my other product (MessagingToolkit). This free Android app is now available at Google Play Store.
Of course there are other similiar solutions available, just Google "Android SMS gateway" and you can see all other options available.
Disclaimer: I am the developer for myMobKit and MessagingToolkit.
Using the code
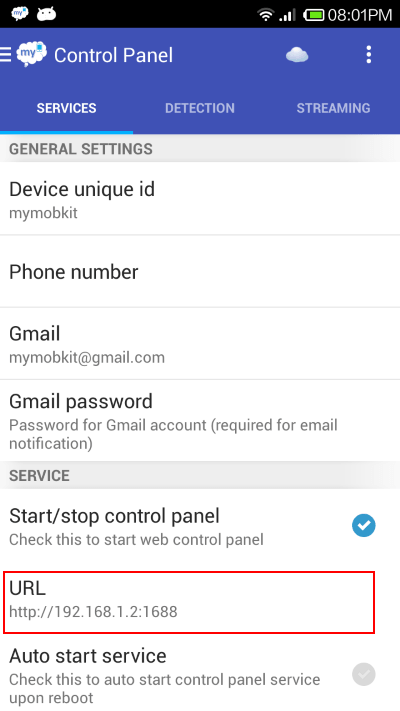
In order to turn your Android phone into a SMS gateway, you will need to install the free app myMobKit available at Google Play Store.
After installing, start the control panel service, and you should be able to see the URL to access the hosted website.
The hosted website shows the available APIs and their usage. You can use the APIs to access device information, photos and video, as well as send and receive SMS.

To get started quickly, you can use Chrome extensions like Advanced REST Client or Postman - REST Client to access the messaging services. Below is a screen capture of Advanced REST Client retrieveing all the SMS in the phone.

Using C# to access the APIs is straightforward using ASP.NET Web API client library.
In Visual Studio, from the Tools menu, select Library Package Manager, then select Package Manager Console.
In the Package Manager Console window, type the following command:
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNet.WebApi.Client
To retrieve all messages in the phone, use the following code snippet.
using (var client = new HttpClient())
{
string url = ConstructBaseUri();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(url);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Clear();
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtUserName.Text) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtPassword.Text))
{
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue(
"Basic",
Convert.ToBase64String(
ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(
string.Format("{0}:{1}", txtUserName.Text, txtPassword.Text))));
}
HttpResponseMessage response = await client.GetAsync(MessagesUrlPath);
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
GetMessageResponse result = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<GetMessageResponse>();
if (result.IsSuccessful)
{
txtOutput.Clear();
foreach (DeviceMessage msg in result.Messages)
{
AddToOutput(msg.ToString());
AddToOutput("");
}
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(result.Description, Application.ProductName, MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(response.ToString(), Application.ProductName, MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
To send a message, use the following code snippet,
using (var client = new HttpClient())
{
string url = ConstructBaseUri();
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(url);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Clear();
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtUserName.Text) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtPassword.Text))
{
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue(
"Basic",
Convert.ToBase64String(
ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(
string.Format("{0}:{1}", txtUserName.Text, txtPassword.Text))));
}
var postData = new List<KeyValuePair<string, string>>();
postData.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, string>("to", txtContact.Text));
postData.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, string>("message", txtMessage.Text));
HttpContent content = new FormUrlEncodedContent(postData);
HttpResponseMessage response = await client.PostAsync(MessagesUrlPath, content);
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
PostMessageResponse result = await response.Content.ReadAsAsync<PostMessageResponse>();
if (result.IsSuccessful)
{
txtOutput.Clear();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(result.Description, Application.ProductName, MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(response.ToString(), Application.ProductName, MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
The screenshot of the sample application.

History
December 29, 2014 - Initial version.
