WCF (Windows Communication Foundation) is a mechanism which enables applications to communicate whether they are on the same computer, across the Internet, or on different application platforms.
Thus, it allows you to build a Service Oriented application which focuses on integrating across platforms.
Before diving into the basics (ABCs) of WCF, we should understand the core functionality of WCF which is “WCF Runtime Components”. When we say there arises a need to talk to the outer world, we intend to send “Messages”. Similarly WCF also uses “Messages” to interact.
WCF Runtime Components
“Message” class is a core part of the WCF Runtime Component.
There are 2 important subparts of WCF Runtime, viz.
- Channel Stack: This is the block which does the actual work of transferring a message through the channel which then gets picked up at the other end. For now, you can consider this to be a black box which takes the Message as input, packages into a suitable format which could result in an output like TCP/HTTP packets or Queuing Messages in MSMQ or writing messages in database or saving to file share, etc. It then gets transported and on the other side again you find a Channel Stack which takes the input and converts it into a Valid Message.The diagrammatic representation of Channel Stack is as below:
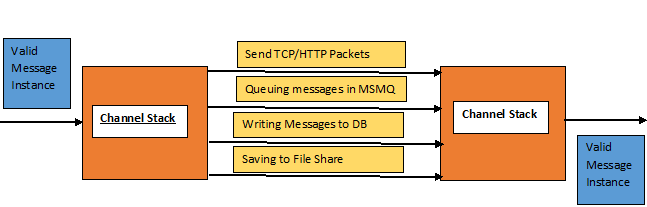
- Service Framework: In actual, only the
Message class and Channel Stack is enough to send the data across the channel, but you will not have Metadata support and it is a difficult and cumbersome process to write the Channel Stack. Due to this, we use a Service Framework to construct and Receive Message objects. Ideally, the Service Framework sits before the Channel Stack and generates the necessary valid Message class from the user friendly method which you write. Service Framework does the actual tearing down of the call into a Message and provides input to the Channel Stack. Also on the receiving end, the vice-versa procedure occurs. For e.g.: Consider the below Operation which you want to perform:
[ServiceContract]
public interface IAirfareFinderService
{
[OperationContract]
int FindAirfare(string FromCity, string ToCity);
}
The Service Framework takes the method as input and from the parameters “FromCity” and “ToCity” constructs a Message instance and passes it to the Channel Stack to be sent. Channel Stack then performs its operation and passes through the Channel.
This then is received on the server by the Channel Stack and it then converts back to a Valid Message. This is then fed to the Service Framework which constructs back the method and then the suitable method gets called.
The output of the method is again transported back to the client in the same way. A diagrammatical representation is shown below:

Service Framework + Channel Stack
Now as we have seen how the WCF service works, we will see briefly what the Message actually consists of:
- Message Body: It actually consists of the actual data which is in the form of XML Infoset. Streaming is also supported.
- Message Header: It consists of the XML Infoset associated with Name, Namespace, etc. Streaming is not supported.
- Message Properties: Any .NET Framework object that is associated with
string name.
For more information on Message, you can visit:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.servicemodel.channels.message(v=vs.110).aspx
In our next post, we will look at the internal structure and behavior of Channel Stack.








