Introduction
Here, We will know about the Visitor design pattern. This article will explain in details about
- What it is ?
- Why it is ?
- How it is ?
Why this Article? Well, A lot of article on the web can be found but most of them, fails to describe the fundamentals. Most of explanation or implementation found on the web creates confusion about their real world usage. So, I tried to fix the gap and made the best effort to illustrate the problems that this pattern targets, and, also how it handles that. This article which helps developers, not only to learn the implementation, but they also understand the core concept so that they can identify the actual scenario where they can fit this pattern. At the end of this article, I hope you will be able to describe yourself about the use and benefits of Visitor Pattern.
Background
Visitor Pattern is, in general opinion, is the most complicated design pattern because of the nature of problem it solves. We will look what it is, how it works and how it should be implemented in real scenarios.<o:p>
Every one among us might get into the situation, when we have a complex class hierarchy and we want to add or modify their behaviors without changing their original code. The “Complex” word I have used because in the hierarchy, every object are of different types and we want to add operation which will run on specific type’s .i.e. different operation for different types of object. Frankly saying, most of time we do type/instance checking to determine the type and then select the operation via If-else statement. This approach has its own limitations and, of course, not an object oriented way. To fix this type of problems in an object oriented way – Visitor Pattern came into picture.<o:p>
What is it?
The standard definition of Visitor Pattern (according of G.O.F) is
Represent an operation to be performed on elements of an object structure. Visitor lets you define a new operation without changing the classes of the elements on which it operates.
Basically, visitor pattern has two important aspects -
- There is an iterating mechanism, which knows how to iterate on Object hirerachy.it doesn’t know anything about the behavior of objects in the hierarchy.
- The new behaviors which needs to be implemented knows nothing about the iteration mechanism, they don't know how to iterate the object hierarchy.
Both the aspects are independent of each other, and they shouldn’t be messed with each other. So, this is all about OOPs principal known as Single Responsibility principal.
Classes which holds the new behaviors are commonly known as Visitors.
In visitor pattern, the key players are
- Visitor - An Interface which defines Visit operation. This is the core of visitor pattern. It defines a Visit operation for each type of Concreate Element in the object structure.
- ConcreateVisitor - Implements the operations defined in the Visitor interface.
- ElementBase : It is an Abstract/Interface which defines Accept operation that takes the visitor as an argument.
- ConcreateElement - These types implements Accept method of Element interface.
- Object Structure - It holds all the element of the data structure as a collection, list or something which can be enumerated and used by the visitors. It provide the interface to all visitor to visit its element. These element include the method called "Accept”. The collection is then enumerated
The Key concept is to create data model with limited functionality and the set of visitors with specific functionality that will operate upon the data. The pattern allows the each element of the data structure to be visited by the visitor passing the object as an argument to the visitor methods. The Key benefits of separating the algorithm from its data model is the ability to add new behaviors easily. The classes of data model are created with the common method called Visit which can accept visitor object at runtime. Then different visitor object can be crated and passed it to this method, then this method had a callback to the visitor method passing itself to it as a parameter.
Adding a new type to the object hierarchy requires changes to all visitors, and this should be seen as an advantage as it definitely forces us to add the new type to all places where you kept some type-specific code. Basically it don't just let you forget that.
The visitor pattern is only useful
- If the interface you want implemented is rather static and doesn't change a lot.
- If all types are known in advance, i.e. at design time all objects must be known.
Why is it?
The new behaviors are not directly integrated into the object, because it need to change the source code, and, as there might be many behaviors which needs to be implemented in future, so, every time we can't just go and change the original code of the object. So the behavior is separated to different new object. So, whenever we need to introduce new behaviors to an object hierarchy, we simply create new object for that and this new behaviors will be applied to the object at runtime through polymorphism. So this is simple and neat solution to extend functionality of an object without having to modify its class codes.
This pattern allows us to add new behavior to an object without altering its original source code by separating the new behavior to the separate class and then apply those behaviors to their respective objects dynamically.
Visitor implements the following design principals
- Separation of Concern - Visitor pattern promotes this principle, multiple aspects/concerns are separated to multiple other classes, as it encourages cleaner code and code re-usability, and also code is more testable.
- Single Responsibility Principle - Visitor pattern also enforce this principle. An object should have almost one responsibility. Unrelated behaviors must be separated from it to another class.
- Open Close Principle - Visitor pattern also follows this principal, as if, we want to extend an object behavior, the original source code is not altered. The Visitor pattern provide us the mechanism to separate it to another class and apply those operations for an object at run time.
Benefits of Visitor implementations are
- Separate the behavior of data structure from them. Separate visitors object are created for to implement such behavior.
- It solve Double Dispatch problem which are rarely faced but has important impact.
In summary, if you want to decouple some logical code from the elements that you're using as input, visitor is probably the best pattern for the job.
Note : To keep this article small, i am not going to foucs on Double Dispatch problem. A good article is here.
How is it?
Till now, we have understand What and Why aspects fo visitor patten.Now it's time to do some coding.
Let's start with a scenario. We are going to build tax calculator system for an airport. This system is used to calculate tax/import duty to the products that are imported. System will calculate the import duty on the basis of some rules.
Note: For the sake of simplicity, it is assumed that only three type of products i.e. Book, Car, Wine can be imported only.
Currently,the Airlines application only provides a single class, i.e passengers can only travel on Normal class ticket, but in future it will be expanded to Corporate and Executive class.The table below shows the rules of taxation for Normal class...
Type of Passenger Book Car Wine
================================================
Normal 10% 30% 32%
Above table shows the rules based on which our application will calculate the tax/duty. When we see the rules, we will find that there are different taxation percentage for different types of items imported, i.e. for Normal class passenger, 10% tax is applicable for Book and 30% of tax is applicable to the Car and 32% of tax will be charged for Wine, and, different tax will be chargeable for other class of passengers.<o:p>
First of all we will define the interface which we call IVisitable. It will define a single Accept method which will accept an argument of IVisitor. This interface will serve as the base for all types in the product list. All types like Book, Car and Wine (in our example) will implement this type.<o:p>
internal interface IVisitable
{
void Accept(IVisitor visit);
}
Let’s create the type for the tree types of products, .i.e. Book, Car and Wine. All types will implement IVisitable interface, which allow these concreate classes to define Accept method. This Accept method simple accept a parameter of type IVisitor and make the callback to a specific method defined inside the Visitors classes, Thus Visitor method is selected by this Accept method.<o:p>
Note - In our example code below, I have both Interface and the Abstract Class. In this simple example we didn’t need both, i.e. we can run this example by any one of them, but i want to use both, because in real scenarios, abstract class will present to hold some common behaviors across the hierarchy and interface will be defined to enforce certain rules to the class. So, i have used both to show such scenario.<o:p>
#region "Structure Implementations"
internal abstract class Product : IVisitable
{
public int Price { get; set; }
public abstract void Accept(IVisitor visit);
}
internal class Book : Product
{
public Book(int price)
{
this.Price = price;
}
public override void Accept(IVisitor visitor)
{
visitor.Visit(this);
}
}
internal class Car : Product
{
public Car(int price)
{
this.Price = price;
}
public override void Accept(IVisitor visitor)
{
visitor.Visit(this);
}
}
internal class Wine : Product
{
public Wine(int price)
{
this.Price = price;
}
public override void Accept(IVisitor visitor)
{
visitor.Visit(this);
}
}
#endregion "Structure Implementations"
Lets' create a Vaisitor interface. It will hold a visit method for all the types of items in the product, i.e. currently, our application supports only three item Book,Car and Wine, so there is only three methods of each type.
internal interface IVisitor
{
void Visit(Book book);
void Visit(Car car);
void Visit(Wine wine);
}
Now, we will create concreate visitor class BasicPriceVisitor, which will implement the above defined interface i.e. IVisitor. As it has method for all types, this class can give its own implementation for each types. In this current example, we are calculating the duty for each types, as each type have different percentage of taxation.
#region "Visitor Implementation"
internal class BasicPriceVisitor : IVisitor
{
public int taxToPay { get; private set; }
public int totalPrice { get; private set; }
public void Visit(Book book)
{
var calculatedTax = (book.Price * 10) / 100;
totalPrice += book.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
public void Visit(Car car)
{
var calculatedTax = (car.Price * 30) / 100;
totalPrice += car.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
public void Visit(Wine wine)
{
var calculatedTax = (wine.Price * 32) / 100;
totalPrice += wine.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
}
#endregion "Visitor Implementation"
As shown above, inside method of each type, we have calculated the duty on the basis of type, thus, different taxation rules are implemented for each type.<o:p>
Now it's time for see it in action. We have created a list of Product, then created a BasicPriceVisitor object. Now, we simple iterate on the products list and pass the BasicPriceVisitor instance to each item.<o:p>
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program.ShowHeader("Visitor Pattern");
List<Product> products = new List<Product>
{
new Book(200),new Book(205),new Book(303),new Wine(706)
};
ShowTitle("Basic Price calculation");
BasicPriceVisitor pricevisitor = new BasicPriceVisitor();
products.ForEach(x =>
{
x.Accept(pricevisitor);
});
Console.WriteLine("");
}
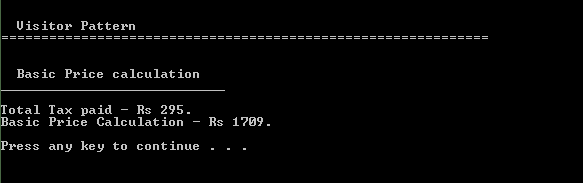
After executing, following result will shown on commond line.
How it is Extensible ?
After sometime, Airlines decided to introduce two new class of passengers with different taxation benefits, let's say it as a Corporate and Executive class. The new import duty applied to this new Executive Class are given below.
Type of Passenger Book Car Wine
====================================================
Corporate Offer 7% 20% 20%
Executive Offer 5% 10% 10%
Foe this new requirement, we will create two different classes, say CorporateOfferVisitor and ExecutiveOfferVisitor. Both of these classes will implement IVisitor interface as it provide a way to handle different types of items in different manner. CorporateOfferVisitor class provide different taxation rules for Book, Car and Wine, and in the same way ExecutiveOfferVisitor offers different duty percentages. Please see the below code carefully...
#region "Visitor Implementation"
internal class CorporateOfferVisitor : IVisitor
{
public int taxToPay { get; private set; }
public int totalPrice { get; private set; }
public void Visit(Book book)
{
var calculatedTax = (book.Price * 7) / 100;
totalPrice += book.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
public void Visit(Car car)
{
var calculatedTax = (car.Price * 20) / 100;
totalPrice += car.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
public void Visit(Wine wine)
{
var calculatedTax = (wine.Price * 20) / 100;
totalPrice += wine.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
}
internal class ExecutiveOfferVisitor : IVisitor
{
public int taxToPay { get; private set; }
public int totalPrice { get; set; }
public void Visit(Book book)
{
var calculatedTax = (book.Price * 5) / 100; ;
totalPrice += book.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
public void Visit(Car car)
{
var calculatedTax = (car.Price * 10) / 100;
totalPrice += car.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
public void Visit(Wine wine)
{
var calculatedTax = (wine.Price * 10) / 100;
totalPrice += wine.Price + calculatedTax;
taxToPay += calculatedTax;
}
}
#endregion "Visitor Implementation"
Lets use the above new visitors to our program.These new visitors will be used in the same way as we did with our previous visitor BasicPriceVisitor, i.e. We will pass these visitor to each items in the list.
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program.ShowHeader("Visitor Pattern");
List<Product> products = new List<Product>
{
new Book(200),new Book(205),new Book(303),new Wine(706)
};
ShowTitle("Basic Price calculation");
BasicPriceVisitor pricevisitor = new BasicPriceVisitor();
products.ForEach(x =>
{
x.Accept(pricevisitor);
});
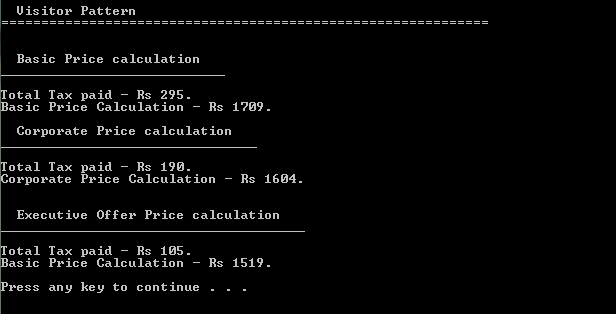
Console.WriteLine("Total Tax paid - Rs {0}.", pricevisitor.taxToPay);
Console.WriteLine("Basic Price Calculation - Rs {0}.", pricevisitor.totalPrice);
ShowTitle("Corporate Price calculation");
CorporateOfferVisitor offervisitor = new CorporateOfferVisitor();
products.ForEach(x =>
{
x.Accept(offervisitor);
});
Console.WriteLine("Total Tax paid - Rs {0}.", offervisitor.taxToPay);
Console.WriteLine("Corporate Price Calculation - Rs {0}.", offervisitor.totalPrice);
Console.WriteLine("");
ShowTitle("Executive Offer Price calculation");
ExecutiveOfferVisitor executiveOfferVisitor = new ExecutiveOfferVisitor();
products.ForEach(x =>
{
x.Accept(executiveOfferVisitor);
});
Console.WriteLine("Total Tax paid - Rs {0}.", executiveOfferVisitor.taxToPay);
Console.WriteLine("Basic Price Calculation - Rs {0}.", executiveOfferVisitor.totalPrice);
Console.WriteLine("");
}
So, we have seen, how easily we can extend our sample to accommodate two new features without editing the existing code or any existing types like Book, Car or Wine. This is the beauty of Visitor pattern. The whole idea is to define the behavior in a method of a separate class, and call it via callback.
Points of Interest
Visitors object represents an operation to be performed on the elements of an object structure.
The visitor pattern is used when:
- We want to operate similar type of operation on objects of different types grouped together in hierarchy or collection.
- We want to separate the distinct and unrelated behaviors from the type class (i.e. Car in above example), to another class and want to switch the behaviors dynamically.
- We have the stable object hierarchy which is not likely to be changed, but there is a strong probability of addition of new operation in future. Since this Visitor pattern allow us to separate the operation from the object structure, it is now easy for us to add new operations in the form of Visitors. This will work as long as the object structure remain unchanged.
This should not be used when:
- Visitor Pattern requires that the arguments and the return type for the Visiting methods must be known at design time. So this pattern is not good for the situation where types are added frequently, because once the new type is introduces, all the visitor must be changes accordingly.
- The behaviors are specific to specific type not for the hierarchy. Such behaviors should not be implemented via visitor, as visitor is used to define behaviors (visitors) which will be applied to the whole hierarchy.
Keep Coding...
