Introduction
Datagrid controls are great for displaying data that is stored in a table. One row in the database table equals one row in the datagrid. When data is stored in multiple tables, say table A and B, and the row A has a one-to-many (also called 1:N, parent-child, or master-detail) relation to a row in table B, then row A can reference multiple rows in table B. This type of data can be shown in a master-detail data view type. Another type of data relation is the type many-to-many (also called N:M relation). The row of table A can have multiple references to rows in table B. But in addition to the previous case, a row of table B can be referenced by multiple rows of Table A.
This article describes a method many-to-many relations can be displayed and modified in a WPF datagrid control. The rows and columns can be added, removed and modified by editing the rows of the A and/or the B table.
This article is split in two parts. In this first part, I focus on the solution of handling dynamic columns. In order to simplify the solution, I broke an architectural constraint, which is that objects of a top layer should not be used in lower layers (in this case, the grid columns that are a part of the GUI layer, and not the view model layer). The second part of this article fixes this constraint.
Using the Code
The Application
The sample code implements a user administration form in which users, roles and the user-role assignment can be administered. The roles and the users are displayed in two data grids. The user role assignment is done in the user data grid. Therefore this grid has the dynamic contents, displaying each role as a separate check box column. The user-role assignment is done by checking the respective check box.
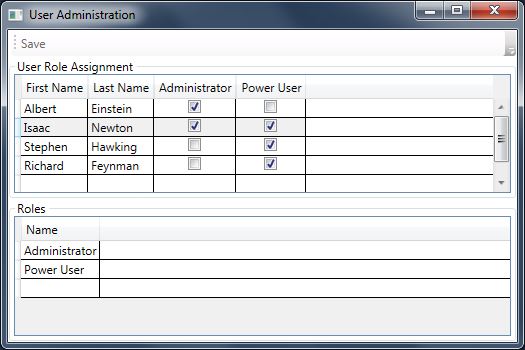
The Data Model
The data model of this sample consists of a User and a Role table, and a UserRole table that is the correlation table between the other two tables. An entry in the UserRole table means that the user (referenced by its user id) has a role assigned (referenced by the role's id). If there is no entry for a certain user-role combination, then that means that the user in question does not have the corresponding role assigned.

The data model is implemented using the .NET DataSet. It is a good in-memory database with referential integrity, and it contains built-in notification delegates that publish the insertion, removal and modification of data rows. Its contents can be stored to an XML file, which is used as a persistence mechanism in this example.
The Component and Class Diagram
The next component diagram shows the application's layering:
- Application: contains the GUI elements
- ViewModel: contains the business logic
- DataModel: contains the data definition, and persistency

Application
MainWindow: the GUI definition, written in XAMLDataGridColumnsBehavior: an attached behavior that allows the modification of the columns of the attached DataGrid control.UserRoleValueConverter: The value converter implementation that defines what happens, when the user checks or unchecks the checkbox
ViewModel
MainViewModel: contains the display data table properties for the view and the data logic for the dynamic column handlingColumnTag: attached property for tagging objects to instances that derive from DependencyObject, in this case DataGridColumn
DataModel
DatabaseContext: singleton instance that contains the UserRoleDataSetUserRoleDataSet: the database implementation, based on DataSet
Implementation
Data Binding
The application is written using the MVVM design pattern. This means that the main window is bound to the main view model, and the view controls are bound to the main view model's properties.
| Reference | View Control Property | ViewModel Property |
| 1 | MainWindow:DataGridRoles.ItemsSource | MainViewModel.Roles |
| 2 | MainWindow:DataGridUsers.ItemsSource
| MainViewModel.Users |
| 3 | MainWindow:DataGridUsers.Column | MainViewModel.UserRoleColumns |
Ad 1: Binds the database role table to the roles data grid control
Ad 2: Binds the database user table to the users data grid control
Ad 3: Binds the column's observable collection to the users grid control's columns property. The dynamic column behavior is achieved via this property, because the logic in the view model adds and removes the columns from and to this collection.
The data grid control's column property is declared as read-only, so it cannot be bound to a view model property. The DataGridColumnsBehavior is an attached behavior that overcomes this limitation. The original article and source can be found here.
<Window x:Class="Application.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:attachedBehaviors="clr-namespace:Application.AttachedBehaviors"
xmlns:viewModel="clr-namespace:ViewModel;assembly=ViewModel"
Title="User Administration" Height="350" Width="525">
<Window.DataContext>
<viewModel:MainViewModel/>
</Window.DataContext>
<DockPanel LastChildFill="True">
<ToolBar DockPanel.Dock="Top">
<Button Content="Save" Command="{Binding SaveCommand}"/>
</ToolBar>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="146*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="147*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<GroupBox x:Name="UsersGroupBox"
Grid.Column="0"
Header="User Role Assignment">
<DataGrid x:Name="DataGridUsers"
ItemsSource="{Binding Users}"
attachedBehaviors:DataGridColumnsBehavior.BindableColumns=
"{Binding UserRoleColumns}"
AutoGenerateColumns="False"
EnableRowVirtualization="False"/>
</GroupBox>
<GroupBox x:Name="RolesGroupBox"
Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0"
Header="Roles">
<DataGrid x:Name="DataGridRoles"
ItemsSource="{Binding Roles}"
AutoGenerateColumns="False">
<DataGrid.Columns>
<DataGridTextColumn Header="Name"
Binding="{Binding Name}"/>
</DataGrid.Columns>
</DataGrid>
</GroupBox>
</Grid>
</DockPanel>
</Window>
Data Handling
The data is kept in three tables in the UserRoleDataSet (Role, User and UserRole). The Role and User tables are bound to the data grid controls via a DataView. The DataView allows the modification, insertion and removal of rows and the prevention of these actions. Filtering and sorting can be setup on the DataView as well. The data grid control can handle the data manipulation using the DataView. Rows can be inserted, modified and removed in the data grid control (there is a new item row at the bottom of the grid, and rows are be removed when the delete key is pressed) and the data tables are directly updated through the DataView.
public class MainViewModel
{
public MainViewModel()
{
--- Code omitted ---
this.UserRoleColumns = new ObservableCollection<DataGridColumn>();
--- Code omitted ---
}
public DataView Users
{
get
{
return this.dataContext.DataSet.User.DefaultView;
}
}
public DataView Roles
{
get
{
return this.dataContext.DataSet.Role.DefaultView;
}
}
public ObservableCollection<DataGridColumn> UserRoleColumns { get; private set; }
}
The DataSet can be used together with database connections to store and retrieve data from SQL servers, etcetera. In this application, I use the persistence mechanism to store to and retrieve data from an XML file.
Every DataSet table has a set of events that can be used to get notified on data modifications.. This mechanism is used to add, remove and update the dynamic columns when the role table is modified.
public class MainViewModel
{
public MainViewModel()
{
--- Code omitted ---
this.dataContext = DatabaseContext.Instance;
this.dataContext.DataSet.Role.RoleRowChanged += this.RoleOnRowChanged;
this.dataContext.DataSet.Role.RoleRowDeleted += this.RoleOnRoleRowDeleted;
--- Code omitted ---
}
private void RoleOnRowChanged(object sender,
UserRoleDataSet.RoleRowChangeEvent roleRowChangeEvent)
{
switch (roleRowChangeEvent.Action)
{
case DataRowAction.Change:
this.UpdateRoleColumn(roleRowChangeEvent.Row);
break;
case DataRowAction.Add:
this.AddRoleColumn(roleRowChangeEvent.Row);
break;
}
}
private void RoleOnRoleRowDeleted(object sender,
UserRoleDataSet.RoleRowChangeEvent roleRowChangeEvent)
{
if (roleRowChangeEvent.Action == DataRowAction.Delete)
{
this.DeleteRoleColumn(roleRowChangeEvent.Row);
}
}
}
Business Logic
Default Column Definition
The user data grid column definition is stored in the UserRolesColumns collection. This means that the default columns, the user's first and last name, have to be in this collection too. Two DataGridTextColumns are instantiated for the first and the last name, and the cell content are bound to the data row through the binding to the row's respective fields.
public class MainViewModel
{
public MainViewModel()
{
this.GenerateDefaultColumns();
--- Code omitted ---
}
private void GenerateDefaultColumns()
{
this.UserRoleColumns.Add(new DataGridTextColumn
{
Header = "First Name", Binding = new Binding("FirstName")
});
this.UserRoleColumns.Add(new DataGridTextColumn
{
Header = "Last Name", Binding = new Binding("LastName")
});
}
}
Dynamic Column Definition
The dynamic column handling is separated into the 3 operation types:
AddRoleColumn: is called when a role is added to the Role table. It instantiates a new DataGridCheckBoxColumn, assigns the CheckBoxColumnStyle and the UserRoleValueConverter. The latter implements the user-role assignment logic (see below). The column is tagged with the role instance, so that the assignment logic can work. The column's header is set to the role name.UpdateRoleColumn: is called when the contents of a role row is modified. The logic scans the dynamic column collection for the column that is tagged with the role instance that is modified. Once found, the column's header is updated with the role name. The binding mechanism automatically updates the column header in the data grid.DeleteRole: is called when a role is removed from the Role table. The logic scans the dynamic column collection for the column that is tagged with the role instance that was deleted and removes the column.
public class MainViewModel
{
private void AddRoleColumn(UserRoleDataSet.RoleRow role)
{
var resourceDictionary = ResourceDictionaryResolver.GetResourceDictionary("Styles.xaml");
var userRoleValueConverter = resourceDictionary["UserRoleValueConverter"] as IValueConverter;
var checkBoxColumnStyle = resourceDictionary["CheckBoxColumnStyle"] as Style;
var binding = new Binding
{
Converter = userRoleValueConverter,
RelativeSource =
new RelativeSource(RelativeSourceMode.FindAncestor,
typeof(DataGridCell), 1),
Path = new PropertyPath("."),
Mode = BindingMode.TwoWay
};
var dataGridCheckBoxColumn = new DataGridCheckBoxColumn
{
Header = role.Name,
Binding = binding,
IsThreeState = false,
CanUserSort = false,
ElementStyle = checkBoxColumnStyle,
};
ObjectTag.SetTag(dataGridCheckBoxColumn, role);
this.UserRoleColumns.Add(dataGridCheckBoxColumn);
}
private void UpdateRoleColumn(UserRoleDataSet.RoleRow role)
{
if (role != null)
{
foreach (var userRoleColumn in this.UserRoleColumns)
{
var roleScan = ColumnTag.GetTag(userRoleColumn) as UserRoleDataSet.RoleRow;
if (roleScan == role)
{
userRoleColumn.Header = role.Name;
break;
}
}
}
}
private void DeleteRoleColumn(UserRoleDataSet.RoleRow role)
{
if (role != null)
{
foreach (var userRoleColumn in this.UserRoleColumns)
{
var roleScan = ColumnTag.GetTag(userRoleColumn) as UserRoleDataSet.RoleRow;
if (roleScan == role)
{
this.UserRoleColumns.Remove(userRoleColumn);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
User-Role Assignment
The DataGridCheckBoxColumn binds the check box control to a (nullable) boolean property of the data in the row that it is displaying. In this case, it would be a boolean property in the user data row, which represents the user to role assignment. Since there is no such property in the UserTable definition, another solution has to be implemented. Instead of binding to the check box control, a value converter is instantiated and bound to the DataGridCell that will contain the CheckBox control. The Binding definition in the AddRoleColumn method shown above contains an assignment to the value converter. The relative source of the bound control is set to the DataGridCell, found as an ancestor of the CheckBox control (the binding is defined on the CheckBox level).
The value converter's Convert method is called, every time the DataGrid cell is initially modified or lost its focus. In both cases, the user and the role roles are retrieved and the conversion result (if the user has the role assigned or not) is returned. The user row is fetched from the DataGridCell's DataContext, which contains the DataRowView instance that has the user row in its Row property. The role is retrieved from the ColumnTag that is assigned to the column when it was added.
The CheckBox control's Checked event is subscribed to when the DataGridCell is in editing mode, and unsubscribed when not.
public class UserRoleValueConverter : IValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
bool result = false;
var dataGridCell = value as DataGridCell;
if (dataGridCell != null)
{
var dataRowView = dataGridCell.DataContext as DataRowView;
if (dataRowView != null)
{
var user = dataRowView.Row as UserRoleDataSet.UserRow;
var role = ColumnTag.GetTag(dataGridCell.Column) as UserRoleDataSet.RoleRow;
if (user != null && role != null)
{
var checkBox = dataGridCell.Content as CheckBox;
if (checkBox != null)
{
if (dataGridCell.IsEditing)
{
checkBox.Checked += this.CheckBoxOnChecked;
}
else
{
checkBox.Checked -= this.CheckBoxOnChecked;
}
}
result =
DatabaseContext.Instance.DataSet.UserRole.Any(
x => x.UserRow == user && x.RoleRow == role);
}
}
}
return result;
}
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
The CheckedBoxOnChecked method is called whenever the check box state is modified. The logic searches for the CheckBox's DataGridCell and gets the user and role instances that belong to it. It will add or delete the user-role entry depending on the CheckBox.IsChecked state and whether a UserRoleRow is already present.
private void CheckBoxOnChecked(object sender, RoutedEventArgs routedEventArgs)
{
var checkBox = sender as CheckBox;
var dataGridCell = ControlHelper.FindVisualParent<DataGridCell>(checkBox);
if (dataGridCell != null)
{
var dataRowView = dataGridCell.DataContext as DataRowView;
if (checkBox != null && dataRowView != null)
{
var user = dataRowView.Row as UserRoleDataSet.UserRow;
var role = ObjectTag.GetTag(dataGridCell.Column) as UserRoleDataSet.RoleRow;
if (user != null && role != null)
{
if (checkBox.IsChecked == true
&& DatabaseContext.Instance.DataSet.UserRole.Any(
x => x.UserRow == user && x.RoleRow == role) == false)
{
DatabaseContext.Instance.DataSet.UserRole.AddUserRoleRow(user, role);
}
else
{
var userRole =
DatabaseContext.Instance.DataSet.UserRole.FirstOrDefault(
x => x.UserRow == user && x.RoleRow == role);
if (userRole != null)
{
userRole.Delete();
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Points of Interest
Checkbox Column Style Handling
As an added bonus (and to prevent extra state logic) I added the functionality that the CheckBox control is not shown in the user data grid new item row. The DataGridCheckBoxColumn style has to be modified, and the Visibility flag of the CheckBox has to be set, depending on the contents of the DataGridCell. If the data row is the new item row, then it has a NewItemPlaceHolder. A converter is used to get this information and it is mapped to the CheckBox's Visibility flag. The solution to this problem can be found here.
The CheckBox style is defined in the Style.xaml file in the Application layer. It is appended to the application's resource in a merged dictionary. A helper class in the ViewModel layer called ResourceDictionaryResolver iterates through the dictionaries in the merged dictionary container and searches for the dictionary with the given name (the name is in the dictionary Source property). The check box style can then be extracted from the resource dictionary through its key name.
Object Tagging
The standard WPF DataColumn doesn't allow object tagging. Object tagging is the functionality that allows objects to be tagged to a control. This can be used in situations where the control is available, but an object cannot be accessed using standard application logic. In the case of this sample, the available control is the CheckBox in the DataGridCell and the required object is the role that corresponds to the column. The role is tagged to the column and can be retrieved at a later time. The ObjectTag itself is a DependencyProperty that can be attached to any type of control that is derived from DependencyObject. The solution to this problem can be found here.
Database Save Handling
As second small bonus, I implemented the database saving, when the data is modified. The command is bound to the save toolbar button, and checks the database context for changes. The DataSet has built-in functionality that tests its contents for modifications. The button is enabled when the DataSet has changes, otherwise it is disabled. The Command's CanExecuteChanged is connected to CommandManager.RequerySuggested when it is subscribed to. The button state is then automatically checked when the application is idle by calling the CanExecute method in the main thread context.
Conclusion
This article shows an implementation of dynamic column handling for WPF DataGrid controls. It is a straight forward MVVM implementation where the dynamic column handling is done in the view-model layer. The drawback of this solution is that GUI components spilled over into the ViewModel layer. In the next article, I will show a solution that implements the same application, but with a more strict separation of business logic and GUI controls into their respective layers.
