All SPA libraries that I’ve tried have long tutorials to show you have to use and configure them. It’s not unusual that they allow you to structure your application just as you like, which might be great for powerful users, but make it more confusing for newcomers. Here is an introduction to my own library which should be reasonably easy to get started with.
Griffin.Yo is as the name applies a library that should be easy to get started with, but hopefully powerful enough to satisfy more advanced users. only dependency that the library has is on the vanillajs framework. All you need to get started is just a few lines of code and a single JavaScript.
Disclaimer: I’ve never used a SPA library. I’ve just read about a few and how they work. Hence I’m no expert. This library is just something that I cooked up during a weekend. My goal is however to keep building and maintain it. It’s perfect to combine with my Command/Query library (serverside/clientside).
To get started, all you need is to include the script, define a main view tag, a few routes:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="YoView">
</div>
<div class="navigation">
<a href="#users/1">Show user</a>
<a href="#/">Index</a>
</div>
<script src="Yo.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var spa = new Griffin.Yo.Spa('DemoApp');
spa.mapRoute('', 'home/index');
spa.mapRoute('user/:id', 'users/details');
spa.mapRoute('users/', 'users/list');
spa.run();
</script>
</body>
</html>
DemoApp which is passed to the Spa constructor is the application name and is used to move everything from the global namespace in JavaScript (i.e. all view models must be in this namespace). The only required HTML thingy is the id="YoView" which is used to locate where the view should be loaded.
Griffin.Yo uses a conventional approach where scripts and views have to be located in certain folders. For the above example, the following structure is required:
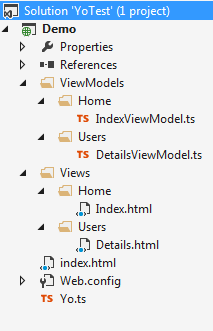
- View models should be located under
ViewModels where the subfolder represents the path in the second argument to spa.mapRoute(), i.e. ‘users/details’ makes Griffin.Yo request ViewModels/Users/DetailsViewModel.js from the server. - Views should be located under
Views, in the user case it looks for Views/Users/Details.html
Once views and models have been loaded, they are cached in the browser (the cache is emptied if the browser is reloaded). Thus as long as the user continues to use the site as a SPA application, everything is only loaded once from the server.
Views
Views are simple HTML pages. There are no directives like in KnockoutJS or Angular. At most, you add the data-name attribute to your elements to be able to adapt the output. The adaption is however done from the ViewModel and not in the view. Another difference is that views are never bound to a model or vice versa. You need to take care of that yourself.
The details view for users looks like this:
<div id="DetailsView">
<h1 data-name="Name"></h1>
<table>
<tbody>
<tr data-name="Users">
<td data-name="Id"></td>
<td data-name="UserName"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div data-name="Address">
<div data-name="Postal">
<span data-name="ZipCode"></span>
<span data-name="City"></span>
<input name="Name" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
The ID of the root tag is just there if you want to render something partial at a later stage in the page life cycle.
Any modifications/adaptations that is required for the views must be made from the view model (read the ‘Rendering’ chapter).
View Models
View models are used to bind data to the view. A view model typically calls the server side through a web socket or through Ajax to load information. The built in HttpClient supports caching (using the If-Modified-Since header). That means that the server side load from view models will also be greatly reduced.
The users view model looks like this:
module DemoApp.Users {
import Yo = Griffin.Yo;
export class DetailsViewModel implements Yo.IViewModel {
public getTitle(): string {
return 'User details';
}
public activate(context: Yo.IActivationContext): void {
context.render({ Name: 'Hello world users' });
Yo.Http.get('/user/' + context.routeData['id'], xhr => {
context.render(xhr.responseBody);
});
}
public deactivate() {
}
}
}
The IActivationContext provides a scope which applies for this view model. You can see it as representing a limited part of the web page. You can for instance use view models to handle side bars, etc. too. With the help of the context, the VM doesn’t need to be aware of where its produced result goes.
To control the output, you map the VM like this:
spa.mapRoute('/user/:userId/panel', 'users/panels/detail', 'userPanelId');
... where the last argument is the HTML div that the view should get rendered in.
Binding Fields
If you need to act upon actions in the view, you can use the ‘handle’ class.
export class DetailsViewModel implements Yo.IViewModel {
public getTitle(): string {
return 'User details';
}
public activate(context: Yo.IActivationContext): void {
context.handle.click('.reloadButton', onReload);
}
public deactivate() {
}
public onReload(e: MouseEventArgs) {
e.preventDefault();
}
}
}
Rendering
The renderer currently supports:
- objects/json: Send any object to the renderer
- Complex/hierarchical objects: Nested models are no problem
- Partial objects: You can update only a portion of the view by just passing the fields that you want to update
- Collections: Tables, lists, etc. will be rendered correctly
- Directives: More complex adaptations of the data
Identifying View Mapping
Rendering of views is done by identifying elements using the attributes below (and in order specified below).
- data-name attribute
- name attribute (typically on form elements)
- id attribute
i.e., if a field is named ‘FirstName’, the rendered will first look for data-lang="FirstName", then name="FirstName" and finally after id="FirstName". It will stop when it finds the first match. However, if multiple elements are using the same attribute, like data-lang="FirstName", all will be rendered with the same value.
<h1 id="Name"></h1>
<table>
<tbody>
<tr data-name="Users">
<td data-name="Id"></td>
<td data-name="UserName"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<input name="Age" />
All fields above would be filled when the following object is used:
var dto = {
Name: 'Jonas Gauffin',
Age: 38,
Users: [
{ Id: 1, UserName: 'jgauffin' }
]
}
context.render(dto);
Basics
Rendering is done with the help of the ViewRenderer class. It’s typically used through the IActivationContext as in the view model examples above, but also be used directly:
var renderer = new Yo.ViewRenderer('#someView');
renderer.render({ FirstName: 'Jonas', LastName: 'Gauffin', Age: 38 });
The constructor can take a HTMLElement (great if the view has not been attached to the document yet, i.e. prepopulate it with data), an ID or a selector.
Complex Objects
Works just like regular rendering.
View:
<div data-name="Address">
<div data-name="Attention"></div>
<div data-name="Postal">
<span data-name="ZipCode"></span>
<span data-name="City"></span>
</div>
</div>
Script:
var renderer = new Yo.ViewRenderer('#Address');
renderer.render({ Attention: 'Jonas Gauffin', Postal: { ZipCode: 1234, City: 'Falun' });
Partial Objects
Sometimes, you just want to update a portion of the view. Here is a partial update of the previous view:
var renderer = new Yo.ViewRenderer('#Address');
renderer.render({ Postal: { City: 'Falun' });
.. which will just update the City.
Directives
Some elements like links have to have multiple modifications which of course is impossible if only one mapping is made. To solve that, this library supports something that I call directives. Directives simply tells the renderer that multiple modifications should be done to a mapped element.
Let’s say that you got a simple link:
<a data-name="UserName"></a>
It requires that both the href and the text are updated.
To achieve that, you create a directive like this:
var directives: {
UserName: {
text: function(value) {
return value;
},
href: function(value, parentModel) {
return '#user/' + parentModel.id;
}
}
};
var renderer = new Yo.ViewRenderer('#Address');
renderer.render({ UserName: 'Arne', Id: 1 }, directives);
The structure of the directive object is a mirror of the data that is rendered. But instead of containing a single value, it contains a property for each HTML attribute that should be attached to the HTML element. In this case, the text property represents element.innerText while the href property adds the ‘href’ attribute to the rendered element.
Thus the final result would be:
<a href="#user/1" data-name="UserName">Arne</a>
For INPUT elements, you would use the ‘value’ property instead of ‘text’.
If value/text/html is omitted in the directive, they will be rendered per default by the renderer.
Attributes with dashes are also supported, simply enclose them in quotes:
var directives: {
UserName: {
"data-stuff": function(value) {
return value;
}
}
};
var renderer = new Yo.ViewRenderer('#Address');
renderer.render({ UserName: 'Arne', Id: 1 }, directives);
Routing
The final part is the routing. Default values are currently not supported.
To use url parameters, you prefix segments with colon:
spa.mapRoute('/user/:userId', '/users/detail');
.. to get the userId you retrieve it from the routeData in the view model:
export class DetailViewModel implements Yo.IViewModel {
public getTitle(): string {
return 'User info';
}
public activate(context: Yo.IActivationContext): void {
var userId = context.routeData['userId'];
}
public deactivate() {
}
}
Feature Requests
What do you think about the library?
Is there anything fundamental missing? Is it easy to get started with?
Have I made any major design flaws that need to be addressed?
Leave a comment.
Code
The code is available at github. It also contains a few examples that demonstrate different features.
Do note that it’s an early beta, some inner workings might get refactored while the public API should be reasonably stale. Suggestions and feedback are most welcome.
