Introduction
Have you ever felt like having 30% to 40% of your source code been made up of SQL statements sucks?
You are not alone. The good news is, a solution exists that takes away most of the SQL statements from the application into the database. A stored procedure is a single or group of T-SQL statements that are all executed at once. Think of a stored procedure as a method. We usually create functions for reusability purposes. When calling methods, we pass in parameters. The same concept applies to stored procedures.
Background
Have you ever written a method before and SQL statements, then congratulations. You have already done 90% of the work required. If you haven’t yet, there is still good news for you. There is no rocket science involved in creating stored procedures. In this tutorial, we are going to create stored procedures that:
- Insert new data into tables
- Update existing records
- Delete existing records
- Retrieve all existing records
- Retrieve a single record based on the primary key
Creating the Tutorial Database in SQL Server
Run the following script to a database in SQL Server and a table employees.
CREATE DATABASE SPTutorial
GO
USE SPTutorial
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[employees](
[employee_id] [numeric](18, 0) IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[full_name] [nvarchar](75) NULL,
[gender] [nvarchar](6) NULL,
[department] [nvarchar](25) NULL,
[position] [nvarchar](50) NULL,
[salary] [float] NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_employees] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[employee_id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, _
ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
SQL Server Stored Procedures Naming Conventions
In this tutorial, we will use the following convention to name user defined stored procedures usp_tableName_action.
HERE,
- "
usp" will be used to identify user defined stored procedures. System defined stored procedures start with the prefix sp. - "
tableName" is the singular or plural of the table that the stored procedure manipulates. - "
action" is the action to be performed such as INSERT a new record, UPDATE or DELETE an existing record or SELECT record(s).
Stored Procedures Dictionary
The following table shows the stored procedures that we will create for the employees table.
| S/N | Procedure Name | Description | Parameters |
| 1 | usp_employee_insert | Creates a new employee record | full_name, gender, department, position, and salary |
| 2 | usp_employee_update | Updates an existing employee record | full_name, gender, department, position, salary and employee_id |
| 3 | usp_employee_delete | Deletes an existing employee record based on the id parameter value | employee_id |
| 4 | usp_employee_get_all | Retrieves all employee records | |
| 5 | usp_employee_get_by_id | Retrieves a single employee record based on the id parameter value | employee_id |
SQL Server INSERT Row Stored Procedure
Run the following code to create a stored procedure that add a new employee to the
USE SPTutorial
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_employee_insert]
@full_name varchar(75),@gender varchar(6), @department varchar(25), _
@position varchar(50),@salary float
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO employees (full_name,gender,department,position,salary)
VALUES (@full_name,@gender,@department,@position,@salary)
END
GO
HERE,
- "
USE SPTutorial" ensures that the stored procedure is created in SPTutorial database - "
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_employee_insert] @full_name varchar(75),@gender varchar(6), @department varchar(25), @position varchar(50),@salary float AS" tells SQL server to create a stored procedure named usp_employee_insert. The stored procedure accepts full_name, gender, departments, position and salary parameters. - "
BEGIN INSERT INTO employees (full_name,gender,department,position,salary) VALUES (@full_name,@gender,@department,@position,@salary) END" is the T-SQL statement that will be executed whenever this procedure is called. As you can see, the procedure is nothing more than standard SQL statements that you are already used to.
Executing a Stored Procedure from SQL Server
Expand the programmability node.
Expand stored procedures node.
Right click on usp_employee_insert.
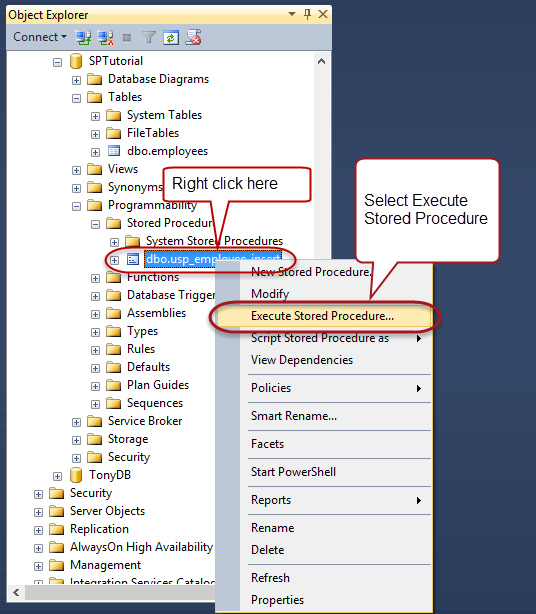
Select Execute Stored Procedure…
You will get the following results:

Click on OK button when done.
Run a simple SELECT query. You will get the following results:

SQL Server UPDATE Row Stored Procedure
USE SPTutorial
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_employee_update]
@full_name varchar(75),@gender varchar(6), @department varchar(25), _
@position varchar(50),@salary float,@employee_id numeric(18,0)
AS
BEGIN
UPDATE employees SET full_name = @full_name
,gender = @gender
,department = @department
,position = @position
,salary = @salary
WHERE employee_id = @employee_id
END
GO
HERE,
- The above stored procedure uses a standard SQL
UPDATE statement to update a table record.
SQL Server DELETE Row Stored Procedure
USE [SPTutorial]
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_employee_delete]
@employee_id numeric(18,0)
AS
BEGIN
DELETE FROM employees WHERE employee_id = @employee_id
END
GO
HERE,
- The above stored procedure uses a standard SQL
DELETE statement to delete a table record.
SQL Server SELECT ALL Row Stored Procedure
USE SPTutorial
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_employee_get_all]
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT * FROM employees
END
GO
HERE,
- The above stored procedure uses a standard SQL
SELECT statement to retrieve all the records in a table.
SQL Server SELECT Single Row Stored Procedure
USE SPTutorial
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_employee_get_by_id]
@employee_id numeric(18,0)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE employee_id = @employee_id
END
GO
HERE,
- The above stored procedure uses a standard SQL
SELECT statement to retrieve a single record.
Summary
In this tutorial, we learnt how to create stored procedures that add, update, delete and retrieve records from a table. We also learnt a few conventions that simplify working with stored procedures in SQL Server.
History
- v1.0, 07-07-2015: Initial release
