Introduction
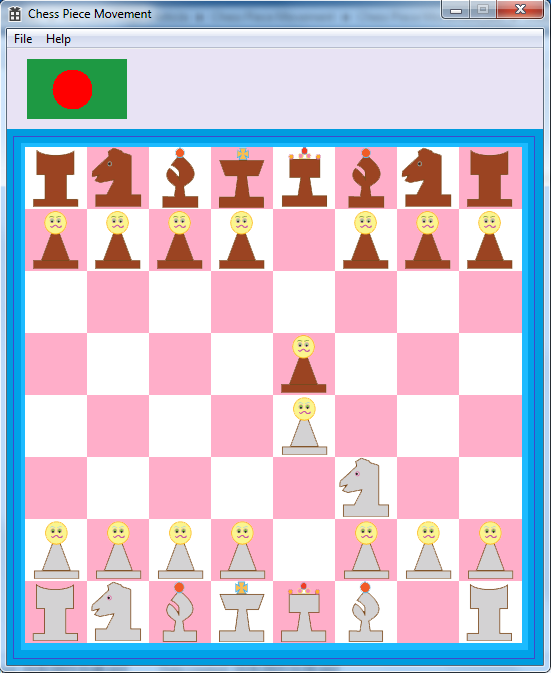
This tip is a simple chess game project which shows the basic technique of chess piece movement.
The movement technique will not prevent you from moving pieces illegally which means all the pieces can be moved forward, backward, sideways, or diagonally. In fact, you can move pieces from a square to any square if the square remains empty.
Board and Piece Images
The chess board is a 537x537 bitmap image and pieces are 62x62 transparent png images.
By the way, all the pieces are designed by my little sister Zeba. She is very good graphics designer.
Description Of Project Source Code
The project is developed in C++ and it uses GDI+ library for drawing chessboard and all the pieces. This Chess piece movement project has three classes for various purposes. CPiece, CBoard and CGame.
The CPiece class contains information for each piece. It contains position, size, type and row column information for each piece.
The following code shows all the member declarations of the class:
class CPiece
{
private:
INT m_nX;
INT m_nY;
public:
CPiece();
~CPiece();
int init(CBoard* pBoard, TCHAR* lpFileName, enum EBlockPiece eColor,
enum EPieceType ePieceType, UINT row, UINT column, UINT pieceIndex);
void moveTo(INT pieceIndex, enum EBlockPiece eColor, UINT row, UINT column);
void draw(Graphics* g);
};
init: It is used for initializing the piece data. It also updates information of square of given row and column.
int CPiece::init(CBoard* pBoard, TCHAR* lpFileName, enum EBlockPiece eColor,
enum EPieceType eType, UINT row, UINT column, UINT index)
{
. . . . . . . .
SChessBlock* pBlock = pBoard->getBlockAt(row, column);
this->m_nX = pBlock->x;
this->m_nY = pBlock->y;
pBlock->ePiece = eColor;
pBlock->pieceIndex = index;
moveTo: This function moves a piece from its current row and column to given row and column. It changes the value of m_nX and m_nY variable. It also updates data of both old and new square of the piece.draw: This function draws the piece to the main window.
The other class is called CBoard. This class holds information of chess board and
it contains a 8x8 array variable called m_aChessBlocks of type SChessBlock which holds information for each square.
struct SChessBlock {
INT row;
INT column;
INT x;
INT y;
. . . . . . . . .
. . . . . ..
};
Here is the declaration of CBoard Class:
class CBoard
{
private:
Image* m_pImage;
. . . . . . .
. . . . .
public:
CBoard() ;
~CBoard() ;
void init(TCHAR* lpFileName, UINT x, UINT y, UINT width, UINT height);
SChessBlock* getBlockAt(UINT row, UINT column);
void draw(Graphics* g);
};
getBlockAt: Returns pointer to square information of given row and column.draw: Draws the board image.
The last class is CGame which contains instance to CBoard class and CPiece class and it also contains code for piece selection movement.
class CGame
{
private:
CPiece m_aBlackPieces[16];
CPiece m_aWhitePieces[16];
CBoard m_Board;
SChessBlock* m_pSelectedBlock;
public:
CGame();
~CGame();
void init();
void onLButtonDown(INT x, INT y);
void onLButtonUp(INT x, INT y);
void draw(Graphics* g);
};
The init member function initializes the chess board and all the pieces. The main window initializer will call this function after creating the main window:
. . . . . . . .
g_Game.init();
. . . . . . .
g_Game is a global variable instance to the CGame class.
The init function calls the init member function of CBoard class and passes an image file name called 'ChessBoard2.bmp' to its parameter to initialize the chess board with this image. Then it calls the init member function of CPiece class for each element of m_aBlackPieces and m_aWhitePieces array variable to initialize them.
void CGame::init()
{
m_Board.init(L".\\ChessBoard2.bmp", 0, 80, 537, 537);
for(UINT col=0;col<8;col++) {
m_aBlackPieces[col].init(&m_Board, L".\\Pawn.png", EPT_PAWN, 1, col, col);
}
m_aBlackPieces[8].init(&m_Board, L".\\Rook.png", EPT_ROOK, 0, 0, 8);
m_aBlackPieces[9].init(&m_Board, L".\\Knight.png", EPT_KNIGHT, 0, 1, 9);
. . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . ..
The CGame class has two member functions called onLButtonDown And onLButtonUp. Our main window procedure function will call those functions on WM_LBUTTONDOWN and WM_LBUTTONUP message.
case WM_LBUTTONDOWN:
g_Game.onLButtonDown(LOWORD(lParam), HIWORD(lParam));
break;
case WM_LBUTTONUP:
g_Game.onLButtonUp(LOWORD(lParam), HIWORD(lParam));
break;
The onLButtonDown function is used for checking whether the mouse clicked at any square of our chess board or not.
The onLButtonDown function loops through all the rows and columns of chess board:
for(UINT row = 0;row < 8;row++)
{
for(UINT col = 0;col < 8;col++)
{
SChessBlock* pBlock = m_Board.getBlockAt(row, col);
. . . . . .
The getBlockAt member function of CBoard class returns pointer to square information of given row and column.
Then it checks whether the mouse pointer is inside the square or not:
if ( ( x >= px && x <= (px + 62)) && (y >= py && y <= (py + 62)) )
{
. . . . . . .
Size of each square is 62.
And finally it checks whether the game should perform a piece movement or just mark the square as selected:
if ( pBlock->eStatus == EBS_NONE )
{
if ( pBlock != m_pSelectedBlock ) {
if ( m_pSelectedBlock && m_pSelectedBlock->ePiece == EBP_BLACK )
{
if ( pBlock->ePiece == EBP_EMPTY )
{
if ( m_pSelectedBlock->ePiece == EBP_BLACK )
{
INT pieceToMove = m_pSelectedBlock->pieceIndex;
this->m_aBlackPieces[pieceToMove].moveTo
(pieceToMove, EBP_BLACK, pBlock->row, pBlock->column);
m_pSelectedBlock->eStatus = EBS_NONE;
m_pSelectedBlock = nullptr;
::InvalidateRect(hWnd, NULL, TRUE);
break;
}
else if ( m_pSelectedBlock->ePiece == EBP_WHITE )
{
INT pieceToMove = m_pSelectedBlock->pieceIndex;
this->m_aWhitePieces[pieceToMove].moveTo
(pieceToMove, EBP_WHITE, pBlock->row, pBlock->column);
m_pSelectedBlock->eStatus = EBS_NONE;
m_pSelectedBlock = nullptr;
::InvalidateRect(hWnd, NULL, TRUE);
break;
}
}
}
}
pBlock->eStatus = EBS_SELECTED;
if ( m_pSelectedBlock ) {
m_pSelectedBlock->eStatus = EBS_NONE;
}
m_pSelectedBlock = pBlock;
::InvalidateRect(hWnd, NULL, TRUE);
break;
}
The draw member function of CGame class will draw board and all the pieces of our chess game. The WM_PAINT message handler of main window will call this function.
case WM_PAINT:
{
. . . . .. . .
HDC drawDC = ::CreateCompatibleDC(hdc);
HBITMAP hBitmap = ::CreateCompatibleBitmap(hdc, rcClient.right, rcClient.bottom);
HBITMAP hOldBitmap = (HBITMAP)::SelectObject(drawDC, hBitmap);
Graphics g(drawDC);
g_Game.draw(&g);
::BitBlt(hdc, 0, 0, rcClient.right, rcClient.bottom, drawDC, 0, 0, SRCCOPY);
::SelectObject(drawDC, hOldBitmap);
::DeleteDC(drawDC);
::DeleteObject(hBitmap);
. . . . .
}
Points of Interest
From this tip, you can learn the basic starting of chess game creation. And also, you can apply various movement techniques to the project for experiment purposes.
Conclusion
I've added only very few features in this Chess Piece Movement project, but I hope this project will help you to develop chess games and other games.
Next time, I will try to show the technique of legal movement calculation for each different piece.
