Once one of my friends was discussing about the SQL queries and he was a bit confused about GROUP BY, then we have long been discussing about only this clause. And, that gave me an idea which I am putting down in this tip.
This is a simple tip to describe the GROUP BY clause and when we use this in our SQL statements with and without using HAVING clause.
Introduction
This tip would be helpful to get an insight into the GROUP BY in SQL queries like how it works and when we need to use GROUP BY.
Before we jump into GROUP BY and related stuff, we should need to understand the logical order in which QL query gets executed.
Logical Processing Order
This tip would be helpful to get insight into GROUP BY in SQL queries like how it works and when we need to use GROUP BY.
Before we start jumping into GROUP BY and related stuff, we should need to understand first about how SQL query gets executed:
Let's see what we have in MSDN
The following steps show the logical processing order, or binding order, for a SELECT statement. This order determines when the objects defined in one step are made available to the clauses in subsequent steps. For example, if the query processor can bind to (access) the tables or views defined in the FROM clause, these objects and their columns are made available to all subsequent steps. Conversely, because the SELECT clause is step 8, any column aliases or derived columns defined in that clause cannot be referenced by preceding clauses. However, they can be referenced by subsequent clauses such as the ORDER BY clause. Note that the actual physical execution of the statement is determined by the query processor and the order may vary from this list
- FROM
- ON
- JOIN
- WHERE
- GROUP BY
- HAVING
- SELECT
- DISTINCT
- ORDER BY
- TOP
Let’s look at an example to describe the above logical processing order of the below SQL statement.
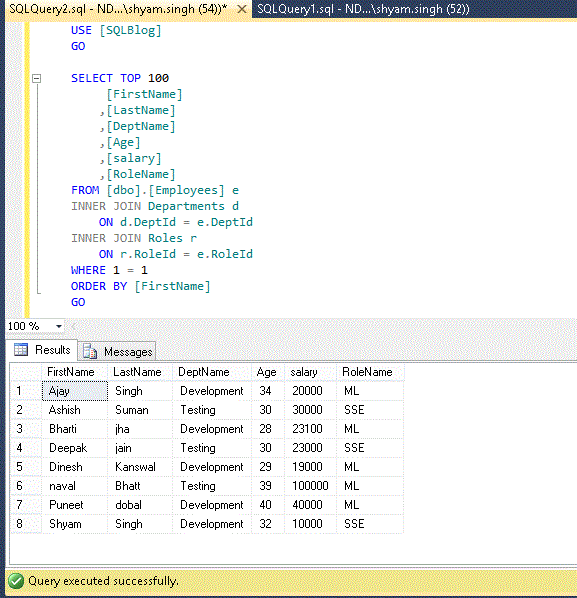
So, when we execute the above query, the outcome would come according to the logical processing order of SQL. Let’s see how its parts would be:
- Find the table ‘
Employees’ – collective all the columns JOIN ON table ‘Departments’ using DepitId – collective all the columnsJOIN ON table ‘Roles’ using RoleId – collective all the columns- Applying
WHERE condition to filter out records – (in this case, SQL query engine will ignore the 1 = 1 condition ) SELECT required columns which is mentioned like FirstName, LastName, etc.- Now result set would be
ORDER BY FirstName - Finally the
TOP – (number of records)
Hope this will help to understand the result outcome process of query.
Now, let’s move to get the glimpse of GROUP BY.
GROUP BY
The GROUP BY clause will as its name suggests groups the rows by column(s) specified in SELECT and will aggregate functions (using HAVING) to be performed on the one or more columns as WHERE clause could not be used with aggregate functions.
Oh, sounds too confusing to get? No worry, let’s go through a real life scenario with the small example.
“Suppose I have a store room and in store room there are shirts of black, white and yellow color and also have pants in black, gray and blue color. Now I need to arrange all the items so if I need to pick any item, I don’t mess up with all the clothes.
So, I will have a grouping approach: I will create a cell using Color for Shirt or Pant as we have both. When I complete the shell work, then I might not have any issue to find out any stuff regarding shirt or pant. Exactly the same thing applies in SQL when we use GROUP BY clause.
Let’s go the SQL way...
When We Use GROUP BY Clause
There are too many scenarios where we need to use GROUP BY instead of using other approaches, I am discussing 3 of them where we need to use GROUP BY:
- We want to know how many employees in each department are taking
salary >= 23000 - We want to know who is getting minimum salary in each department and the
salary is > 9000 - We want to know employee who is getting lowest salary having Testing role.
(If we have millions of records for all the transactions).
Let’s discuss scenarios 1 and 2, I am sure that you would be capable to complete the scenario after reading the complete article.
1. We want to know how many employees are taking salary >= 23000 department wise – (if we are talking about millions of records).

Explanation

2. We want to know who is getting minimum salary in our all departments and the salary would be greater than 9000

Explanation

I hope you would enjoy the tip. Please let me know if someone has any doubts on that.
Keep SQLing :)
