Print DataTable To Console at GitHub.
Introduction
Once in a while, I need to test some code very quickly or write a new piece of code from scratch. More often than not, the code is small enough to test it in a side project and after that to incorporate it into the main project. I imagine that these kind of necessities arise for most programmers, .NET or else, in their day-to-day work.
For cases like these, I have a side project - a snippet console solution - whose sole purpose is for a quick on-the-fly code. This snippet solution is loaded with all the DLL references that I may need for development & QA and it includes all kinds of class helpers that I wrote or picked up over the years. Once I open the solution, I'm up and ready to go.
With this article, I would like to share with you one helper class, a very useful one at that, that I have for debugging purposes. Its main functionality is to print DataTable to Console. Debugging a code doesn't necessarily mean setting break points and hitting them, it can also be printing whatever to the Console. This approach can be a more convenient way of examining your output on a small scale. Since DataTable doesn't lend itself to printing, I took the time to write this helper class for that. The helper is implemented as extension methods.
Now, the most likely scenario that you might encounter is to print a DataTable to the Console. However, the helper has more functionalities under the hood. It can:
- Print
DataTable, DataView, DataSet, DataRow[] (= DataTable.Select()) - Print Columns
- Print in tabular format and list format
- Print to
Console, StringBuilder, Stream
All the examples in this article will be performed on a products DataTable with columns Id int, ProductName string, InStock bool, DateAdded DateTime. All the DataTable extension methods that you see in these examples have equivalent extension methods for DataView, DataSet, DataRow[].
DataTable products = new DataTable();
products.TableName = "Products";
products.Columns.Add("Id", typeof(int)).AllowDBNull = false;
products.Columns.Add("ProductName", typeof(string));
products.Columns.Add("InStock", typeof(bool));
products.Columns.Add("DateAdded", typeof(DateTime));
Print
The Print extension method prints the DataTable in a tabular format. The parameters are:
rowOrdinals - Whether to print the ordinal index of the DataRow in the DataTabletop - Print only the first top rows. If top is less than or equal to 0, than print all rowstoString - A delegate that can be used to override the default ToString() for certain types of objects or certain columns.columnNames - List of columns to print in a given order. If this parameter is empty, than print all the columns. You can pass the same column name several times to columnNames parameter. For example, you may want to print the Id column twice, as the first column and as the last column.
Print(
this DataTable dataTable,
bool rowOrdinals = false,
int top = 0,
ValueToStringHandler toString = null,
params string[] columnNames
);
delegate string ValueToStringHandler(object obj, DataRow row, DataColumn column);
This is the simplest print. Prints all products to the console.
products.Print();
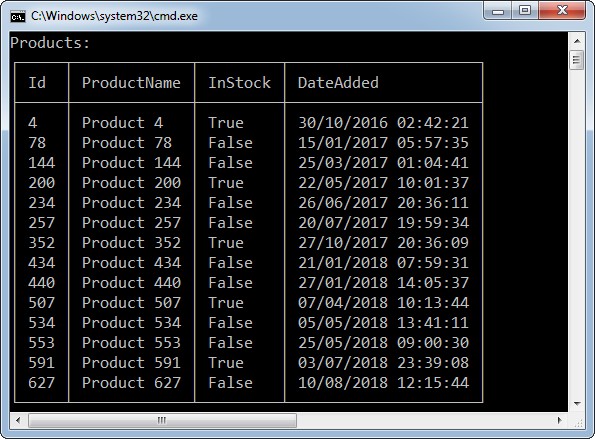
This will print the top 5 products with row ordinals, and it will print the Id column on both sides of the table.
products.Print(true, 5, "Id", "DateAdded", "InStock", "Id");

This will print the DateAdded column in a yyyy-MM-dd format. Any other column will be printed based on its default ToString() data type.
products.Print((obj, row, column) =>
{
if (obj == DBNull.Value)
return null;
if (column.ColumnName == "DateAdded")
return ((DateTime)obj).ToString("yyyy-MM-dd");
return obj.ToString();
});

PrintList
The PrintList extension method prints the DataTable in a list format. The default is a 2-columns vertical layout. PrintList layout the results the same way DataList control display its layout.
The parameters rowOrdinals, top, toString and columnNames are the same as the Print parameters.
repeatColumns - Number of layout columnsrepeatDirection - Vertical or horizontal layoutdelimiter - The delimiter between the column name and the row value
PrintList(
this DataTable dataTable,
bool rowOrdinals = false,
int top = 0,
ValueToStringHandler toString = null,
int repeatColumns = 2,
RepeatDirection repeatDirection = RepeatDirection.Vertical,
string delimiter = ": ",
params string[] columnNames
);
Prints all products with 2-columns vertical layout.
products.PrintList();

Prints Id and ProductName columns with 3-columns horizontal layout.
products.PrintList(3, PrintDataExtensions.RepeatDirection.Horizontal, "Id", "ProductName");

PrintColumns
The PrintColumns extension method prints information about the columns of the DataTable. The outputs are Column Ordinal, Column Name, Data Type, Nullable, Data Member. Data member is a made-up data member declaration which may come in handy.
PrintColumns(
this DataTable dataTable,
params string[] columnNames
);
Prints the columns of the products DataTable.
products.PrintColumns();

Output to Console, StringBuilder or Stream
The default output is to the Console. However, you can redirect to output to a StringBuilder or a Stream (MemoryStream, FileStream, ...). The default encoding for Stream is UTF8. Remember that you have to redirect the output before you print the DataTable. The redirection extension methods are straightforward:
PrintDataExtensions.SetOutputConsole();
PrintDataExtensions.SetOutputStringBuilder(StringBuilder builder);
PrintDataExtensions.SetOutputStream(Stream stream, Encoding encoding = Encoding.UTF8);
Prints to a StringBuilder.
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
PrintDataExtensions.SetOutputStringBuilder(builder);
products.Print();
Prints to a MemoryStream. The (default) encoding is UTF8.
byte[] buffer = null;
string output = null;
using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream())
{
PrintDataExtensions.SetOutputStream(stream);
products.Print();
buffer = stream.ToArray();
output = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer);
}
Prints to a FileStream.
string path = @"C:\output.txt";
using (FileStream stream = File.OpenWrite(path))
{
PrintDataExtensions.SetOutputStream(stream);
products.Print();
}
Border
The characters that make up the border are actually part of an Extended ASCII characters set. Extended ASCII codes start from code 128. These characters may not necessarily be mapped to box characters, it depends on your computer localization. If the border comes out garbled, you can change the way the border is printed to regular ASCII characters. There is also an option to remove the border completely.
PrintDataExtensions.ExtendedASCIIBorder();
PrintDataExtensions.ASCIIBorder();
PrintDataExtensions.ClearBorder();
You have to set the border before printing.
PrintDataExtensions.ASCIIBorder();
products.Print();

