Just download the TFS build template and enjoy. :)
Introduction
In this article, we will explain how to customize the TFS2012 build default template to add pre and post PowerShell scripts and create environment variables like the drops path and build number. These features exist by default in TFS2013 and TFS 2015.
Step 1: Edit Build Template
1. Add Workflow Arguments
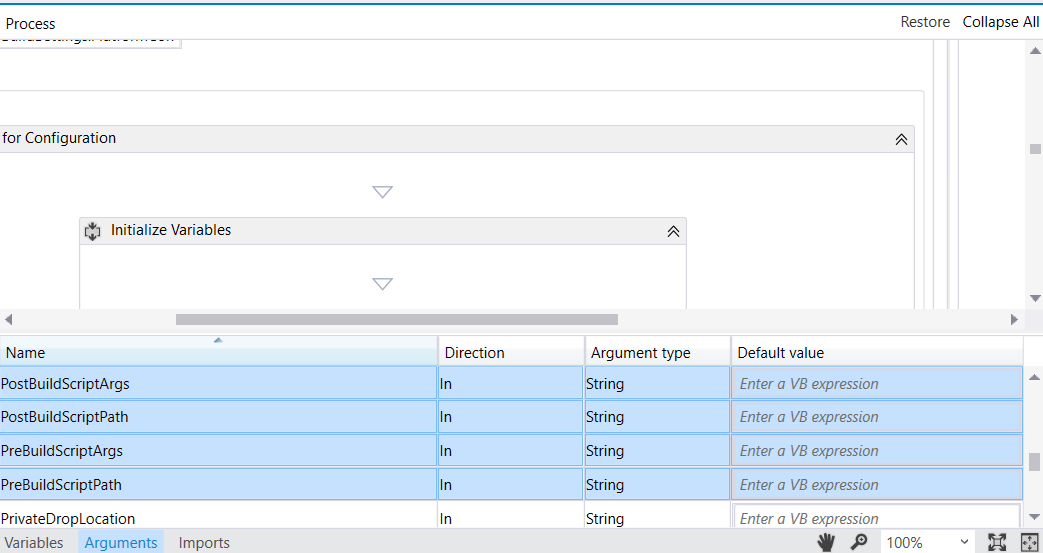
Open your build's default template workflow "DefaultTemplate.11.1.xaml", then click on Arguments tab and add those four workflow arguments:
PostBuildScriptPathPreBuildScriptPathPreBuildScriptArgsPostBuildScriptArgs
Create Hooks Script Section of the Build Process Parameters
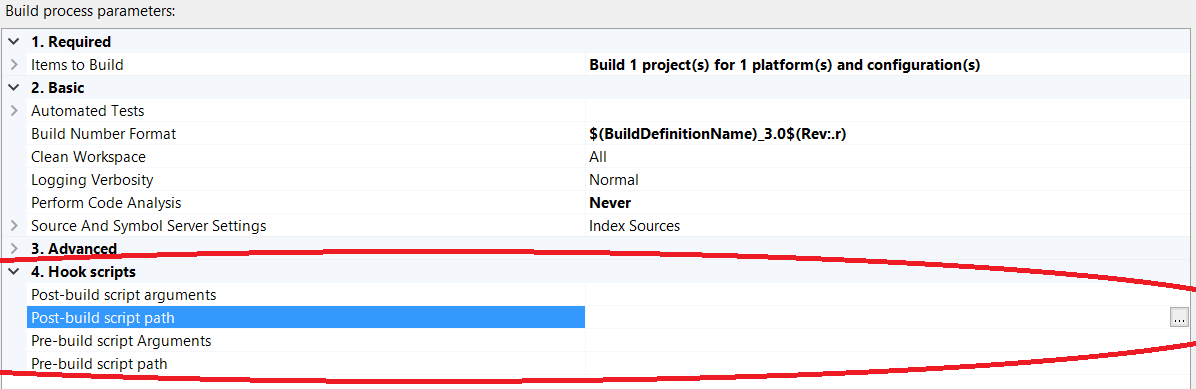
We will create a new section "Hook scripts" of the build process parameters that contains the script arguments and their descriptions, and we will add File Browser for PreBuildScriptPath and PostBuildScriptPath arguments to pick script's location from source control.
In the Arguments tab, select the Metadata argument and click on the button "..." in the "Default value" column and add the metadata for the script arguments like below:
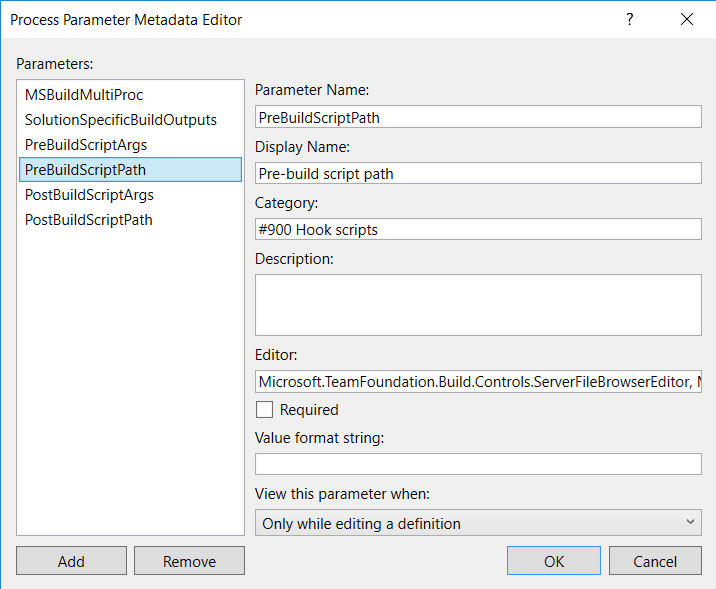
To add File Browser for PreBuildScriptPath and PostBuildScriptPath arguments, fill the Editor field with value "Microsoft.TeamFoundation.Build.Controls.ServerFileBrowserEditor, Microsoft.TeamFoundation.Build.Controls"
2. Add Pre-script Workflows
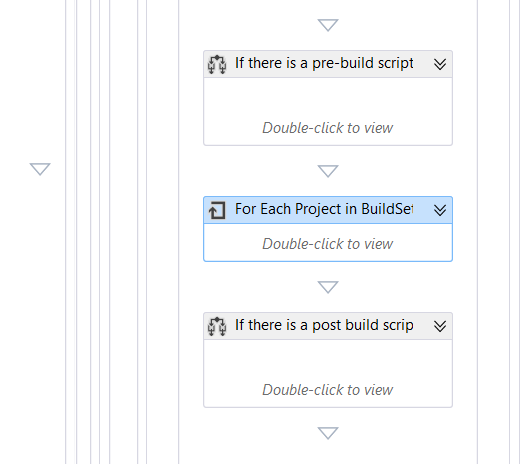
In the workflow, find the sequence called "Compile and Test for Configuration" that does the compilation, then drag an If activity from the toolbox and drop it above the foreach called "For Each Project in BuildSettings.ProjectsToBuild" and set its properties to:
DisplayName: If there is a pre-build script
Condition
Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(PreBuildScriptPath)
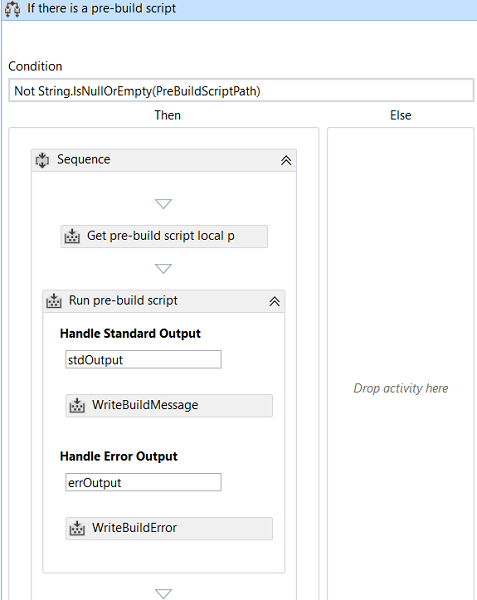
From the toolbox, drag ConvertWorkspaceItem activity and InvokeProcess activity and drop them in the Then of the "If" activity like the image above.
Right click on the sequence activity that contains your activities and click create variable. Add three variables:
preBuildScriptLocalPath (string)postBuildScriptLocalPath (string)scriptResult (Int32)
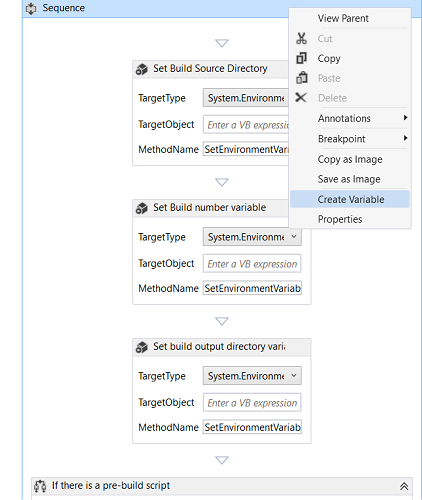
On the ConvertWorkspaceItem activity, set the following properties:
DisplayName: Get pre-build script local pathInput: PreBuildScriptPathResult: preBuildScriptLocalPathWorkspace: Workspace
Then, in the InvokeProcess activity:
- Drag a
WriteBuildMessage and drop it below stdOutput and set Message property:
- Drag
WriteBuildError and drop it below errOutput and set Message property:
On the InvokeProcess activity, set the following properties:
Arguments:
String.Format(" ""& '{0}' {1}"" ", preBuildScriptLocalPath, PreBuildScriptArgs)
DisplayName: Run pre-build scriptFileName: "PowerShell"Result: scriptResult
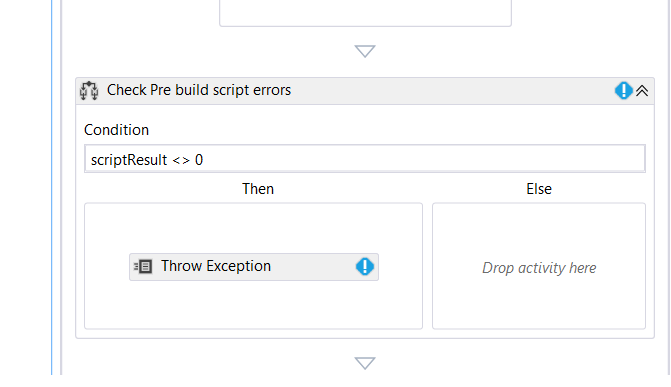
Now to handle script errors, add an if activity after the InvokeProcess activity and fill its properties with:
DisplayName: Check Pre build script errorsCondition:
scriptResult <> 0
Then from toolbox, drag Throw component in the "Then" of the If activity and fill its Exception property with:
New GenericException("Pre build script failed - please check the log For errors")
This will make the build process stop if the script fails.
Notice That
You have to use in your PowerShell Scripts "exit 0" for success and "exit 1" for unexpected errors.
3. Add Post-script Workflows
Now, let's do the same for the post-build script we will copy the pre-build script "If" activity and paste it below the foreach called "For Each Project in BuildSettings.ProjectsToBuild" and change its properties, the ConvertWorkspaceItem activity and the InvokeProcess activity properties to use post-build variables and arguments.
Step 2: Environment Variables
What if we need some information about the build itself? Like the SourceDirectory and BuildNumber, in TFS2013 and TFS2015, those variables and more are available for you! They are stored as environment variables, but in TFS2012, these variables aren't set so we have to add them.
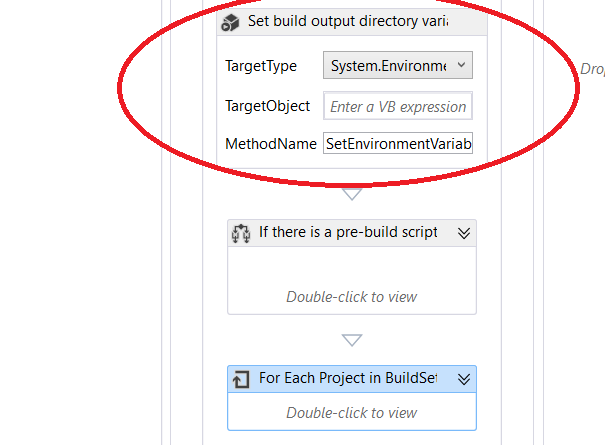
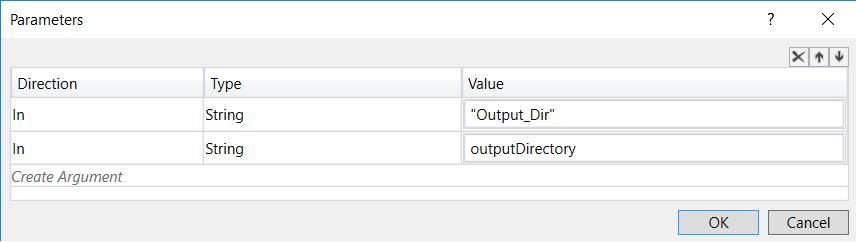
Let's create an environmental variable called Output_Dir that stores the build output directory, So from the toolbox, drag InvokeMethod activity and drop it above the If activity of your prebuild script and set its properties to:
DisplayName: Set build output directory variableMethodName: SetEnvironmentVariableTargetType: System.EnvironmentParameters:
- In
String "Output_Dir" - In
String outputDirectory
Now you can use OutPut_Dir variable in your PowerShell script like below:
Param([string]$outDir = $env:Output_Dir)
Notes
GitHub
If you want to contribute, just check the GitHub repository.
