Introduction
As its name suggests, Virtual IP address (VIP) is an IP address that doesn't have an actual physical network interface. Incoming packets are sent to the VIP, but all packets travel through the real network interfaces.
Virtual IP address is commonly used for database high availability. Applications use it for database connections instead of the normal host IP address. When the active database fail, the VIP will be shifted to the newly promoted host.
Tutorial
Step 1
Run this command to show the current network configuration and see the configured network interface of the server:
ip addr show
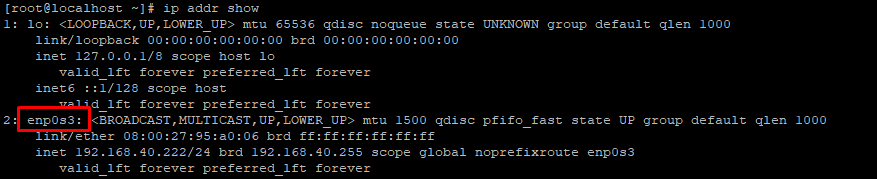
From the above output, we can see that the network interface is enp0s3.
Step 2
The configuration file for the enp0s3 network interface can be found in:
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts.
In order to create a virtual network interface, we need to copy first the master configuration file.
cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
cp ifcfg-enp0s3 ifcfg-enp0s3:1
Step 3
Edit its content to set an appropriate network interface name and IP address - DEVICE, NAME, IPADDR in the virtual network configuration file.
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/cat ifcfg-enp0s3
TYPE="Ethernet"
PROXY_METHOD="none"
BROWSER_ONLY="no"
BOOTPROTO="none"
DEFROUTE="yes"
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
IPV6INIT="yes"
IPV6_AUTOCONF="yes"
IPV6_DEFROUTE="yes"
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE="stable-privacy"
NAME="enp0s3"
UUID="b1d44459-6b90-435a-950e-9b6001cfcf1b"
DEVICE="enp0s3"
ONBOOT="yes"
IPADDR="192.168.40.222"
PREFIX="24"
GATEWAY="192.168.40.60"
DNS1="192.168.40.60"
IPV6_PRIVACY="no"
ZONE=public
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3:1
TYPE="Ethernet"
PROXY_METHOD="none"
BROWSER_ONLY="no"
BOOTPROTO="none"
DEFROUTE="yes"
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
IPV6INIT="yes"
IPV6_AUTOCONF="yes"
IPV6_DEFROUTE="yes"
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE="stable-privacy"
NAME="enp0s3"
UUID="b1d44459-6b90-435a-950e-9b6001cfcf1b"
DEVICE="enp0s3:1"
ONBOOT="yes"
IPADDR="192.168.40.224"
PREFIX="24"
GATEWAY="192.168.40.60"
DNS1="192.168.40.60"
IPV6_PRIVACY="no"
Step 4
Once you have edited the virtual network interface file, restart the network service.
systemctl restart network
Step 5
Check your network settings again and you’ll see the configured virtual network interface:
ip addr show

