Introduction
This article describes how to send and receive JSON or string by RaspberryPi or Ubuntu desktop and use it as server.
Background
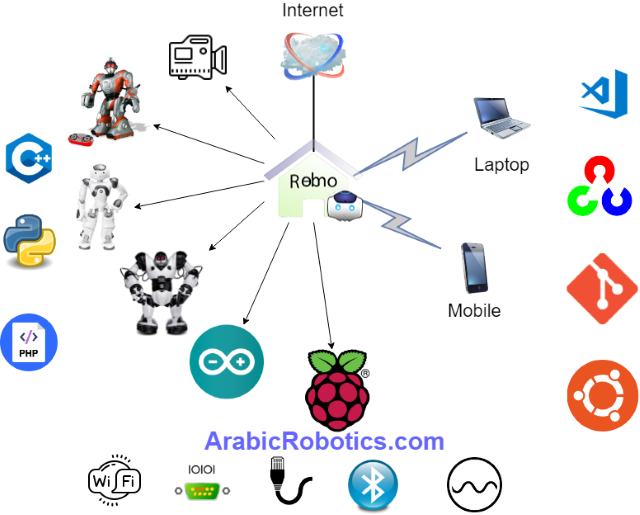
I developed a robotics server system using RaspberryPi named RemoRobo. I can control any robot or anything else by connecting and passing the required data to other connected devices. It receives data from Socket, voice or camera and compiles it in RemoRobo System which is based on RaspberryPi, and it can control any moving robot, Arduino, LEDs, NAOqi robots, Arduino multiple led strips or any other robots using Bluetooth, Serial, Network.
To see how to control Arduino multiple led strips at the same time, you can check my article: Arduino Multitasking Using Loops. It can also Catch Camera streaming and send it to clients.
In this article, I will describe how to use RaspberryPi as Server to send and receive data from clients using Socket.
How It Works
RaspberryPi receives data using socket (IP and PORT), it receives and sends data using local network or Internet.

RaspberryPi as Server
Using Socket, clients can send data as JSON to command RaspberryPi to get or set data on RaspberryPi or connected devices.
Before We Start
Before we start, we should mention some principles the code is based on classes. These classes are connected, which means you should use your mind to modify it to fit your case. Most classes in this code are in Python Language. This code is tested on RaspberryPi and "ubuntu" desktop.
Listen to Socket
Class name SocketServer. This class is listening to any device connected and gets data from it, at the same time, it is based on Threads, which means it can listen and continue work while listening to more commands and execute them in parallel.
__datasetter(self,c) function saves the data received in the object so we can use it later on after that.threaded(self,c) starts a new thread for new connection and get data.Start starts the serversend sends Data to Connected Client.shutDown and __exit__ for Turn off the server.
# import socket programming library
import socket
# import thread module
from thread import *
import threading
import time
from clsLog import clsLog
from clsjsoninfoLoader import GlobalInfo
from clsServerRobot import ServerRobot
print_lock = threading.Lock()
# thread function
class SocketServer (object):
"""This class for listening and get data from clients """
def __init__(self):
"""This initialization for
"""
try:
self.Halt = False
self.receivedData = None
self.ServerRobot = ServerRobot()
self.c = None
self.s = None
self.running = False
return
except Exception as (e):
logger = clsLog()
logger.error(str(e))
return
def __datasetter(self,c):
""" This Method for
@type paramName: Bool
@param paramName : Description
@rtype: Boolean
@return: True : everything went fine
False : Something went wrong
"""
try:
self.receivedData = c
print self.receivedData
return True
except Exception as (e):
logger = clsLog()
logger.error(str(e))
return False
def threaded(self,c):
try:
self.c = c
while True:
if self.Halt:
self.__exit__()
return True
try:
data = self.c.recv(1024)
if not data:
print('Bye')
# lock released on exit
print_lock.release()
return True
# reverse the given string from client
#data = data[::-1]
start_new_thread(self.__datasetter, (data,))
# send back reversed string to client
#self.c.send(data)
except Exception as (e):
print "error reading from socket."+str(e)
return
# connection closed
self.c.close()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print "[N]I will Exit the program"
self.shutDown()
GlobalInfo.Halt = True
def Start(self):
""" This Method for
@type paramName: Bool
@param paramName : Description
@rtype: Boolean
@return: True : everything went fine
False : Something went wrong
"""
try:
host = ""
# reverse a port on your computer
# in our case it is 12345 but it
# can be anything
port = self.ServerRobot.Port
self.s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.s.bind((host, port))
print("socket binded to post", port)
# put the socket into listening mode
self.s.listen(5)
print("socket is listening")
# a forever loop until client wants to exit
self.running = True
while True:
if self.Halt:
self.__exit__()
return True
# establish connection with client
self.c, addr = self.s.accept()
# lock acquired by client
print_lock.acquire()
print('Connected to :', addr[0], ':', addr[1])
# Start a new thread and return its identifier
start_new_thread(self.threaded, (self.c,))
self.s.close()
print "Done"
return True
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print "[N]I will Exit the program"
self.shutDown()
GlobalInfo.Halt = True
except Exception as (e):
print "error while Start the Server Socket , I will exit"
print e
GlobalInfo.Halt = True
logger = clsLog()
logger.error(str(e))
return False
def shutDown(self):
""" This Method for
@type paramName: Bool
@param paramName : Description
@rtype: Boolean
@return: True : everything went fine
False : Something went wrong
"""
try:
print "socket is closing ..."
self.Halt=True
time.sleep(0.9)
if self.running:
self.running = False
return self.__exit__()
except Exception as (e):
print "error on Exit Socket"
print e
logger = clsLog()
logger.error(str(e))
return False
#------------------------------------------------
def __exit__(self):
""" This Method for
@type paramName: Bool
@param paramName : Description
@rtype: Boolean
@return: True : everything went fine
False : Something went wrong
"""
try:
print "socket is closing ..."
self.Halt=True
time.sleep(0.1)
self.s.shutdown(socket.SHUT_WR)
#self.s.shutdown(socket.SHUT_RDWR)
self.s.close()
print "Socket Closed."
return True
except Exception as (e):
print "error on Exit Socket"
self.s.close()
print e
logger = clsLog()
logger.error(str(e))
return False
def send(self,data ="hi"):
""" This Method for Send data to the client
@type paramName: string
@param paramName : data
@rtype: Any
@return: True : everything went fine
False : Something went wrong
"""
try:
self.c.send(data)
return True
except Exception as (e):
logger = clsLog()
logger.error(str(e))
return False
def Main():
server = SocketServer()
threading.Thread(target=server.Start,name="").start()
server.Halt = True
time.sleep(3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Main()
Sending Data
RemoRobo is receiving data as JSON , you can send it with structure like this:
'{"op":"set","device":"robot",
"details":{"name": "Leds", "data":
{"op": "c", "n": 1,"s":2}}}'
In RemoRobo, it compiles it like this way:

Note: You can use json like this or any other native string, but you should compile it in your system.
Sending Commands using Sockets
I wrote an article about how to send string or JSON from Socket using PHP in this article: Connect, Send and Receive data from web page to control PC/RaspberryPi.
History
To make the modules compact and useful, I posted the RaspberryPi Server Side, I will write another article for how to send commands to any device from RaspberryPi , and use it as (Client Side) later on. I will try also to post the full Server and Client sides code on gitHub or contact us on website www.ArabicRobotics.com if you need RemoRobo as it is. But you can use the ServerRobot and customize it to fit your project.
