Examples are based on this talk.
Below is the old and rusty way of generating random numbers. Don’t do it!
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
for(int n = 0; n < 10; ++n)
printf("%d ", rand() % 1000);
printf("\n");
}
Below is the new and shiny way of generating random numbers. Do that instead! Comments inline and a benchmark of each random number generator included. Program output first:
random_device min = 0, max = 4294967295
mt19937 min = 0, max = 4294967295
mt19937_64 min = 0, max = 18446744073709551615
10 -1 6 10 5 -4 -3 2 6 -3
8.73366 3.81724 2.11837 4.14365 9.58442
vector of ints: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
shuffled to : 3 1 6 7 9 4 8 5 0 2
generating 100000000 random numbers…
random_device duration in ms = 142080
mt19937 duration in ms = 553.894
uniform_int_distribution duration in ms = 2719.63
uniform_real_distribution duration in ms = 1070.29
Complete Listing
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
using namespace chrono;
const int COUNT = 100'000'000;
int main()
{
random_device rd;
mt19937 mt(rd());
mt19937_64 mt64(rd());
uniform_int_distribution int_dist(-10, 10);
uniform_real_distribution real_dist(1.0, 10.0);
cout << "random_device min = " << rd.min() << ", max = " << rd.max() << endl;
cout << "mt19937 min = " << mt.min() << ", max = " << mt.max() << endl;
cout << "mt19937_64 min = " << mt64.min() << ", max = " << mt64.max() << endl;
for(int n = 0; n < 10; ++n)
cout << int_dist(mt) << " ";
cout << endl;
for(int n = 0; n < 5; ++n)
cout << real_dist(mt) << " ";
cout << endl;
vector<int> v;
for(int n = 0; n < 10; ++n)
v.push_back(n);
cout << "vector of ints: ";
for(auto it : v) cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
shuffle(begin(v), end(v), mt);
cout << "shuffled to : ";
for(auto it : v) cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "generating " << COUNT << " random numbers..." << endl;
auto start = high_resolution_clock::now();
int result{0};
for(int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i)
result += rd();
auto end = high_resolution_clock::now();
auto duration = duration_cast<microseconds>(end - start).count() / 1000.0f;
cout << "random_device duration in ms = " << duration << endl;
start = high_resolution_clock::now();
result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i)
result += mt();
end = high_resolution_clock::now();
duration = duration_cast<microseconds>(end - start).count() / 1000.0f;
cout << "mt19937 duration in ms = " << duration << endl;
start = high_resolution_clock::now();
result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i)
result += int_dist(mt);
end = high_resolution_clock::now();
duration = duration_cast<microseconds>(end - start).count() / 1000.0f;
cout << "uniform_int_distribution duration in ms = " << duration << endl;
start = high_resolution_clock::now();
result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i)
result += real_dist(mt);
end = high_resolution_clock::now();
duration = duration_cast<microseconds>(end - start).count() / 1000.0f;
cout << "uniform_real_distribution duration in ms = " << duration << endl;
}
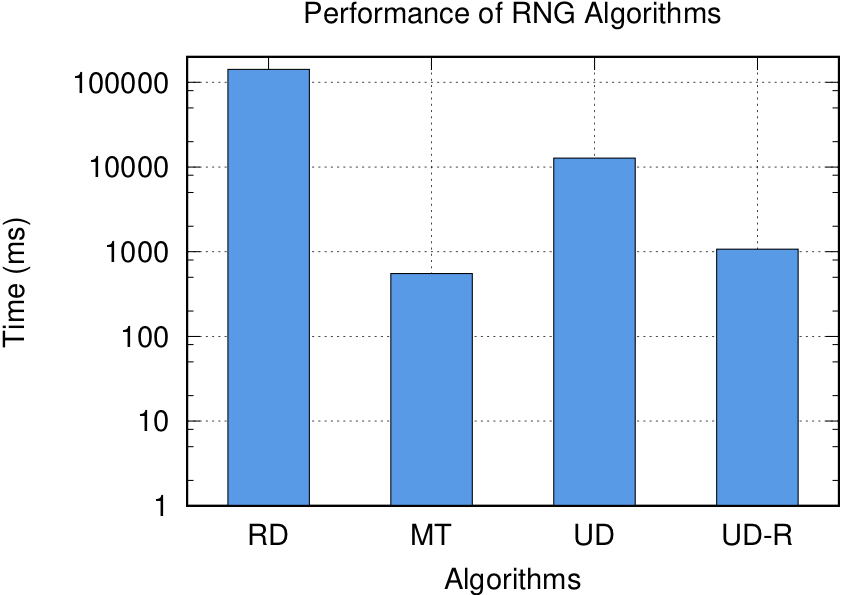
Time to generate 100,000,000 random numbers on 2012 MacBook Pro i7 2.3GHz. On a logarithmic scale, where RD = std::random_device, MT = std::mt19937, UD = std::uniform_int_distribution, and UD-R = std::uniform_real_distribution.
Graph created using gnuplot.
