Introduction
This tip/trick will demonstrate how you can save and read data in your program to/from a custom file format or extension, and how to associate the file type to your program in Windows.
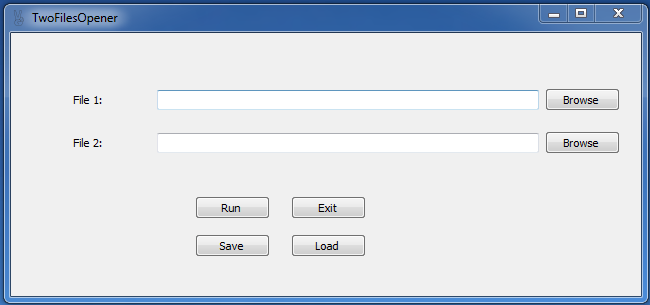
I'm going to use a small application I made just as an example to make it easier to explain the technique. The program is called TwoFilesOpener, it takes any two file names and locations, and open them both at the same time. The program allows users to save and load their TwoFiles in a custom file type, I called it ".tfo".
Background
So, let's take a short tour around every component in the application:
- Browse buttons:
It uses the OpenFileDialog class, to show a file browsing dialog, which stores the path of the file selected in a string, that can be used later in the run button to open the file. We will copy that string to the adjacent textbox and to an array of 2 strings called filesToOpen[].
private void btnBrowseFile1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog browser1 = new OpenFileDialog();
DialogResult locRes = browser1.ShowDialog() ;
if (locRes == DialogResult.OK)
{
txtboxFile1.Text = browser1.FileName;
filesToOpen[0] = txtboxFile1.Text;
}
}
private void btnBrowseFile2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog browser2 = new OpenFileDialog();
DialogResult locRes = browser2.ShowDialog();
if (locRes == DialogResult.OK)
{
txtboxFile2.Text = browser2.FileName;
filesToOpen[1] = txtboxFile2.Text;
}
}
- Run button:
The run button will just run the files specified from filesToOpen[] using the System.Diagnostic.Process class:
private void btnRun_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (filesToOpen[0] == null && filesToOpen[1] == null)
MessageBox.Show("No Files selected");
int i = 0;
while (i < filesToOpen.Length)
{
if (filesToOpen[i] != null && filesToOpen[i] != "")
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(filesToOpen[i]);
i = i + 1;
}
}
- Save and Load buttons
The Save button uses the SaveFileDialog class to take the path and filename where the user wants to save his file. It will write the string values
from filesToOpen[] and save them in a path the user specifies + filename + ".tfo", the custom extension of our program.
private void btnSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SaveFileDialog saver = new SaveFileDialog();
DialogResult LocRes = saver.ShowDialog();
if (LocRes == DialogResult.OK)
System.IO.File.WriteAllLines(saver.FileName + ".tfo", filesToOpen);
}
up to now, we have a file, that contains our data and have a custom file extension.
Now we move on to the load button. The load operation is better be handled by an independent method rather than an event handler, and we use that method
inside the load button event handler, the reason is that we are going to use the load operation in other place other than the load button, we will see where in a second.
private void load(string file)
{
if (System.IO.Path.GetExtension(file).Equals(".tfo"))
{
filesToOpen = System.IO.File.ReadAllLines(file);
txtboxFile1.Text = filesToOpen[0];
txtboxFile2.Text = filesToOpen[1];
}
else
MessageBox.Show("Unrecognized File");
}
private void btnLoad_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog loader = new OpenFileDialog();
DialogResult locRes = loader.ShowDialog();
if (locRes == DialogResult.OK)
load(loader.FileName);
}
The parameter file of method load(str) must contain a path, a filename and an extension, then we can apply a rule which only accepts
filenames having an extension of ".tfo", otherwise, it displays an error message. With that in hand, we can use the load method inside
the btnLoad_Click event-handler.
Using the code
Now, that we finished the tour around the application, let's see how we can open a file of our format/extension by our program.
First, we have to identify the caller of our program, to do that, we have go to program.cs in the Solution Explorer and we need to add a string parameter to main(), for example:
static void Main(string [] args)
This way we store the filename of the caller in the args array. So, if we have a caller, we can pass it to our form, if we don't, we just use the normal form call:
static void Main(string [] args)
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
if (args.Count() == 1)
Application.Run(new Form1(args[0]));
else
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
In other words, we need to have two constructors for our form, one of them takes a string as parameter, and the other is the default one:
public Form1(string caller)
{
InitializeComponent();
load(caller);
}
Then, we use that string to pass it to load(str) method, which in turn will check if the file type is ours or not, and do whatever it needs to do after that.
So, now that we have all this, we can associate the new extension in Windows to our program in a normal fashion. Just double click on a .tfo file,
choose the program location to be the default program for that file type and press OK; don't forget to check the option "Always use the selected program
to open this kind of file", and make sure to put the executable in a static place, so it'll remain associated all the time.
