Abstract
IT Service Management and Service Desk implementation is a promising potential which draws a framework of service delivery, although as a way of capturing
comparative advantages in the face of the growing service delivery methods, the failure percentage of ITSM
and Service Desk implementation is still
relatively high which causes increasing concerns for many corporations. The aim of this paper is to extend the line of knowledge about outcomes of ITSM and
Service Desk Implementation, proposing a conceptual framework for successful ITSM and Service Desk implementation, phases of implementation cycle, and different success factors.
Introduction
IT Service Management and Service Desk implementation is considered as an important management decision which is filled with uncertainty and change. Hidden obstacles lurk
around every stage of implementation process. In spite of the warnings and analyst statistics, in general many organizations agree that ITSM and Service
Desk implementation improves service delivery process. “IT Service Management is a people process supported by technology”. While the majority of business
firms strive to implement ITSM and Service Desk, they face the disappointing reality of the significant percentage of failure within their ITSM &
Service Desk implementation. ITSM & Service Desk process comes with benchmarking & metrics to produce substantial insight into the underlying
processes that drive performance. ITSM employs ITIL documented best practices and in many cases extends beyond into additional areas such as enhanced
processes and implementation to provide additional value-added functionality. At present, ITSM methods have evolved to include specific ways to enable and
optimize assessment, planning and implementation of ITIL best practices. ITSM provides integrated services that are process bases with a focus on satisfying
business requirements. Although managing technology is the most crucial component of most ITSM solutions, whereas business objectives, service level agreements
and technology infrastructure play critical role in any ITSM method paradigm.
ITSM Methodology
ITSM is based on ITIL, an integrated, process based, set of best practices to manage IT Services. Where ITIL defines and documents the best practices, ITSM employs
them to meet customer requirements and priorities.
ITSM Methodology has two areas:
- IT Service Support
- Configuration Management - physical and logical information of the IT infrastructure and the IT services
- Change Management - standard methods and procedures for effective managing of all changes
- Release Management - testing, verification, and release of changes to the IT environment
- Incident Management - the day-to-day process that restores normal acceptable service with a minimal impact on business
- Problem Management - the diagnosis of the root causes of incidents in an effort to proactively eliminate and manage them
- Service Desk (Function) - this provides a central point of contact between users and Information Technology
- IT Service Delivery
- Availability Management - optimize IT infrastructure capabilities, services, and support to minimize service outages and provide sustained levels of service to meet business requirements
- IT Service Continuity - managing an organization's capability to provide the necessary level of service
- Capacity Management - enables an organization to tactically manage resources and strategically plan for future resource requirements
- Service Level Management - maintain and improve the level of service to the organization
- Financial Management for IT Services - managing the costs associated with providing the organization with the resources needed to meet requirements
Industry Trends and Directions
- Through 2010, 75% of IT Organizations will seek to formalize their day-to-day Service Delivery Processes to build in repeatability and consistency – Gartner 2005 Assumption
- Current State: More than 90% are involved in the process, governance or quality initiatives. Most organizations (60%) are in early stage implementation.
- Business Drivers: Improved Performance, Better Integration across the IT organization, Address Regulatory Requirements.
- Mandatory Planning Requirements:
- Define Direction for Enterprise and IT Organization
- Intent of Performance Improvement Initiatives (Example: ITIL Implementation)
- Detailed Requirements of how IT Organization is going to perform in the future
ITSM & Service Desk Implementation Process
ITSM and Service Desk Implementation projects are characterized by typical size of the company, its core business and course of action. There are time-tested
project blue-prints available which can serve as a guideline for implementing ITSM
and Service Desk process.
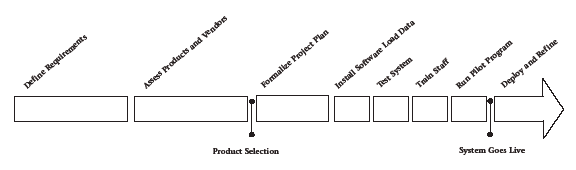
Implementation Process:
- Requirement Definition: During this phase all vital information is being gathered and activity plan is being drafted. Best
Practices: Establish a
Steering Committee to establish membership levels, objectives, project plan and planning framework.
- Selection of the Software: Selection of software for ITSM and Service Desk can be tricky process; many options are available in the
market from ready-made software to custom build open source software. When selecting the software, it should comply with the company requirements to
manage all the ITIL Processes. Best Practices: Consultation with ITSM Implementation experts and Consultants is necessary in this stage, who will play a role as Liaison between
the organization and the application provider.
- Preparation of Requirements for Software Configuration: After software had been selected specific information concerning its
installation and initial configuration shall be figured out. A clear understanding of SLA (Service Level Agreement) and OLA (Operational Level
Agreement). During this stage project timelines should be drawn, with all the phases of installation, configuration and training. Best
Practices: Establish
working session’s team, who will be responsible to draw a project planning for implementing the software and draw the requirements.
- Implementation and Testing of the Software: After the ITSM and Service Desk software is installed, it’s filled in with data for example
end-users, responsible experts, support units, SLA times, configuration units, operator instructions etc... After all installation and configuration
activities are finished system operational testing can be performed. The best way is to define special group of employees whose real incidents will
registered in service desk support system so allowing for operational testing to use data an gathering additional knowledge that can be used in case system
changes. Best Practices: The Project Management team is comprised of personal from technical and application functional areas. These include the Project Manager,
Level 2 Support, Specialists, Network Operations Center, Level 3 Support Specialists, Database Management units. Security and Application support, who
will detect, resolve and avoid failures that (potentially) affect the implementation.
- User Training: This stage includes trainings for service desk operators and for other involved parties. Of course main priority is given
to service desk operator trainings since they are the first level of contact in ITSM & Service Desk models. Best
Practices: Develop learning solutions to address the issues
such as – objectives and policies and ownership of calls. Specialized training should focus on Customer Service, Service Desk and Incident Resolution information.
- Realization of Pilot Project: After all involved parties are trained and software is properly configured and tested, pilot project can
be started with a purpose to make final assessment of company employees and the system itself. If at this stage no serious issues are discovered service desk
can be considered fully operational. Best Practices: Establish live sessions, real-time working models and an observation team with technical
& management team members to monitor changes in the process or in the application.
- Continuous Improvement of Service Desk Functions: Also after successful implementation, it’s obligatory to continue to improve its
functions. Various metrics, service support functions should be improved and perfected. Continuous processes and services improvement is also part of ITIL
best practices and in 3rd version of ITIL framework is defined as separate set of processes.
Best Practices: Creating awareness and training among the user levels, strategy consulting on ITSM, Service Desk
and ITIL, Establishing metrics/KPI and SLM reporting, Acquisition and customization of Tools with Automation of Process and Service Management Operations with Continual Process and Service Improvement.
Implementing Best Practices
- Provide improved business results
- Move you from a reactive to proactive organization
- Improve effectiveness and efficiency of IT processes which often leads to reduced IT Costs
- Improve Service Delivery
References:
- ITSM & Service Desk Implementation problem @ RL Consulting IT Service Management Implementation guidelines 2003.
- Official ITIL® Website, “What is ITIL?” [Online]. Available: http://www.itilofficialsite.com/AboutITIL/WhatisITIL.asp
[Accessed: April. 07, 2012].
- Framework for ICT Technical Support (FITS) “Guide – How to Implement a Service Desk” – [Online]
http://www.eictsupport.org/fits/Sec/reactive-processes/servicedesk/F120102_Guide_-How_to_Implement_a_Service_Desk.html.
- Polar Software web-based help desk portal, “Short Guide through the Successful Help Desk ITIL Implementation”, Feb. 26, 2009.
- Image from “Implementing your Help Desk: A Practical Guide” Data Watch 2005.
