Introduction
This article shows the key logic points which must be taken care while implementing a Sorted Cyclic Linked List.
It is useful specially for students and beginners in development.
Background
Today a fresher engineering graduate asked me can I help her solving the Sorted Cyclic Linked List problem, I thought a working code will be best way to solve her problem.
Uploading here to help other freshers and students in the similar need.
Using the code
The code it self is very simple, it contains a
Visual Studio solution.
Just open that in Visual Studio 2010 and run (F5). On the form you can start giving integer value to let that added in a cyclic linked list,
the output (flattened) will keep appearing on the form itself.
Full source code is attached with this article, you will need Visual Studio 2010 to open it.
If you have some previous version of Visual Studio then you can add the Form1.cs, Form1.Designer.cs, Form1.resx, and Node.cs to add in a new project.
User Interface
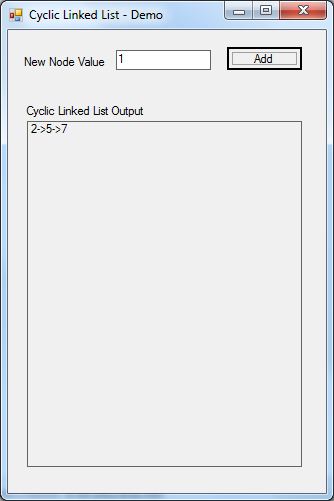
Points of Interest
The key method AddNode() is explained below in wording and then in code.
- AddNode(currentNode, valueToAdd)
- First it checks if the current passed node is null if yes (in case of first node getting added), it creates the node and put this newly created node in next of itself.
- Then it check if the
valueToAdd is >= to currentNode's value and <
currentNode.Next's value, if yes, add the node in between currentNode and
currentNode.Next.
It also check if the valueToAdd is less than even the header's value then add it prior to that header (or say after the last node which also contains maximum value) - If nothing above is true, then call
AddNode(currentNode.Next, valueToAdd) so that it keep searching for correct location via recursion
until it find its currect location.
private void AddNode(ref Node currentNode, int valueToAdd)
{
if (currentNode == null)
{
currentNode = new Node(valueToAdd, null);
currentNode.Next = currentNode;
}
else if( ((currentNode.Data <= valueToAdd) &&
(currentNode.Next.Data > valueToAdd) ) || (currentNode.Next == this.header ))
{
Node newNode = new Node(valueToAdd, currentNode.Next);
if (currentNode.Next == header && valueToAdd < currentNode.Next.Data)
this.header = newNode;
currentNode.Next = newNode;
}
else
AddNode(ref currentNode.Next, valueToAdd);
}
