Introduction
A couple of months ago, I wrote a tip on The Code Project about Show Thread in Source feature in Visual Studio. This trick can be found here. In this tip today, I will demonstrate how the similar information could be achieved when either doing a live debugging session or dump file analysis using native debuggers like WinDbg. If you are new to this type of debugging, please visit my blog or watch one of my two videos about it here and here (expand Ottawa or Montreal).
The sample code is the same as the one I used in that previous tip.
class Program
{
static object sync1 = new object();
static object sync2 = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread[] workers = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
workers[i] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Method1));
workers[i].Start();
}
else
{
workers[i] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Method2));
workers[i].Start();
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Thread Creation Completed.");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
workers[i].Join();
}
Console.WriteLine("Done");
}
private static void Method1()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1 called by
ThreadId = {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
lock (sync1)
{
Thread.Sleep(10000);
}
}
private static void Method2()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method2 called by
ThreadId = {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
lock (sync2)
{
Thread.Sleep(30000);
}
}
}
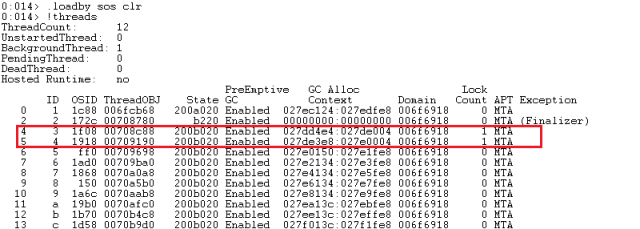
The first step is load sos. Since I am using .NET 4.0, I used load by proxy using clr DLL. Next, let's run !threads command to see managed threads in the process. As you can see from command output shown , Managed thread Ids 4 and 5 own a lock.
You can also verify owning threads info by running !syncblk command as shown below. However this command output does not display the threads that are waiting for these two threads.

Windbg Extension Psscor4 comes to help here. Let's load it first and run the !syncblk command now. As you can see in the figure below, the output of !syncblk command now includes thread Ids for threads that are waiting on these locks.

Of course, you can always view threads call-stacks to inspects what those threads are doing.

I hope you find this tip helpful.
