Linked List in C++ Series
Given a singly linked list, we have to modify it such that all even numbers appear before odd numbers.
For example:
Given Linked List : 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
After Modification : 2, 4, 6, 1, 3, 5, 7
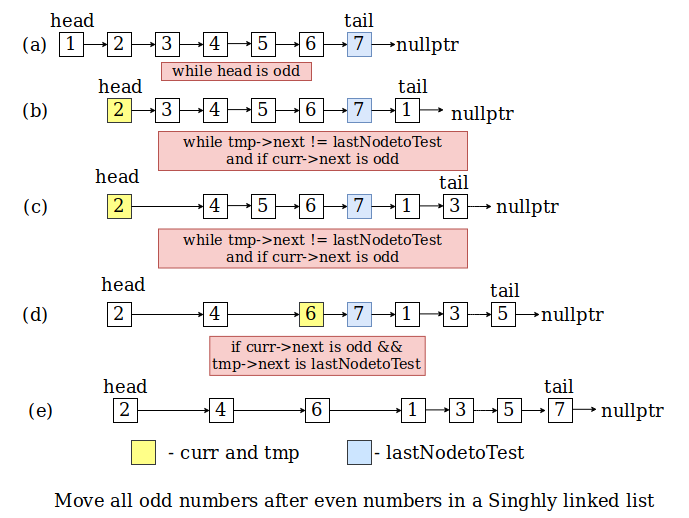
Background
From the above figure, we can see how the function will work.
While the head of the list is odd, the head is copied to an auxiliary node and element next to the head will become the new head. The auxiliary node is added after tail and tail is updated. Similarly, all odd value nodes are removed from their position and added after the tail of the list.
Here are the advance, getLastNode, isOdd and exchangeEvenOdd functions.
static void advance(Node*& node)
{
assert (node != nullptr);
node = node->next;
}
Using this function, node advances to the next node.
Node* getLastNode()
{
Node *node = head;
while (node->next != nullptr)
node = node->next;
return node;
}
This function returns the last node of the linked list.
bool isOdd(int num)
{
if (num % 2 != 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
This function checks whether the entered value is odd or even.
void exchangeEvenOdd()
{
Node *node = nullptr;
Node *lastNodeToTest = getLastNode();
Node *tail = lastNodeToTest;
while (isOdd(head->data) == true)
{
node = head;
advance(head);
tail->next = node;
advance(tail);
}
Node *tmp = head;
Node *curr = head;
while (tmp->next != lastNodeToTest)
{
if (isOdd(curr->next->data) == true)
{
node = curr->next;
curr->next = node->next;
tail->next = node;
advance(tail);
}
else
{
advance(curr);
advance(tmp);
}
}
if (isOdd(curr->next->data) == true && tmp->next == lastNodeToTest)
{
node = lastNodeToTest;
curr->next = lastNodeToTest->next;
tail->next = lastNodeToTest;
advance(tail);
}
tail->next = nullptr;
lastNodeToTest = nullptr;
node = nullptr;
}
C++ Implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
#include <cassert>
class LinkedList
{
struct Node
{
int data;
Node * next = nullptr;
Node(int value) : data(std::move(value)), next(nullptr) {}
};
Node *head;
public:
LinkedList() : head(nullptr) {}
~LinkedList()
{
Node *tmp = nullptr;
while (head)
{
tmp = head;
head = head->next;
delete tmp;
}
head = nullptr;
}
void insert(int);
void exchangeEvenOdd();
void printList() const;
private:
static void advance(Node*& node)
{
assert (node != nullptr);
node = node->next;
}
Node* getLastNode()
{
Node *node = head;
while (node->next != nullptr)
node = node->next;
return node;
}
bool isOdd(int num)
{
if (num % 2 != 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
void LinkedList::insert(int value)
{
Node *node = new Node(std::move(value));
Node *tmp = head;
if (tmp == nullptr)
{
head = node;
}
else
{
tmp = getLastNode();
tmp->next = node;
}
}
void LinkedList::exchangeEvenOdd()
{
Node *node = nullptr;
Node *lastNodeToTest = getLastNode();
Node *tail = lastNodeToTest;
while (isOdd(head->data) == true)
{
node = head;
advance(head);
tail->next = node;
advance(tail);
}
Node *tmp = head;
Node *curr = head;
while (tmp->next != lastNodeToTest)
{
if (isOdd(curr->next->data) == true)
{
node = curr->next;
curr->next = node->next;
tail->next = node;
advance(tail);
}
else
{
advance(curr);
advance(tmp);
}
}
if (isOdd(curr->next->data) == true && tmp->next == lastNodeToTest)
{
node = lastNodeToTest;
curr->next = lastNodeToTest->next;
tail->next = lastNodeToTest;
advance(tail);
}
tail->next = nullptr;
lastNodeToTest = nullptr;
node = nullptr;
}
void LinkedList::printList() const
{
if (head == nullptr)
{
std::cout << "Empty List \n";
return;
}
Node *node = head;
while (node != nullptr)
{
std::cout << node->data << " ";
advance(node);
}
std::cout << "\n";
}
int main()
{
LinkedList ll1;
ll1.insert(1);
ll1.insert(2);
ll1.insert(3);
ll1.insert(4);
ll1.insert(5);
ll1.insert(6);
ll1.insert(7);
std::cout << "Original List : ";
ll1.printList();
ll1.exchangeEvenOdd();
std::cout << "New List : ";
ll1.printList();
}</cassert></utility></iostream>
History
- 4th December, 2019: Initial version
