This post will show you how to play a video clip that is either embedded in the app's resources, or available on the internet by using VideoView and MediaController in Kotlin.
Introduction
Smartphones and tablets are used with many different purposes such as study, entertainment, so on. And watching videos is one of those purposes. So, as Android developers, we must make functions help Android device users to interact with videos easily.
There are many different ways to play a video and control it in an Android app, however, using the VideoView and the MediaController classes can be simplest way.
In this tip, I am going to build a simple app that plays a video clip that is either embedded in the app's resources, or available on the internet by using Kotlin and Android Studio 3.6.1.
Background
VideoView Class
VideoView currently supports the following video formats:
- H.263
- H.264 AVC
- H.265 HEVC
- MPEG-4 SP
- VP8
- VP9
The VideoView class has a wide range of methods that may be called in order to manage the playback of video here. The following methods are used in this article:
setVideoUriseekTostartstopPlaybackpausesetOnPreparedListenersetOnCompletionListenergetCurrentPositionsetMediaController
MediaController Class
The MediaController also provides a set of methods allowing the user to manage the playback of video here. The following method is used in this article:
Using the Code
Create the Project and Layout
Create a new Android project and name it MyFirstKotlinApp, choose the Empty activity template, select Kotlin language and leave all other defaults.
In activity_main.xml, delete the existing TextView, and replace it with a VideoView element and two TextView elements with these attributes:
<VideoView
android:id="@+id/videoview"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="4:3"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/loading"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:text="Loading..."
android:textSize="35sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:textColor="#a84832"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/completed"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:text="Playback completed"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:textColor="#ffff00"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>
Playing a Video File using VideoView
To play a video file embedded with the app's resources, first, we must import the video file (can download https://all-free-download.com/free-footage/snowfall_winter_snowflakes_cold_907.html and name it falling_snow.mp4) with the following steps:
- Right click the res directory in the Project view and select New > Android Resource Directory.
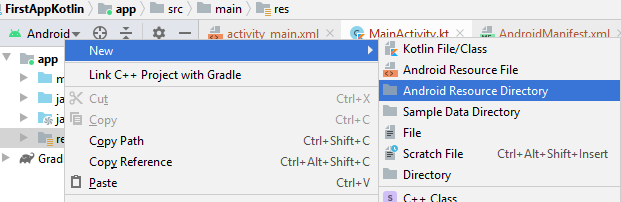
- Change Resource type to "raw" (Directory name is also changed automatically). Leave all other options as is and click OK.

- Move (Copy/Cut) the video file (falling_snow.mp4) into (Paste) the raw directory in our project.

To play a video file from the internet, first, in the Android manifest file, add an internet permission to enable the app to access the video file on the internet before the <application> element, at the top level of the manifest:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.ngocminhtran.myfirstkotlinapp">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<application...>
...
</application>
</manifest>
Next, in MainActivity.kt, add a constant for the name of the video file in our app’s resource:
private val VIDEO_NAME = "falling_snow"
or a URL for video file from the interner:
private val VIDEO_NAME =
"https://images.all-free-download.com/footage_preview/webm/christmas_tree_7.webm"
Also in MainActivity.kt, create a private method called getURI() that tests whether the input string is a URL or a raw resource and return the appropriate URI. This method looks like this:
private fun getURI(videoname:String): Uri{
if (URLUtil.isValidUrl(videoname)) {
return Uri.parse(videoname);
} else {
return Uri.parse("android.resource://" + getPackageName() +
"/raw/" + videoname);
}
}
We also create a new private method called initPlayer() that calls the getURI() and setVideoUri() methods to set the URI that the VideoView will play and start() on the VideoView to start playing:
private fun initPlayer() {
var videoUri:Uri = getURI(VIDEO_NAME)
videoview.setVideoURI(videoUri)
videoview.start()
}
When we stop the video from playing, we must release all the resources held by the VideoView. To do this, we create a private method called releasePlayer(), and call the stopPlayback() method on the VideoView.
private fun releasePlayer(){
videoview.stopPlayback()
}
Before building and running our app, we need to override Activity lifecycle methods:
onStop() to release the media resources when the app is stoppedonStart() to initialize the resources when the app is started againonPause() and add a test for versions of Android older than N (lower than 7.0, API 24). If the app is running on an older version of Android, pause the VideoView here.
The onStop() looks like this:
protected override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
releasePlayer()
}
The onStart():
protected override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
initPlayer()
}
And the onPause():
protected override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
videoview.pause()
}
}
So far, we can build and run our app:

We cannot control the media playback such as pause, play, fast-forward, or rewind. These functions will be added in the next step.
Control the Video using MediaController Class
To add a MediaController that controls our video, we must implement the following steps:
And now, we can built and run app again. Tapping the VideoView to make the MediaController appear:

At the moment, we try to rotate the Android Emulator by clicking the Rotate left button on the Emulator's right bar:

The result looks like this:

We note that the video restarts from the beginning and here is the behavior that we don’t expect. We can solve this problem by preserving playback position throughout the activity lifecycle with the following steps:
- In MainActivity.kt, we add a member variable to hold the video's current position (initially
0) and member variable to hold the key for the playback position in the instance state bundle:
private val PLAYBACK_TIME = "play_time"
private var currentPos = 0
- In
initPlayer(), after setVideoUri() but before start(), check to see whether the current position is greater than 0, which indicates that the video was playing at some point. Use the seekTo() method to move the playback position to the current position:
private fun initPlayer() {
var videoUri:Uri = getURI(VIDEO_NAME)
videoview.setVideoURI(videoUri)
if (currentPos > 0) {
videoview.seekTo(currentPos);
} else {
videoview.seekTo(1);
}
videoview.start()
}
- Override the
onSaveInstanceState() method to save the value of current time to the instance state bundle. Get the current playback position with the getCurrentPosition() method:
protected override fun onSaveInstanceState(outState: Bundle?) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState)
outState?.putInt(PLAYBACK_TIME, videoview.getCurrentPosition())
}
- In
onCreate(), check for the existence of the instance state bundle, and update the value of current time with the value from that bundle. Add these lines before you create the MediaController:
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
currentPos = savedInstanceState.getInt(PLAYBACK_TIME);
}
Build and run the app. Try to rotate Emulator again and note how the playback position is saved.
Preparation and Completion Events
The VideoView class defines listeners for several events related to media playback and Listeners for the preparation and completion events are the most common listeners to implement in a media app.
In Java, we must use the onPrepared() and the onCompletion() callbacks for preparation and completion events. In Kotlin, we just implement:
videoview.setOnPreparedListener{
}
videoview.setOnCompletionListener {
}
In our app, we implement the following steps:
Built and run our app. Each time initPlayer() is called, the loading message should be turned on. It is turned off only when the media is ready to play:

When the video finishes playing, the completed message appears:

Points of Interest
Using VideoView and MediaController is old title in Android programming and you can easily find a lot of documents about them. However, as a Kotlin beginner, I want to learn how to use these classes in Android programming by using Kotlin from scratch as a way to understand more about Kotlin and how to apply it in Android programming.
History
- 15th March, 2020: Initial version
- 16th March, 2020: Second version
