The built in web based editing environment for Apps Script does not interpret function return types, but you can give it a hint.
Introduction
Editing code behind in your Google docs and spreadsheets, etc. does not interpret a variable type when it has its value set from a function call. This means you lose the benefits of the built in method name auto complete and so it's far too easy to introduce bugs. However, this is easily fixed.
The Problem
Consider the following source:
var myLib = (function () {
var _ss
var DATA_SOURCE_ID = '1234567890123456789012345678901234567890ABCD'
function getSS() {
if (!_ss) {
_ss = SpreadsheetApp.openById(DATA_SOURCE_ID)
}
return _ss
}
function countTabs () {
var ss = getSS()
return ss.getSheets().length
}
})()
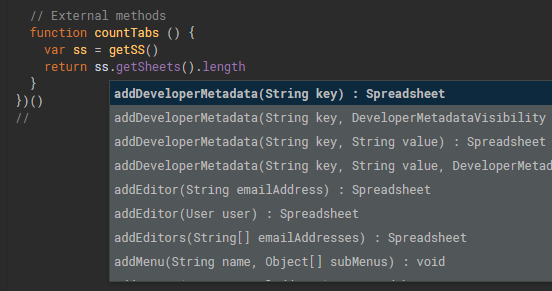
When you are writing the method countTabs and type the ".", you would expect to get a popup IntelliSense panel. However, nothing appears!
The problem is that the Apps Script editor is not able to infer that the call to getSS() always returns a Spreadsheet object.
The Fix
You can fix this problem using a comment.
Change the getSS method function to look like a simple variable assignment in a comment like this:
function getSS() {
if (!_ss) {
_ss = SpreadsheetApp.openById(DATA_SOURCE_ID)
}
return _ss
}
Then when you start wrinting code that has been assigned a value from the function, it will have the correct intellisense, almost as though you were using a typed language.
Hopefully, this will aid your productivity in Apps Script, especially if you are trying to write clean, DRY code, etc.
History
- 6th May, 2020: Initial version
