This tip shows how to obtain a two or three columns list of an ordered field of a table using only SQL statements. The items can be placed by row (e.g., left to right) or by column.
Introduction
I had the problem of getting an ordered list of data on two or three columns using only SQL statements obviously immersed in a programming language (PHP) to visualize the results.
Background
The reader should have a basic understanding of SQL (and possibly PHP); the development is based on some capabilities of the database, in particular Temporary tables, Windowing functions and Join Left options; see Wikipedia Comparison of relational database management systems for databases that support those options.
From Data to Columns
This was obtained by creating a temporary table that, in addition to the field in question, has two other fields of which the first contains a progressive number which will be subsequently modified so that exists at most two or three rows with the same number, the second is used to identify the column where the field will be placed.
Columns Ordered Left to Right
The SQL below creates an ordered table over one field:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE multiCols AS
SELECT ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY FieldName) RowNum,
'0' PlaceHolder,
FieldName
FROM TableName [possible WHERE clause and GROUP BY FieldName clause]
ROW_NUMBER is one of the so-called window functions that assigns a sequential integer to each row of a query’s result set.
An effective example is below:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE multiCols AS
SELECT ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY Name) RowNum,
'0' PlaceHolder, Name
FROM DrugsHandBook WHERE Category IS NULL OR Category = '';
After the creation of the temporary table, we must modify the fields RowNum and PlaceHolder:
UPDATE multiCols SET PlaceHolder = ((RowNum-1) % colsNumber)
RowNum = Rownum - ((RowNum-1) % colsNumber)
Here colsNumber can be 2 or 3, therefore in case of two columns, the below UPDATE statement is more efficient and performing.
UPDATE multiCols SET RowNum = Rownum - 1,PlaceHolder = 1 WHERE (RowNum %2) = 0
After the UPDATE, there are a couple (or a triple) of rows with the same RowNumber and the placeholder having values 0, 1 (and 2) respectively.
Lastly by the SQL below, we obtain the data on two or three columns[1]:
SELECT A.FieldName,BFieldName[,C.FieldName] _
FROM (SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 0) A
LEFT JOIN (SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 1) B
ON A.RowNum = B.RowNum
LEFT JOIN (SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 2) C
ON A.RowNum = C.RowNum;
For two columns, the last LEFT JOIN and C.FieldName are omitted.
Columns Ordered Up to Bottom
In this case, the SQL for create a table is a little more complicated for we need to know how many rows are interested:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE multiCols AS SELECT LAST_VALUE (RowNum) OVER (ORDER BY RowNum
RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING) Count,
0 PlaceHolder,RowNum,FieldName
FROM (SELECT ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY FieldName) RowNum,FieldName FROM TableName
[possible WHERE clause and GROUP BY FieldName clause])
For understanding, note that the last line it is almost similar to the creation of the table for the left right order and in the preceding lines, the LAST_VALUE window function captures the last RowNum of the set (RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING), furthermore there is the field Count which contains the number of rows.
In order to deals only in integer division[2] the below UPDATE statement sets the Count field to the next value multiple of two (or three):
UPDATE multiCols SET Count = Count + colsNumber - (Count % colsNumber)
WHERE (Count % colsNumber) > 0
To obtain the rows coupling and the correct PlaceHolder values, the next statement CREATE one (or two) others TEMPORARY TABLE[3]:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE multiCols2
AS SELECT 1 PlaceHolder,Count,FieldName,Rownum - Count / colsNumber AS RowNum
FROM multiCols WHERE Rownum > Count / colsNumber
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE multiCols3
AS SELECT 2 PlaceHolder,FieldName,Rownum – Count / colsNumber AS RowNum
FROM multiCols2 WHERE Rownum > Count / colsNumber
And the result is obtained, for three columns, by:
SELECT A.FieldName,B.FieldName,C.FieldName
FROM (SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 0 AND RowNum <= Count/3) A
LEFT JOIN multiCols2 B ON A.RowNum = B.RowNum
LEFT JOIN multiCols3 C ON A.RowNum = C.RowNum
Deals With Multi Fields
It is not complicated to show multiple fields: these must be indicated when creating the table like in the example below where the second field is also in the ORDER clause.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE multiCols AS
SELECT ROW_NUMBER () OVER (ORDER BY Autore,Citazione) RowNum,
0 PlaceHolder,Autore,Citazione FROM Citazioni;
UPDATE multiCols SET PlaceHolder = ((RowNum-1) % 3),RowNum = Rownum - ((RowNum-1) % 3);
SELECT A.Autore,A.Citazione,B.Autore,B.Citazione,C.Autore,B.Citazione
FROM (SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 0) A
LEFT JOIN (SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 1) B ON A.RowNum = B.RowNum
LEFT JOIN (SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 2) C ON A.RowNum = C.RowNum;
Using the Code: The PHP Script
The script aims to create a list on two or three columns simply providing table and field(s) name and possibly WHERE or/and GROUP clause; data are retrieved by PDO object.
The PHP multiColumns.php script contains the function multiCols that returns an array of data:
multiCols($dbh,$parms,$Direction = "H",$Cols = 2,$Trace = "off")
Where:
$dbh is the handle of the database;$parms is an array of parameters (see below);$Direction is a direction, i.e., by line (H) the default or by column (V)$Cols the number of columns: 2, the default, or 3;$Trace when on shows the SQL statements.
$parms can contain:
Table: mandatory, table name;Order: example Product COLLATE NOCASE, Price DESC;Fields: a list of fields to show example: Author, Citation;Condition: a WHERE or GROUP BY clause;MySql: true or false (default).
The function returns a two dimensional array:
If Cols is the number of required columns and nFields is the number of fields retrieved:
- Array with the number of rows extracted (
countRows) and the fields name repeated as many times as required columns - Array of dimension
Ceil(countRows / Cols) x nFields * Cols
The script has been tested on SQLite version 3.31.0, PostgreSQL 14.1 and MySql 8.0.27.
Output Example
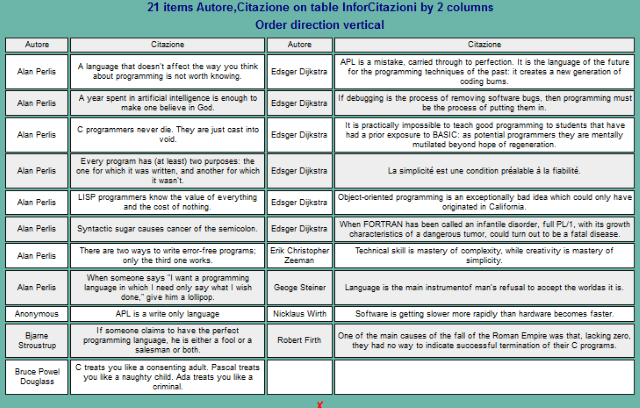
The above image has been generated by the below SQLs.

Note
- ^ For MySql, there are some differences:
It is not possible to refer to a TEMPORARY table more than once in the same query, for this, the final SELECT statement needs two (or three) TEMPORARY table(s) so, after the CREATE TABLE and UPDATE statements, SQLs are:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE multiCols2 AS SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 1
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE multiCols3 AS SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 2
SELECT A.fieldName,B.fieldName,C.fieldName _
FROM (SELECT * FROM multiCols WHERE PlaceHolder = 0) A
LEFT JOIN multiCols2 B ON A.RowNum = B.RowNum LEFT JOIN multiCols3 C
ON A.RowNum = C.RowNum
- ^ This is due to the different treatment of the division between integers, for example SQLite and PostgreSQL return an integer, MySql returns decimals.
- ^ With this solution, all SQL statements are compatible MySql.
History
- 11th January, 2022: Initial version
