The article illustrates a speech-to-text function and how it is integrated into an app.
Introduction
Efficient records management is more relevant now than ever. In our digital age, huge growth of information — audio, video, and more — must be handled in a limited time. This makes a real-time transcription function essential, because it is useful in many scenarios.
In audio or video conferencing, this function records meeting minutes that I can refer to later, which is more convenient than writing them all by myself. I've seen my kids struggling to take notes during their online courses, so I know this process can be so much easier with the help of the transcription function. In short, it removed the job of writing down everything the teacher says, allowing the kids to focus on the lecture itself and easily review the content again later. Also, the live captions provide viewers with real-time subtitles, for a better watching experience.
As a coder, I am a believer in "Actions speak louder than words". That's why I developed a real-time transcription function, with the help of a real-time transcription capability from ML Kit, like this.
Demo
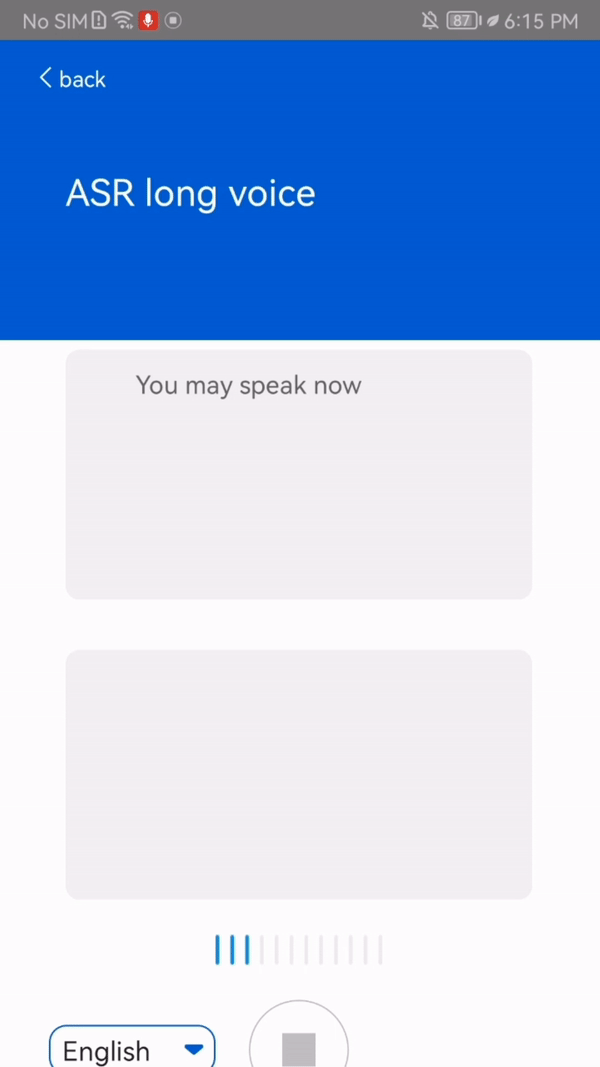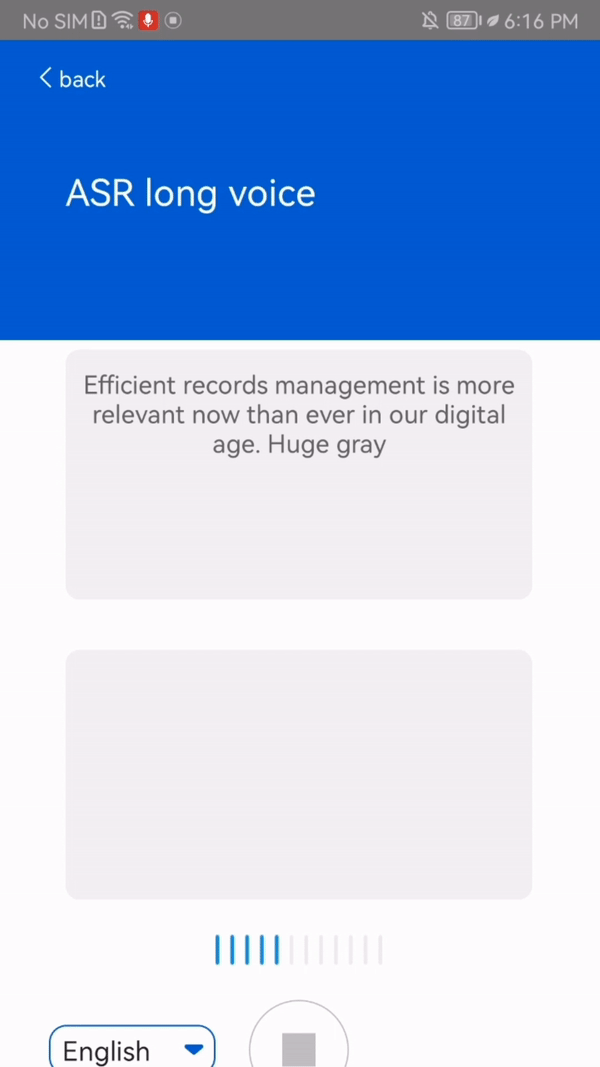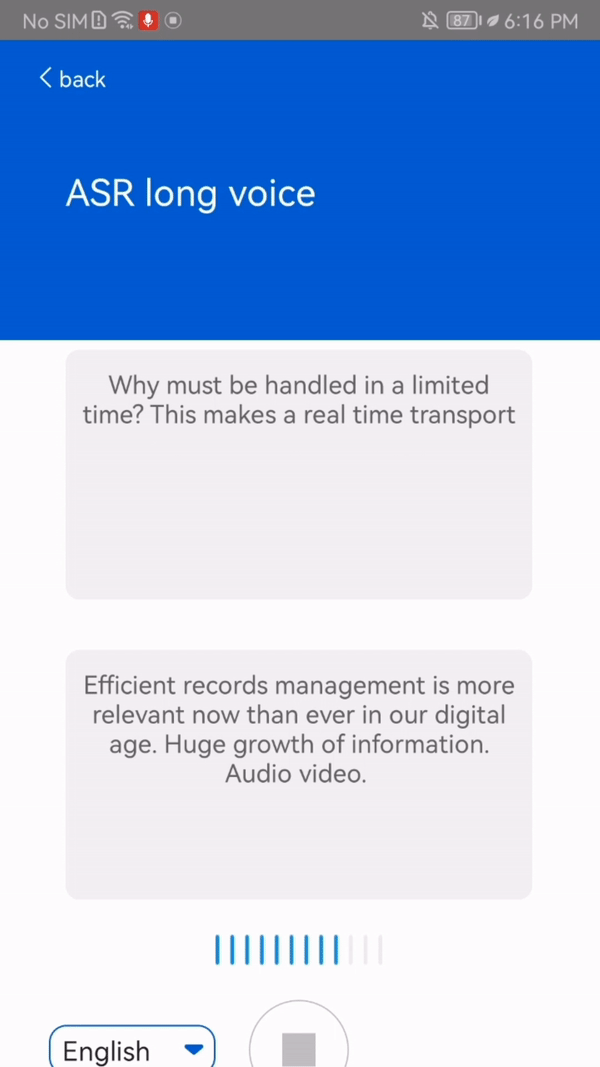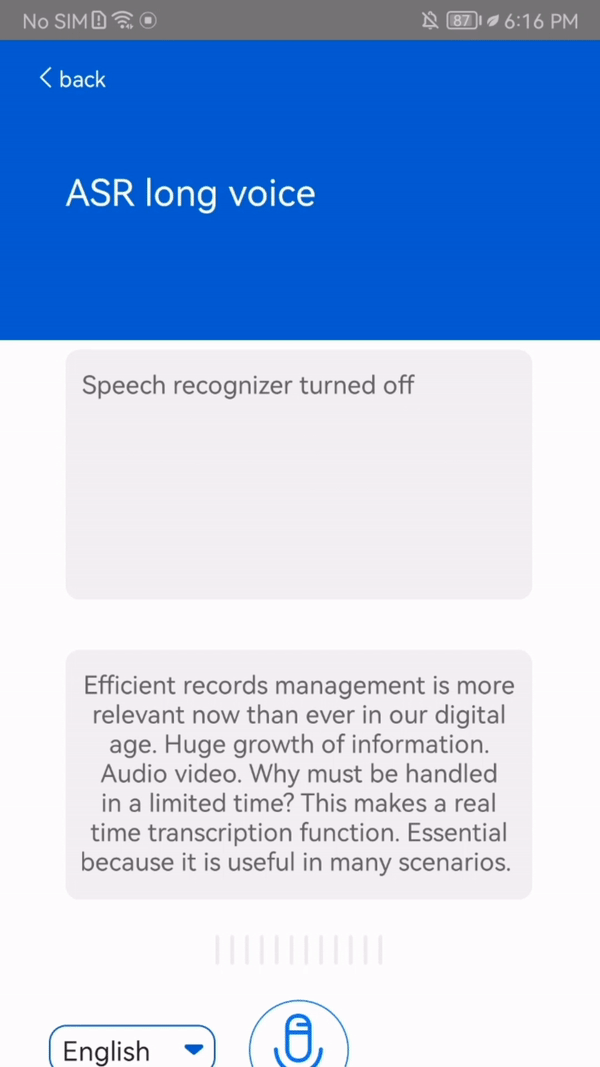
This function transcribes up to 5 hours of speech into Chinese, English (or both), and French languages in real time. In addition, the output text is punctuated and contains timestamps.
This function has some requirements: the support for French is dependent on the mobile phone model, whereas Chinese and English are available on all mobile phone models. Also, the function requires Internet connection.
Okay, let's move on to the point of this article: How I developed this real-time transcription function.
Development Procedure
- Make necessary preparations.
- Create and then configure a speech recognizer.
MLSpeechRealTimeTranscriptionConfig config =
new MLSpeechRealTimeTranscriptionConfig.Factory()
.setLanguage(MLSpeechRealTimeTranscriptionConstants.LAN_ZH_CN)
.enablePunctuation(true)
.enableSentenceTimeOffset(true)
.enableWordTimeOffset(true)
.create();
MLSpeechRealTimeTranscription mSpeechRecognizer =
MLSpeechRealTimeTranscription.getInstance();
- Create a callback for the speech recognition result listener.
Protected class SpeechRecognitionListener
implements MLSpeechRealTimeTranscriptionListener{
@Override
public void onStartListening() {
}
@Override
public void onStartingOfSpeech() {
}
@Override
public void onVoiceDataReceived(byte[] data, float energy, Bundle bundle) {
}
@Override
public void onRecognizingResults(Bundle partialResults) {
}
@Override
public void onError(int error, String errorMessage) {
}
@Override
public void onState(int state,Bundle params) {
}
}
- Bind the speech recognizer.
mSpeechRecognizer.setRealTimeTranscriptionListener(new SpeechRecognitionListener());
- Call
startRecognizing to begin speech recognition.
mSpeechRecognizer.startRecognizing(config);
- Stop recognition and release resources occupied by the recognizer when the recognition is complete.
if (mSpeechRecognizer!= null) {
mSpeechRecognizer.destroy();
}
History
- 6th May, 2022: Initial version
