This article aims to cover reading the result of a basic Windows command, IPCONFIG, and next set the networks parameters without errors. Reading a text file that transcends language is a very important objective because the association of different words together leads to the required result.
Introduction
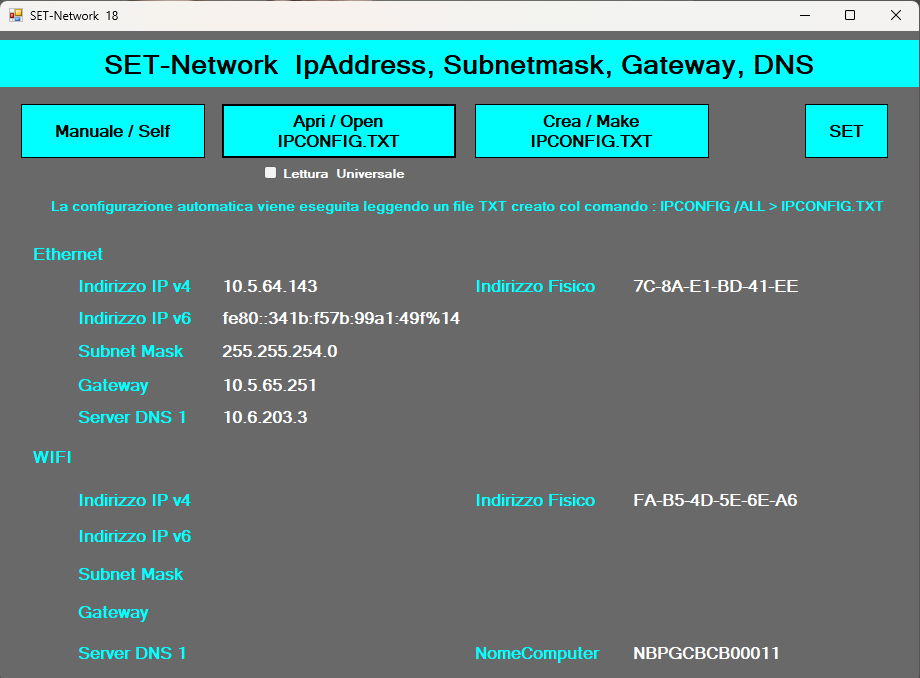
Using the /ALL option, it is possible to save the network parameters to a text file and subsequently reread it to set these parameters again on another PC or on the same one during configuration. We know how difficult it is for administrators of small networks to keep track of the network parameters for all the computers on the network. Obviously, there are software out there that promise and perhaps keep their word to manage the network correctly without wasting time. Unfortunately, in some situations, there is not enough money to spend on this problem, a solution could be to save the network parameters in files, which if managed with the IPCONFIG command, should at least be homogeneous for all computers. Reading and setting network parameters with a text file is both simple and fast. And then, I think all the computer scientists involved know IPCONFIG at least in its basic options.
Method
The method used is text recognition because I believe it is the easiest to implement, in all languages. Furthermore, the recognition of WORD ASSOCIATIONS gives me an advantage in the case in which a text file in a different language such as English and French is treated and read, because within a file saved with IPCONFIG /ALL > IPCONFIG.TXT, there are always the same words in all languages, only translated: Subnet or Passarelle for example.

Using the Code
For the subsequent application of the network parameters, it is appropriate to specify that there are various methods, but I think it is simpler to use the Win32_Management class for the IP, the Subnet Mask, the Gateway. To change the DNS, you can use NETSH. To set a new computer network name (Hostname), a restart is mandatory and therefore it was done with a Batch file.
Declaring variables for the network parameters:
...
Dim IPAddress As String = ""
Dim SubnetMask As String = ""
Dim Gateway As String = ""
Dim nomeHost As String = ""
Dim SuffissoDNSprimario = ""
Dim ElencodiricercasuffissiDNS = ""
Dim universal = 0
...
To begin, we recognize the IPCONFIG macro categories with this code in the case of a known language:
If universal = 0 Then
If strLine.Contains("Configurazione IP di Windows") Then
ConfigValido = 1
End If
If strLine.Contains("Scheda Ethernet Ethernet:") Then
Ethernet = 1
End If
If strLine.Contains("Scheda LAN wireless Wi-Fi:") Then
WIFI = 1
Ethernet = 0
End If
If strLine.Contains("Scheda Ethernet Connessione di rete Bluetooth:") Then
BlueTooth = 1
WIFI = 0
Ethernet = 0
End If
And with this routine in the case of associative transcendental reading:
ElseIf universal = 1 Then
If strLine.Contains("Windows") AndAlso strLine.Contains("IP") Then
ConfigValido = 1
End If
If strLine.Contains("Ethernet") AndAlso (strLine.Contains("Adapter") _
Or strLine.Contains("adapter") Or strLine.Contains("Carte")) Then
Ethernet = 1
End If
If strLine.Contains("Wireless") Or strLine.Contains("Wi-Fi") Then
WIFI = 1
Ethernet = 0
End If
If strLine.Contains("Bluetooth") Then
BlueTooth = 1
WIFI = 0
Ethernet = 0
End If
The next step is to determine the network parameters saved in the file in the case of reading in a known language:
If strLine.Contains(" Nome host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : ") Then
nomeHost = Strings.Replace(strLine, " _
Nome host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : ", "").TrimEnd(" ")
End If
If strLine.Contains(" Suffisso DNS primario . . . . . . . . : ") Then
SuffissoDNSprimario = Strings.Replace(strLine, " _
Suffisso DNS primario . . . . . . . . : ", "").TrimEnd(" ")
End If
And in the case of transcendental reading:
If (strLine.Contains("Subnet") Or strLine.Contains("Mask") _
Or strLine.Contains("mask") Or strLine.Contains("Masque") _
Or strLine.Contains("masque")) AndAlso Ethernet = 1 Then
Dim subnets() As String = Strings.Split(strLine, ":")
SubnetEthernet = Strings.Replace(subnets(1), " ", "")
SubnetMask = SubnetEthernet
End If
Finally, in case you want to change the network parameters and assign them to the values, just read:
Dim objMC As ManagementClass = New ManagementClass("Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration")
Dim objMOC As ManagementObjectCollection = objMC.GetInstances()
For Each objMO As ManagementObject In objMOC
If (Not CBool(objMO("IPEnabled"))) Then
Continue For
End If
Try
Dim objNewIP As ManagementBaseObject = Nothing
Dim objSetIP As ManagementBaseObject = Nothing
Dim objNewGate As ManagementBaseObject = Nothing
objNewIP = objMO.GetMethodParameters("EnableStatic")
objNewGate = objMO.GetMethodParameters("SetGateways")
objNewGate("DefaultIPGateway") = New String() {Gateway}
objNewGate("GatewayCostMetric") = New Integer() {1}
objNewIP("IPAddress") = New String() {IPAddress}
objNewIP("SubnetMask") = New String() {SubnetMask}
objSetIP = objMO.InvokeMethod("EnableStatic", objNewIP, Nothing)
objSetIP = objMO.InvokeMethod("SetGateways", objNewGate, Nothing)
MessageBox.Show("Updated IPAddress, SubnetMask and Default Gateway!")
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show("Unable to Set IP : " & ex.Message)
End Try
Next objMO
Don't forget to import System.Management to your project.
Points of Interest
Definitely two. The first is the use of simple text files for quick configuration, the second is the opportunity to create a robust routine for recognizing any file saved with IPCONFIG in any language by reading that transcends the text and focuses on some simple words.
History
- 24th January 2024: First version
