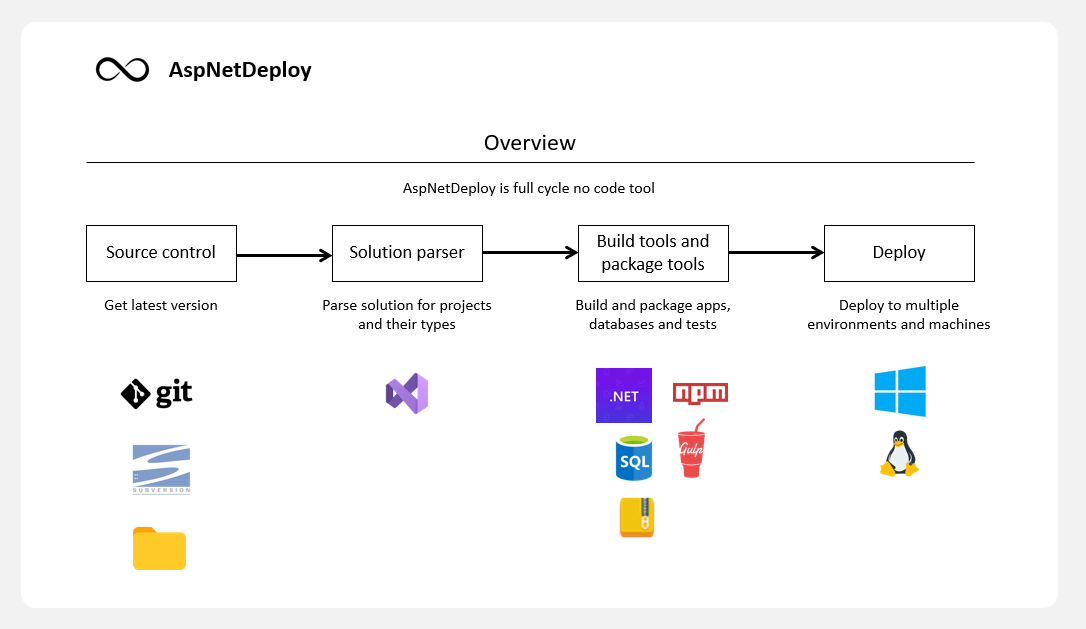
This tip demonstrates the use of AspNetDeploy to build package and deploy ASP.NET app.
Introduction
Somehow, in 2024, we don't have open-source tool that handles CI+CD for ASP.NET from A to Z. Tools like Jenkins are so generic, that are more like a set of command line statements called one by one and having no idea what they are dealing with.
In this article, I would like to share our inhouse tool called AspNetDeploy.
Background
It all started in 2014, I was upset I had to deal with several tools to perform as simple task as build my solution and deploy WebApp to test and production environments. Ten years later in 2024, I'm still asked to write msbuild arguments by hand, how come!
Idea
My tool of choice will:
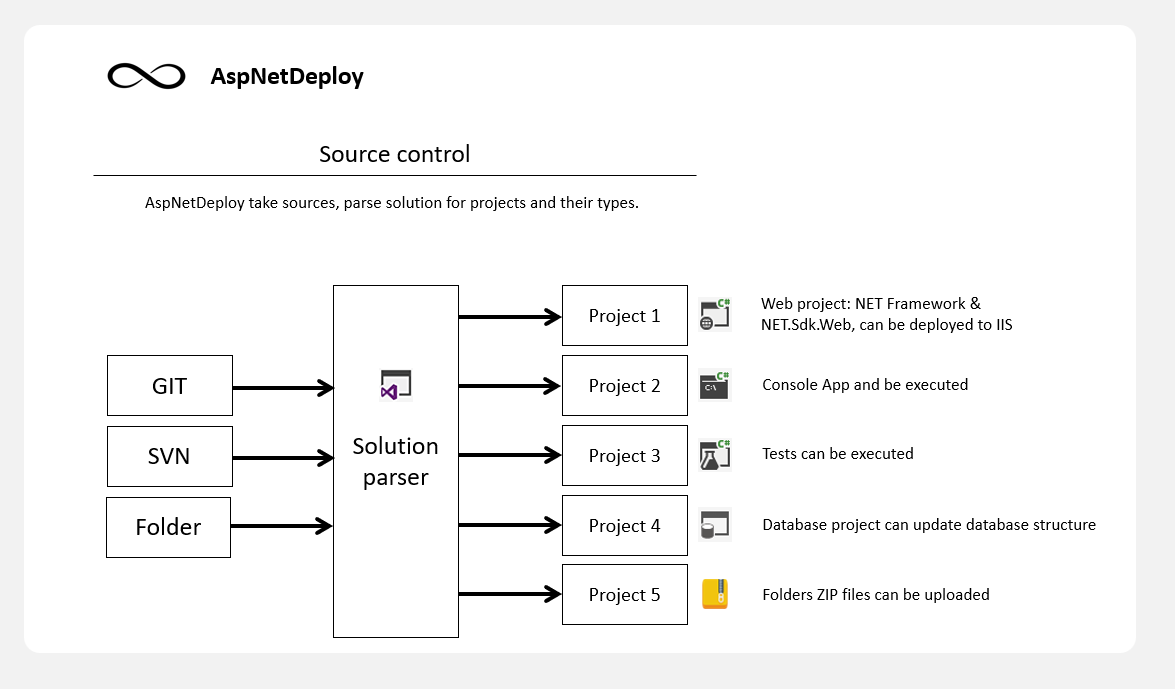
- grab sources and see what's inside by parsing solution and project files
- determine how to pack and build projects by itself
- distribute and configure packages across environments and their assigned machines
Sounds simple.
This project is for you if:
- You are a small to medium company who cares for cloud costs
- Your app runs on bare metal VPS on Windows + IIS
- Your stack is ASP.NET/Core, C#, MSSQL
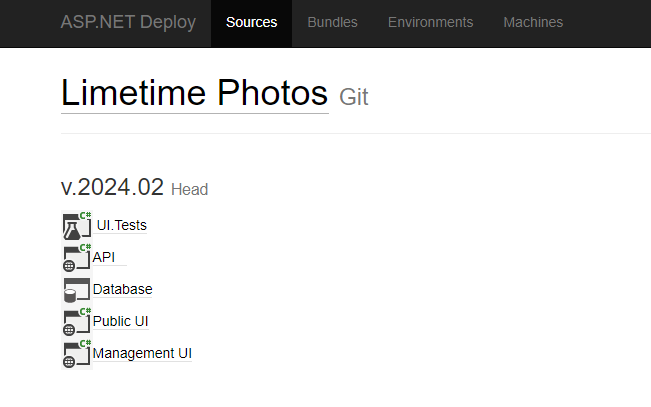
Step 1: Sources
Simply by specifying repository URL, desired branch and credentials, AspNetDeploy will take sources and parse the solution. Instantly, you see projects that have something to do with building, testing and releasing your app.
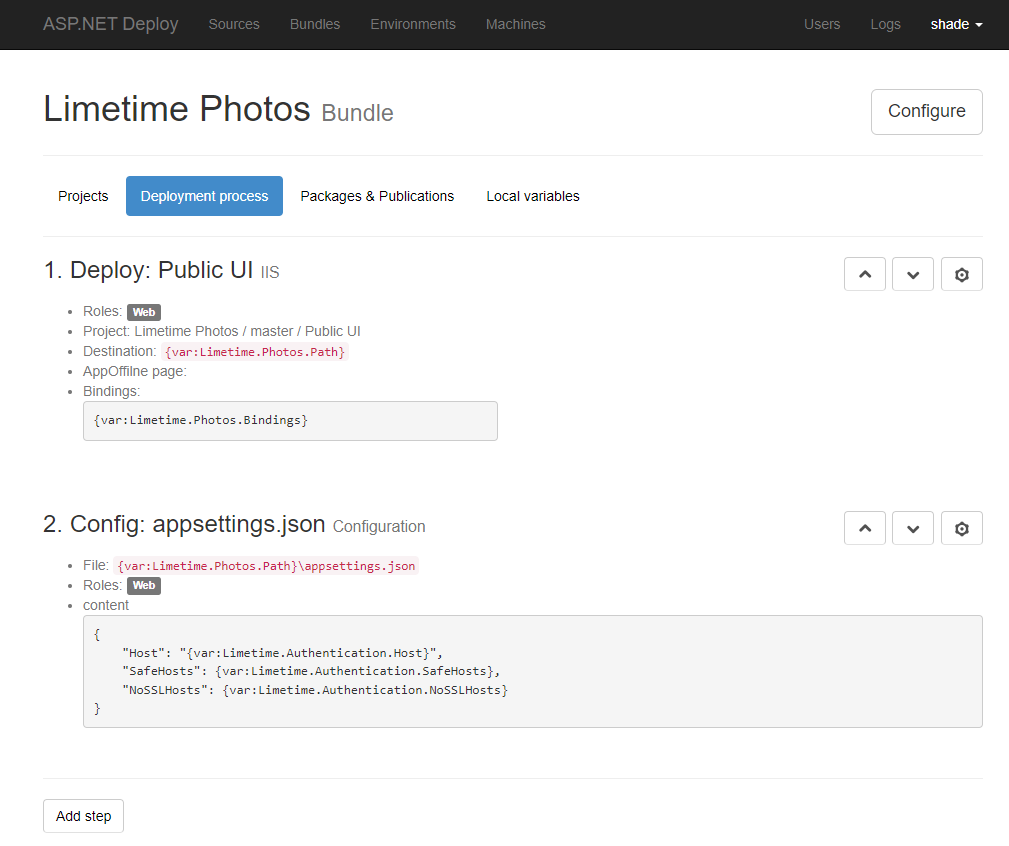
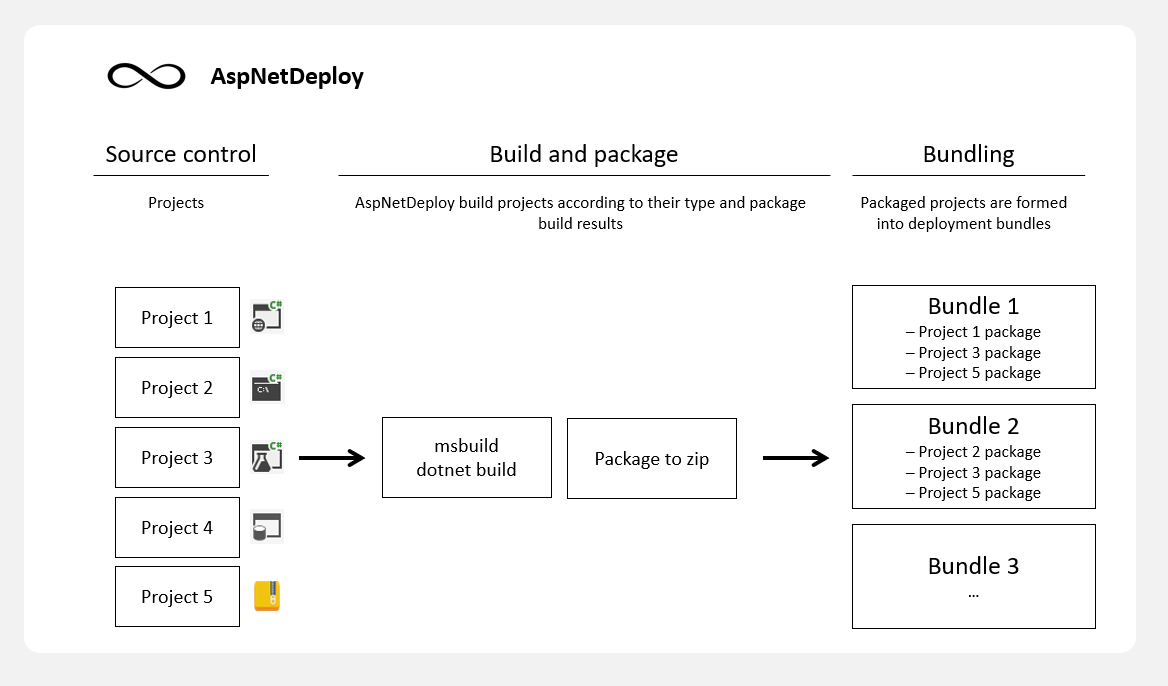
Step 2: Build, Package and Bundle
Projects are formed into bundles to be deployed as a single operation. Simple setup consists of Web project deployment step and configuration step. Here, we specify:
- what project to use and where it should be located on target machines
- IIS bindings
- configuration values
- where to execute each step, can be a machine with specific role like WEB, DB, CDN, test agent, etc.
We use variables that vary their values from one environment to another (Test, Staging, Production...) or machine.
No build paths, no ridiculous setup. AspNetDeploy knows how to handle WebApp, how to restore packages, build, package in release mode, what files to pack, how to update IIS site and pools, etc.
You only asked to install VS2022 Community edition on build machine.
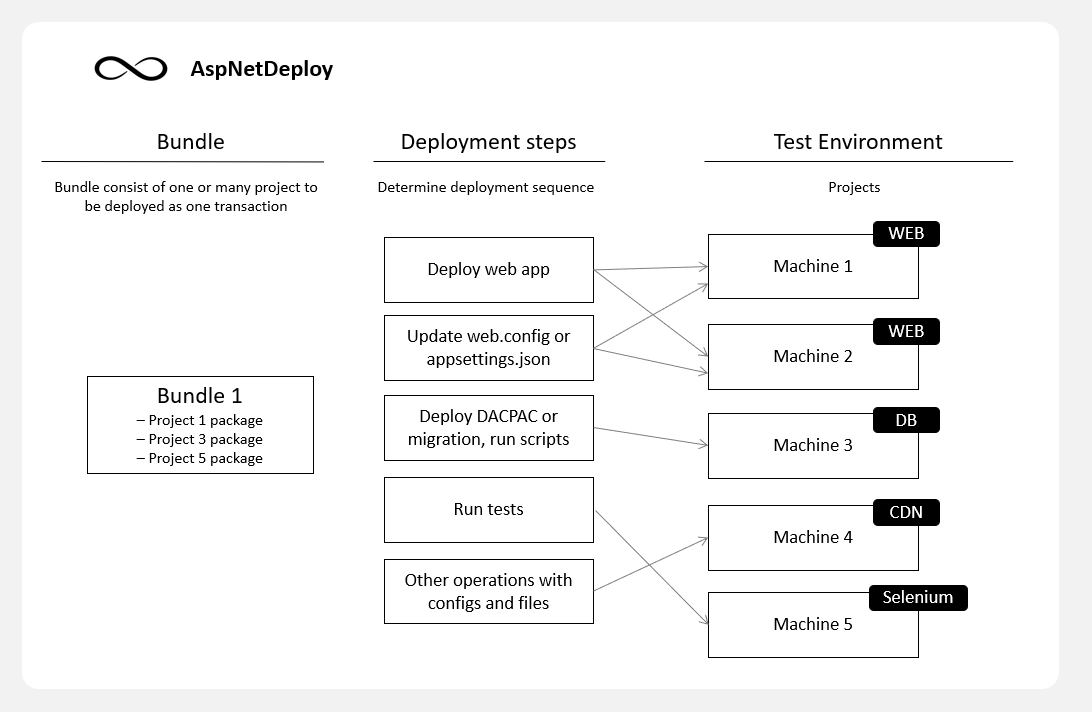
Step 3: Deploy
AspNetDeploy uses Deployment agents installed on each machine. Machine is then assigned to one of the environments with a specific role. This is how we know where to deploy WebApp and where to deploy DB.
Environments are chained one to another, Test -> Stage -> Prelive -> Live
You may have as many as you like.
When it's time to push bundle to environment, deployment steps are executed. If there happens to be a deployment problem, current transaction is reverted to as it was before publication. All you have to do is stare on the progress bar and drink coffee.
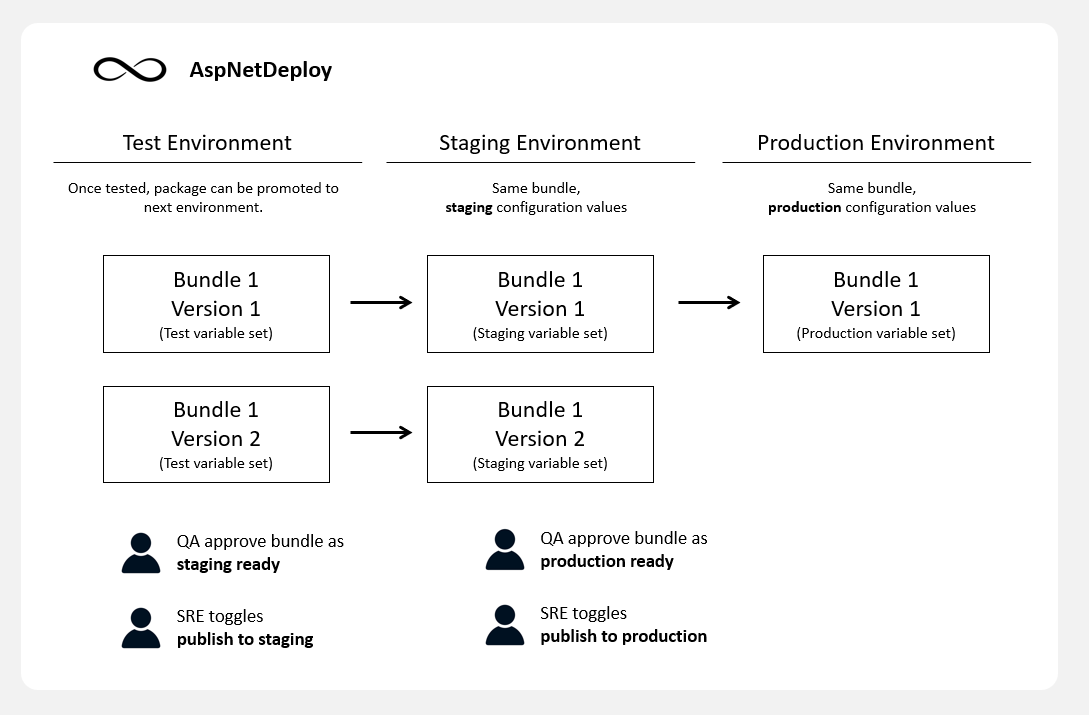
Step 4: Promote Bundle to Production
Most likely, you have several environments for testing, finalizing changes and clients.
This is where your team Devs, QAs and SREs work together by approving and promoting packages to Production environment.
For this demo, we setup Test and Production environments with three machines assigned.
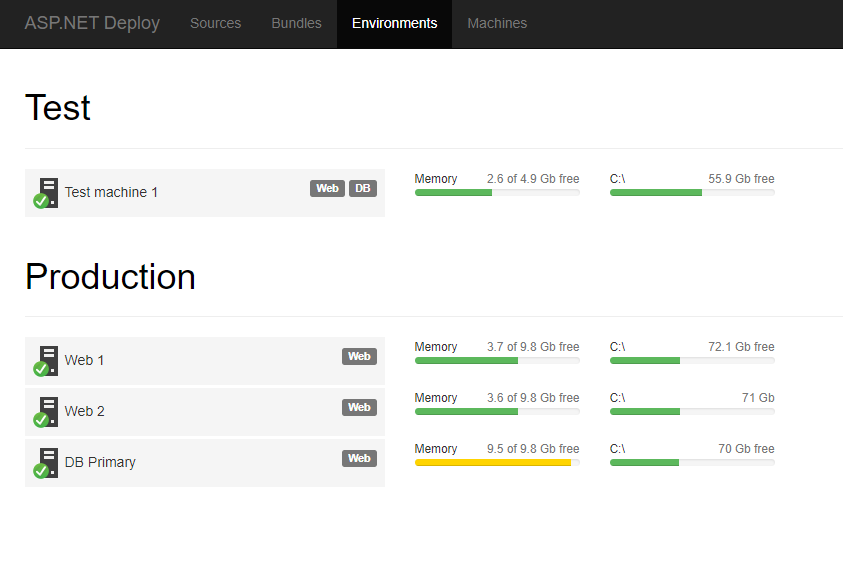
QA approves package, and SREe toggles publication and that's it!
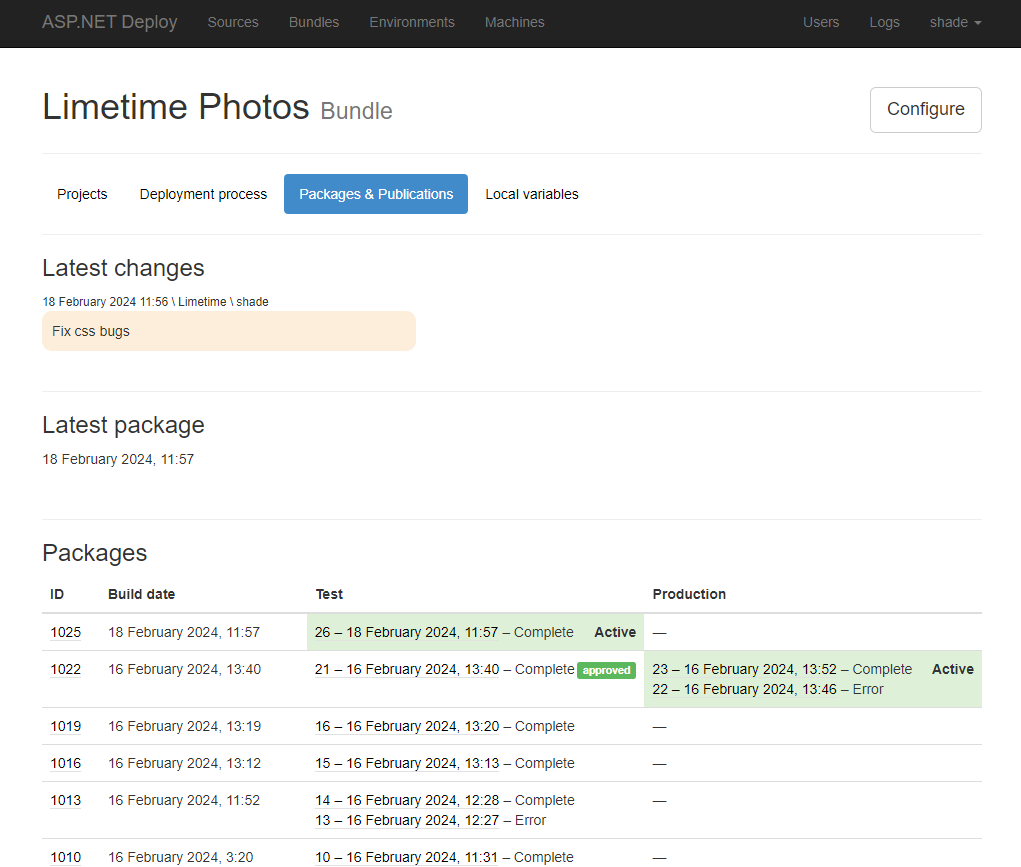
So this is how you get your sources build, tested and rolled out to clients without configuration nightmare. 🚀
Although started 10 years ago, and there were several years when AspNetDeploy was not used at all, I'm happy to realize it works out of the box for latest NET8, MSSQL and Win11 with minor tweaks. 🎉
Points of Interest
I'm happy to communicate with anyone who is willing to try AspNetDeploy for their CD pipeline!
History
