Introduction
Morse code is a method of transmitting string information into a series of dots[.] and dashes[-] encrypting a message between two entities and so making
communication possible between two parties. And we are going to have the fun task of doing just that.
I will be using a simple console application to represent the use of Morse code.
Using Morse
At first we will need to define a dictionary to be able to communicate. Find the Morse code value of the letter we want to type and
instantiate a dictionary Element and the reason for doing so is that we will not have to use all of the redundant if statements or case statements
thus increasing our calculation speeds.
namespace Morse_Code
{
public class TheLib
{
private Dictionary<String, String> m_TheLibrary =
new Dictionary<string, string>();
public Dictionary<String, String> TheLibrary
{
get { return m_TheLibrary; }
set { m_TheLibrary = value; }
}
}
}
This will keep track of all our data. Well now we have to add some data into our little library. Let's create a load method to do the adding of all our Morse values for our characters.
protected void LoadMorse()
{
#region Alphabet A-Z
TheLibrary.Add("A", ".-");
TheLibrary.Add("B", "-...");
TheLibrary.Add("C", "-.-.");
TheLibrary.Add("D", "-..");
#endregion
}
This will enable us to add some values into our library and using the library will be just as easy to do, just by calling on the library and sending our
characters. Let's create a method that will return the Morse encrypted string value.
public String Sentance_To_Morse(String Sentence)
{
String returnString = "";
List<string> Words = Sentence.Split(' ').ToList<string>();
foreach (String Word in Words)
{
for (int letter = 0; letter < Word.Length; letter++)
{
if (TheLibrary.ContainsKey(Word[letter].ToString().ToUpper()))
{
returnString += TheLibrary[Word[letter].ToString().ToUpper()];
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("The Character {0} is not recognized in the Morse Library", letter.ToString().ToUpper());
}
returnString += " ";
}
returnString = returnString.Trim(' ');
returnString += " ";
}
return returnString.Trim(' ');
}
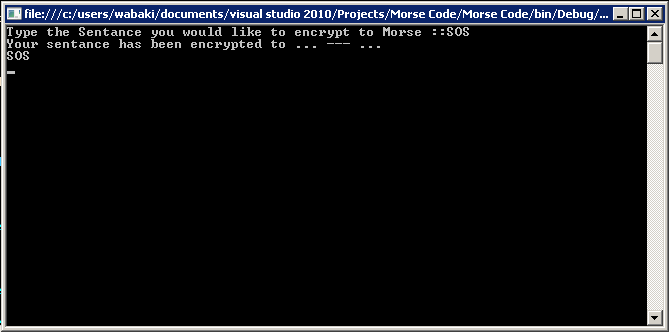
If we call on this method and send through the sentence "SOS SOS".
We will get the value of "... --- ... ... --- ..."
What if we got a series of dots and dashes and wanted to convert it back to a sentence? Let's create a method to do the conversion.
public String Morse_To_Sentance(String Morse)
{
String returnString = "";
Morse = Morse.Replace(" ", ",");
string[] MorceWords = Morse.Split(',');
foreach (String word in MorceWords)
{
if (word != "")
{
String[] MorseCodeLetters = word.Split(' ');
foreach (string MorseCodeLetter in MorseCodeLetters)
{
if (TheLibrary.ContainsValue(MorseCodeLetter))
foreach (KeyValuePair<String, String> MorseItem in TheLibrary)
{
if (MorseItem.Value == MorseCodeLetter)
returnString += MorseItem.Key;
}
}
}
returnString += " ";
}
return returnString.Trim(' ');
}
And that will be all we need for our little converter. Hope this was a great example of a Morse code converter.
Now let's use the class we created:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TheLib m_lib = new TheLib();
Console.Write("Type the Sentence you would like to encrypt to Morse ::");
string MorseSentance = m_lib.Sentance_To_Morse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Your sentence has been encrypted to {0}", MorseSentance);
Console.WriteLine(m_lib.Morse_To_Sentance(MorseSentance));
Console.Read();
}
Points of Interest
Morse code was originally represented by sounds, beeps, and the methods bellow will play the Morse code to simulate a communication. Just add them to the
library TheLib class and call on the method.
I used it three times as a long method. Well all it says
basically is that a dash is three times as long as a dit and
an inter character is as long as a dit.
protected void CreateDAH(int time)
{
Console.Beep(1100, time);
}
protected void CreateDIT(int time)
{
Console.Beep(1100, time);
}
public void playMessage(String message)
{
message.ToList<char>().ForEach((c) =>
{
if (c == '.') CreateDIT(200);
else if (c == '-') CreateDAH(600);
else Thread.Sleep(200);
});
}
