Introduction
Connecting to a cell phone in an easy way and getting information is very important for some applications such as SMS senders and Bluetooth connections and this tip shows how to connect to cell phones that are connected to the computer by Bluetooth or USB cable that have one COM port and request an AT Command from mobile set.
Background
Decrypting and encrypting files and data is a very sophisticated subject but I am using that in this tip just for the main subject.
The project scenario steps are as follows:
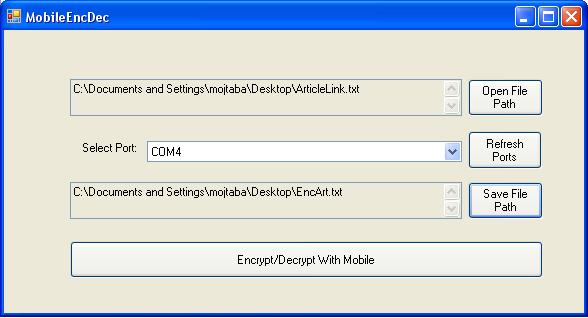
- Connect a cell phone by Bluetooth or other connectivity tools to computer
- Select source file and mobile COM port and select output file path
- Create a target file and get the length of the source file in byte count
- Connect to mobile phone and read its serial number
- Decrypt/Encrypt source file to target file by XOR style that XOR all source file bytes by XOR to key value that in this project is the Mobile Phone serial number
Text and binary files format and their standards vary, for example character standards (ASCII, Unicode v1,2,3,4 and other), video and image files header and data.
For this reason, read and write files must be done in a basic way. Read and write byte to byte (8 bit) from source to target.
Using the Code
Reading COM Ports
From the static method in the SerialPort class load all COM (serial) ports to port combo:
private void btnRefreshports_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
cmbPort.Items.Clear();
string[] lPorts = SerialPort.GetPortNames();
foreach (string str in lPorts)
{
cmbPort.Items.Add(str);
}
if (cmbPort.Items.Count > 0)
cmbPort.SelectedIndex = 0;
}
Main method that reads the serial number from the mobile set
Before reading the mobile serial number, you must accept your mobile clarification about computer connection or pair your mobile set with computer before running the application.
Reading Serial Number Steps
- Prepare SerialPort
- Open SerialPort (connect to mobile set)
- Writing AT command to serial port and waiting in adequate time (2 second or 2000 milliseconds)
- Reading result and export serial number from it
- Return serial number
AT: Attention Command
AT+CGSN: AT Command for requesting product serial number identification (IMEI)
private string GetMobileSerialNumber(string PortName)
{
string key = "";
SerialPort serialPort = new SerialPort();
serialPort.PortName = PortName;
serialPort.BaudRate = 56700;
try
{
if (!(serialPort.IsOpen))
serialPort.Open();
serialPort.Write("AT\r\n");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
key = serialPort.ReadExisting();
serialPort.Write("AT+CGSN\r\n");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
key = serialPort.ReadExisting();
serialPort.Close();
string Serial = "";
for (int i = 0; i < key.Length; i++)
if (char.IsDigit(key[i]))
Serial += key[i];
return Serial;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show("Error in opening/writing to serial port :: " + ex.Message, "Error!");
return "";
}
}
Read from source file
This method reads from the source file fileName from byte number Offset size of bc (byte count):
public byte[] ReadFileToByteArray(string fileName, int bc, long offset)
{
try
{
byte[] buff = null;
FileStream fs = new FileStream(fileName,
FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read);
BinaryReader br = new BinaryReader(fs);
br.BaseStream.Position = offset;
buff = br.ReadBytes(bc);
fs.Close();
return buff;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
Write to target file
This method writes to the target file fileName from byte number Offset size of bc (byte count):
public bool WriteBytesToFile(byte[] buff, string fileName, int bc, long offset)
{
try
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(fileName,
FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Write);
BinaryWriter br = new BinaryWriter(fs);
br.BaseStream.Position = offset;
br.Write(buff, 0, bc);
fs.Close();
return true;
}
catch
{
return false;
}
}
The following method is the manager method for other method calls:
In this method, call the serial number reader method and split the source file in smaller sizes, for example, 1 Mega Byte and read from the source by using the ReadFileToByteArray method and Decrypt/Encrypt bytes and write by WriteBytesToFile method.
private void btnEncDec_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (cmbPort.Text != "" && txtSource.Text != "" && txtDistenation.Text != "")
{
string Key = GetMobileSerialNumber(cmbPort.Text);
if (Key != "")
{
try
{
Stream stream = new FileStream
(txtDistenation.Text, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write, FileShare.Read);
stream.Close();
stream = new FileStream
(txtSource.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read);
long len = stream.Length;
stream.Close();
if (len>=1)
{
try
{
byte[] buffer;
long Used=0;
int Mb=(int) Math.Pow(2,20);
while (Used < len)
{
int Itr = 0;
if (Used + Mb < len)
{
Itr = Mb;
}
else
Itr = (int)(len-Used);
if (Itr >= 1)
{
buffer = ReadFileToByteArray(txtSource.Text, Itr, Used);
for (int i = 0; i < Itr; i++)
{
buffer[i] = (byte)(buffer[i] ^ Key[i%Key.Length]);
}
WriteBytesToFile(buffer, txtDistenation.Text, Itr, Used);
Used += Itr;
}
else
break;
}
MessageBox.Show("Successfully Done!");
}
catch
{
MessageBox.Show("Error!");
}
}
}
catch
{
MessageBox.Show("Error!");
}
}
}
else
MessageBox.Show("Please Fill Information");
}
Points of Interest
- Writing a full AT Command query and result on mobile and modems
History
- Version 1.0 in April 2013
References
