Introduction
HTTP compression technique one of the good techniques to improve performance in web based applications. Both web server and clients make better use of available bandwidth and provide greater transmission speeds between both of them.
The most common compression schemes include gzip and deflate.
Background
One of my senior developers was assigned a task. The scenario was that there were two servers, one was a development server and the other was a production(live) server. The production server was a server firm. In both servers, we deployed a web application, but the problem was when those two applications were run, the two applications show different file sizes when we observe through Firebug tool.
Details
Here, I show some pictures regarding that issue, then explain later.
Development Server
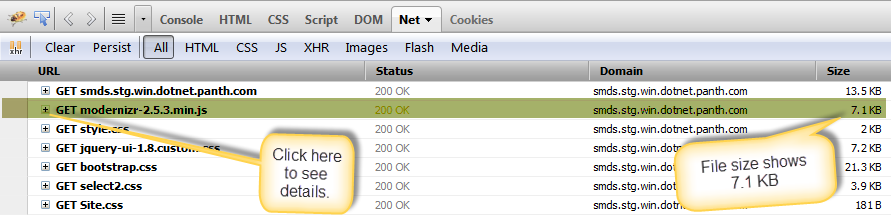
This is the development server application files observing from Firebug. Here you see the modernizr-2.5.3.min.js file size is 7.1 KB.
And the details about those files:

Production Server

This is production server application files observing from Firebug. Here you see the modernizr-2.5.3.min.js file size is 14.9 KB.
When you click on that file, then you see all the details about that file request and response.

All of the files in the production server show more than twice the size than that on the development server and loading those files in production server takes too much time.
At first, I searched in Google why the same file shows different sizes in different servers, but I did not get the desired result.
I copied the content of that file from two different servers and matched with each other and both files matched and I got the same file size, but in Firebug, it shows different sizes.
- Is it the problem of Firebug tool?
- Is it the problem of making the production server as a server firm?
Then, I finally tried to find out what is the difference between two files in Firebug. I saw that in the development server file, content is encoded by gzip term which was not seen in production server file. I searched in Google with that term and finally came to know that it is a compression technique which is configurable from IIS settings.
After enabling HTTP compression, all file sizes are equal in both servers and production server application loading performance is better than in the past.
- For enabling HTTP compression for IIS-6, click here.
- For enabling HTTP compression for IIS-7, click here.
Points of Interest
It's a very simple task to enable or disable HTTP compression, but it's challenging to find out when you browse an application, is it HTTP compressed enabled or disabled? This is because as a developer, you do not have permission to go the production server.
As long as I knew that file size showing in Net tab in Firebug is the actual file size, now I can understand it's not the physical file size. It's the size of data transferred from server to client browser.
Now I can easily find out whether website files are HTTP compression enabled or disabled.
