Introduction
In this tip, I’ll introduce my new .NET library for JSON file. It’s a new simple implementation that lets you parse and create JSON file and serialize your objects to json file and how to get them back (deserialize).
Background
We assume that you know JSON format (if not, check
this). Some C# basics are required since the library is developed in C#.
Classes
The library is composed of 4 major classes:
System.Json.JsonElement: It represents a pair key-value object.
Key is a string value; however Value can be of any Type (int, float, char, bool, string, object, array … etc.)
System.Json.JsonArray: It represents a collection of objects that can be of any type and any dimension.
System.Json.JsonObject: It’s a collection of JsonElement object.
- You can parse json data using class method
JsonObject JsonObject.Parse(string json) , it takes json data as string, then returns a JsonObject - You can fetch
JsonElement using instance method JsonElement JsonObject.GetElementByKey(string key) , it takes a string key, then returns a JsonElement
System.Json.JsonFormatter: It is used for serialization and deserialization
It contains two class methods:
Void JsonFormatter.Serialize(object,Stream): It takes an object to be serialized and a stream object where to save json dataObject JsonFormatter.Deserialize(Type,Stream): It takes type of object to be retrieved and the stream from where to get json data, it returns an object of type Type.
Code Example
Example 1
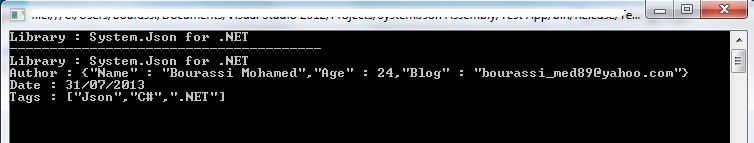
In this example, I'll show you how to parse json data using class method JsonObject.Parse(string). Also how to get specific element using instance method JsonObject.GetElementByKey(string).
C# Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Json;
namespace Test_App
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{ string json = "{" +
"\"Library\" : \"System.Json for .NET\"," +
"\"Author\" : { " +
"\"Name\" : \"Bourassi Mohamed\"," +
"\"Age\" : 24," +
"\"Blog\" : \"bourassi_med89@yahoo\"" +
"}," +
"\"Date\" : \"31/07/2013\"," +
"\"Tags\" : [\"Json\",\"C#\",\".NET\"]" +
"}";
JsonObject jso = JsonObject.Parse(json);
JsonElement element = jso.GetElementByKey("Library");
Console.WriteLine("Library : " + element.Value);
Console.WriteLine("---------------------------------------");
foreach (JsonElement el in jso)
Console.WriteLine(el.Key + " : " + el.Value);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
} 
Example 2
In this example, I'll show you how to create json data, including pairs of simple elements, arrays and objects.
C# Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Json;
namespace Test_App
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
JsonObject jso = new JsonObject();
jso.Add(new JsonElement(){
Key = "IntValue",
Value = 1
});
jso.Add(new JsonElement()
{
Key = "BoolValue",
Value = true
});
jso.Add(new JsonElement()
{
Key = "StringValue",
Value = "string"
});
jso.Add(new JsonElement()
{
Key = "NullValue",
Value = null
});
JsonObject otherJO = new JsonObject();
otherJO.Add(new JsonElement() {
Key = "Fname",
Value = "Bourassi"
});
otherJO.Add(new JsonElement()
{
Key = "Lname",
Value = "Mohamed"
});
otherJO.Add(new JsonElement(){
Key = "Age",
Value = 24
});
jso.Add(new JsonElement(){
Key = "PersonValue",
Value = otherJO
});
JsonArray ja = new JsonArray();
ja.Add("C#");
ja.Add(null);
ja.Add(true);
ja.Add(otherJO);
jso.Add(new JsonElement()
{
Key = "ArrayValue",
Value = ja
});
Console.WriteLine(jso.ToString());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Example 3
In this example, I'll show you how to serialize your objects to json files using class method JsonFormatter.Serialize(object,Stream). This method takes object to be serialized and a Stream object where to put json data.
Note that the generated json data doesn't contain any information about the serialized type, this way you can serialize your object without overhead information.
JsonFormatter class doesn't support for now object that contains generic collections, instead you can use simple arrays.- Your object's class should have a
Serializable attribute in its declaration.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Json;
using System.IO;
namespace Test_App
{
class Program
{
[Serializable]
class Person
{
public string FName { get; set; }
public string LName { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person()
{
FName = "Bourassi",
LName = "Mohamed",
Age = 24
};
FileStream file = new FileStream("file", FileMode.Create);
JsonFormatter.Serialize(person, file);
file.Close();
string output = File.ReadAllText("file");
Console.WriteLine(output);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
} Example 4
In this example, I'll show you how to deserialize your object (how to get them back) from json data using class method JsonFormatter.Deserialize(Type,Stream).
This method takes a Type parameter that represents type of object to get back, and a Stream object, it returns an object that should be converted to your object's type.
Note that in your json data, there is no information about the saved type, this way you can create custom class based on any json file.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Json;
using System.IO;
namespace Test_App
{
class Program
{
[Serializable]
class Person
{
public string FName { get; set; }
public string LName { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
FileStream file = new FileStream("file", FileMode.Open);
Person person = (Person)JsonFormatter.Deserialize(typeof(Person), file);
file.Close();
Console.WriteLine("First Name : " + person.FName);
Console.WriteLine("Last Name : " + person.LName);
Console.WriteLine("Age : " + person.Age);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
} 
Hope this will be useful for some of you. Any suggestions and comments are welcome.
Code Source
You can get the package library from here.
