Introduction
I just
spent a whole day cursing and swearing
on a certificate error that I got using the webservices of one of our clients.
They installed a new certificate since their old one was going to expire in a
few days. No biggie I thought. My server will detect the new certificate,
install it and do its work as usual. Boy was I wrong.
After
navigating to their webservices using a browser, I immediately got the
certificate error. Again no problem I thought. I’ll just install the
certificate manually. Unfortunately, this did not solve the problem. So I went
online searching for a solution. Yet the steps other online articles took
weren’t very clear to get to the solution. Therefore I’m posting this tip.
I was given the error "Certificate not issued by a trusted Certificate Authority" and "Certificate cannot be trusted up to a certificate Authority" on a Windows Server 2008 R2.
What is a SSL “Secure socket layer” certificate?
SSL
Certificates are small data files that digitally bind a cryptographic key to an
organization’s details. When installed on a web server, it activates the
padlock and the https protocol (over port 443) and allows secure connections
from a web server to a browser.
How does a SSL Certificate work?
A CA
“Certification Authority” issues a certificate to a domain. It verifies the
domain because the (web)server that needs
a certificate generates a certificate request. The certificate is then
mailed by the CA to info@domainname.ext
or admin@domainname.ext. This two layer verification prevents the
certificate from falling into the hands of a miscellaneous domain or user.
The
certificate holds a path within. This may sound strange but is actually quite
logical (took me a while to figure it out “I’m not that smart”) Anyone can
issue a certificate. But just because you
issue a certificate does not mean the certificate is valid. Only a
certificate issued by a valid CA is valid.
I can hear you thinking, who decides which CA
is valid and which ones are not?
That
would be you! You decide which CAs can be trusted to issue a certificate.
Microsoft automatically installs a few of these CAs on your computer as
trusted. There are only a few CAs that are commonly used like:
| CA | Market
percentage 2012 |
| GoDaddy.com,
Inc. | 21.72
|
| GeoTrust,
Inc. | 15.21
|
| Verisign | 7.52
|
| COMODO
CA Limited | 7.16 |
To
prevent you from trusting a certificate that is issued by a CA, the CA holds a
root certificate. There can also be additional certificated after that like,
extended validation cert, third party, etc. After all that is the actual domain certificate that is issued to the
holder / requester of the domain
certificate. So you can see the path now
- Root
certificate CA
- Any other certificates (can be more than one)
The
image below shows how this can be viewed on the webpage. Just click on the
little lock next to the URL. Then click view certificates and the below image will
appear.
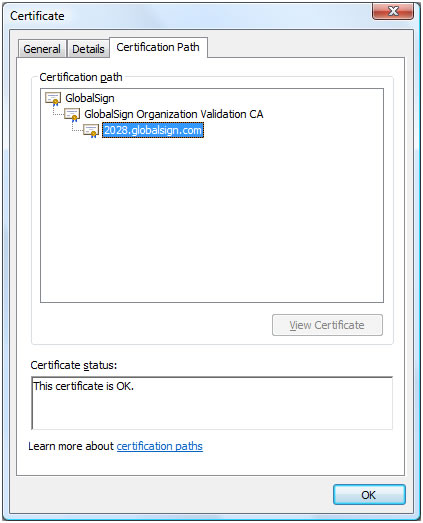
As you
can see, there are actually three certificates used to validate the website you
are requesting.
The
website you are visiting only (in this case) provides the 2028.globalsign.com certificate. The
other two certificates were already on your computer. This is how the
2028.globalsign.com certificate was validated by your computer.
What causes the error then?
Well, you should probably have figured out that you are missing one of the first
two certificates. Therefore, the domain certificate could not be verified. Giving
the error “Not issued by a trusted CA”.
How do I make the CA trusted then?
You’ll
have to download the root certificate from the CA that issued the domain
certificate and install it. You will not be able to see that certificate on the
computer that gives the certificate error. Simply because it isn’t installed.
You’ll have to download it from the website that issued the domain certificate.
Just Google it: “download comodo root certificate”, ” download godaddy root
certificate”, etc.
How do I install it?
After
you downloaded the certificate, double click on it. Then click Install
certificate. You will be prompted with a wizard raising the question where you
want to install it. Select the archive option.
Click on
Browse. If available, select the “Show physical archive selectionbox”. Then select
within the tree options: Trusted
Certification Authorities à local computer
Now that you have done this, we should check if
all the certificates are in the right place.
Go to
Start en type “mmc”. A console application will start up. Within the console
application, do the following. Go to File -> Actions -> Add snap ins.
Another
window will open. Select “Certificates”.
You will be given three options. Current User, Local computer and
applications. Select the Current user. Then perform the same action for Local
computer.
On both
options, you will find a folder called “Trusted Certificate Authorities”. As we
did earlier, we installed the certificates on a local computer. That means it
should be available for users as well. Check this and if you’re missing a
certificate, copy and paste it in the User item or local computer item as needed.
Restart your
browser and navigate to the website that was giving the certificate error. After
that, everything should work perfect. I hope it helps.
Good
luck ...
