Introduction
We will create an entity-relationship diagram for an Auto Insurance company to keep the policy information and you can see the data dictionary of this E-R diagram in Figure 2, which tells the purpose of each column. This is just a sample. If you want to use it in the real world, you need to customize it, in another words, you need to add more tables like archiving the old data if customer renews the policy, etc.
Every application needs a normalized database and it should be designed before writing a code and developing UI. This gives a better picture of the application. Normalized database is one of the most challenging tasks in software development. If database is denormalized or could not support the future enhancement, then you need to re-build your project from scratch which is costly. These days, developers want to use ORM tools so database should be normalized.
Let's talk about our example. We would like to create a database for a small Auto insurance company what information we need to save in our database for example, Policy coverage, Policy holder's address, name, SSN, vehicle information, bill, payment, traffic violation records. These are some of the data that we need to store. Let's create a Policy table to save these data. It's not a good practice to keep all of these information in a single table. These information should be kept in a different table so that we could reduce the data redundancy. Here, we don't want to keep the billing and vehicle information in the same table. Billing information should be kept in one table and vehicle should be kept in another table.
Whenever we design the database, we talk about the Normalization. It is the process of organizing the data to reduce the redundancy.
1st Form of Normalization
We remove the repeating group of columns in the separate table. Therefore, we will keep the Vehicle in Vehicle table and Billing information in Bill table. Each record should have a unique identify column so we will create Primary Key column in every table.
2nd Form of Normalization
We remove the repeating set of records into the separate table and make join between the parent and child table. Here, we will make the Join between Policy and Bill table.
So, we will create a different table to make our database as a Normalized database. Below is the list of tables:
List of Tables
Policy: This table holds the general information about the policy like PolicyNumber, EffectiveDate, PolicyExpireDate, etc.Vehicle: This table keeps the information about the insured vehicle. There could more than one vehicle under a policy so all vehicles will go under this table. There is One-To-Many relationship between Policy and Vehicle table.Driver: There could be more than one driver under a policy. Each drives Name, Date of Birth, SSN, Driver licence number will store under this table. There is One-To-Many relationship between Policy and Driver table.Vehicle_Driver: There is Many-To-Many relationship between Driver and Vehicle and this is the bridge table for Vehicle and Driver table.DriverAddress: This table holds the driver's mailing and garage address, that's why there is One-To-Many relationship between Driver and DriverAddress table.TrafficViolationCode: This table holds the Traffic Violation Code. There is Zero-To-Many relationship between this table and Driver_TrafficViolation_Record. Similarly there is Zero-To-Many relationship between Driver and Driver_TrafficViolation_Record. We have zero to many instead of One-To-Many because some drivers have never violated the traffic rule.Driver_TrafficViolation_Record: There is Many-To-Many relationship between Driver and TrafficViolationCode table and this table acts as bridge table between them.Bill: There could be more than one bill for a policy so we will have One-To-Many relationship between Policy and Bill table.PaymentDetail: There is One-To-Many relationship between the Bill and PaymentDetail table. Customer could make multiple payment transactions or one.Coverage: There are different type of coverage in the Auto Insurance like Liability, Collision, Comprehensive, Rental, Medical Payment, Towing, Mechanical Break Down. Some of them apply only to policy, some only to vehicle and some of them to both. IsPolciyCoverage and IsVehicleCoverage tell, is it applicable to Vehicle or Policy and if it is applicable to both, then these two bool columns will have true value. CoverageName column holds the title of coverage like "Property Damage Liability 100000/300000" or "Property Damage Liability 25000/50000" and CoverageGroup holds information about which coverage this record belong to like "Medical Payment" or "Bodily injury and Property Damage Liability Coverage" or "Uninsured Motorist Coverage".Policy_Coverage: There is Many-To-Many relationship between Coverage and Policy table and this is bridge table between themVehicle_Coverage: There is Many-To-Many relationship between Coverage and Vehicle table and this is bridge table between them.PolicyEditLog: This table keeps the log information if customer updates the policy information like remove vehicle or add driver, etc.
Figure 1 is the E-R Diagram of Policy Database
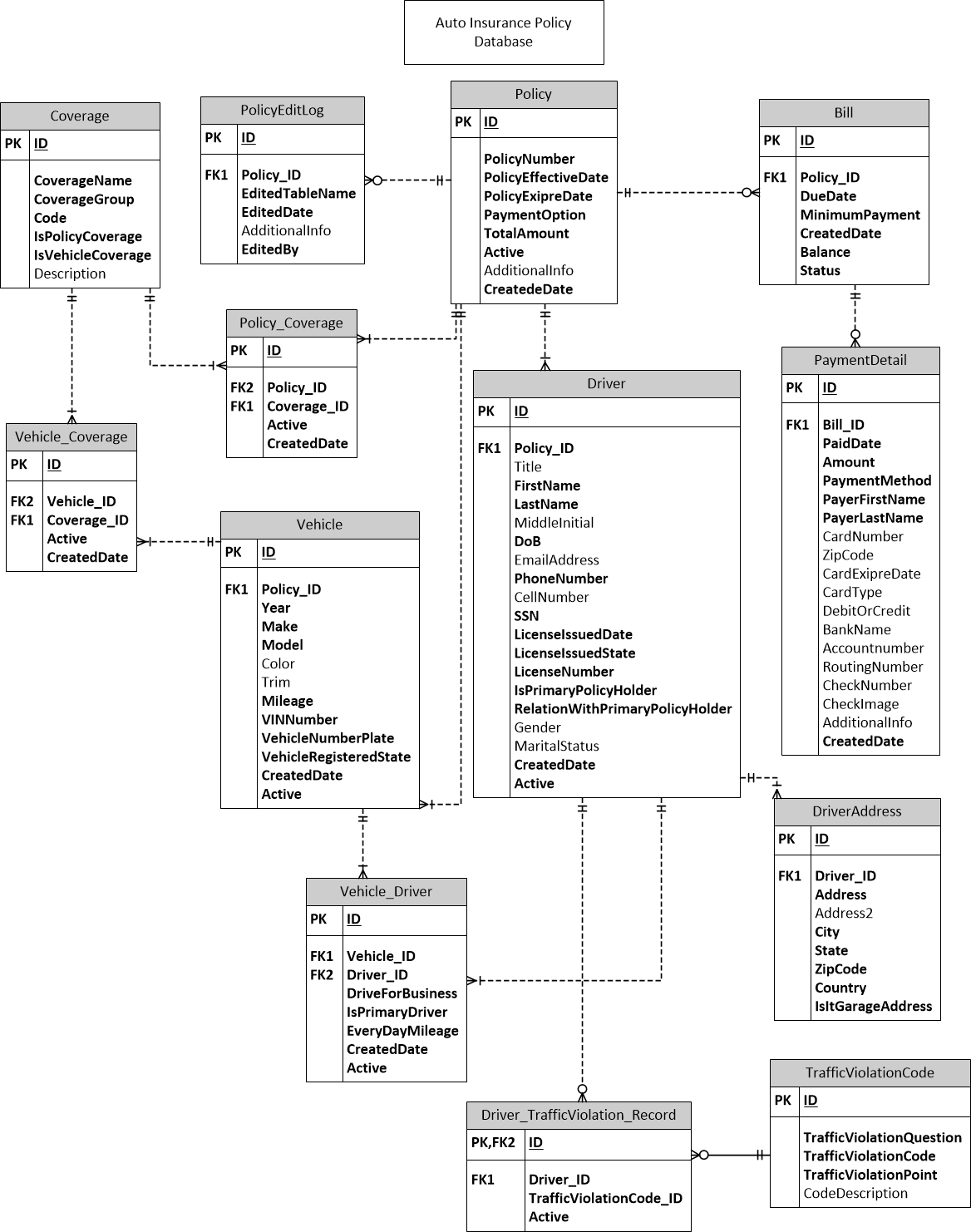
Figure 1
Figure 2 Below is the Data Dictionary of Above ER diagram

Figure 2
