Introduction
My MP3 player requires frequent battery replacement (AAA) to function. What is the effort in building a solar-powered charging station to reliably recharge AAA batteries?
Background
The Nobel Prize in Physics 1921 was awarded to Albert Einstein for his services to theoretical physics and discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect (1905). The photoelectric effect is the discovery that electrons are released when light shines on certain metals. The discovery led to the quantum revolution and influenced the concept of the wave-particle duality.
The solar cell (made of the common metalloid silicon) converts light energy into electricity by using the photovoltaic effect. When light contacts the surface, electrons absorb energy, become excited, jump to the conduction band and become free. Some reach the junction where they generate electromotive force and are converted into electric energy.
Solar cells:
- Absorb light (photons - solar or artificial)
- Form excitons or electron-hole pairs
- Separate charge carriers of opposite types
- Separate extraction of the charge carriers to an external circuit
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and an electron hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force.
Increased efficiency in a solar cell can be gained by focusing on:
- Reflectance efficiency (Light trapping, antireflection coating)
- Thermodynamic efficiency
- Charge carrier separation efficiency
- Conductive efficiency
When a solar cell is exposed to light, a current flows from the solar cell via a diode through the batteries and back to the solar cell. The charge will depend on the amount of light that reaches the solar cell. Allowing the current to pass in only one direction, the diode prevents the batteries from discharging while connected to the "charging station".
The Experiment
Parts
- Breadboard for prototyping electronics
- Solar cell (30mA)
- BAT85 Diode
- Battery holder for two (AAA 1.2V Rechargeable)
- Two discharged AAA Ni-MH 800mAh 1.2V rechargeable batteries
- Small box
- Rubber band
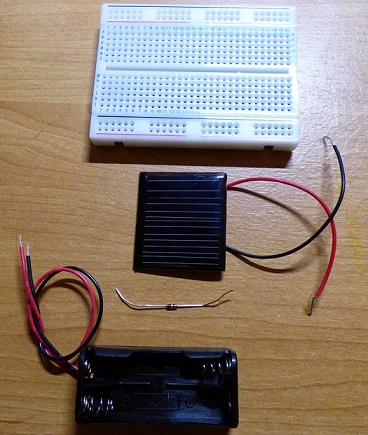
Steps
- Negative for battery holder plugged into D3.
- Positive for battery holder plugged into L8.
- Negative for solar cell plugged into E3.
- Positive for solar cell plugged into K3.
- Negative for BAT85 diode plugged into J8. Negative is the wire coming from the black part of the diode.
- Positive for BAT85 diode plugged into J3.

A warning label on each battery states: "CAUTION: BATTERY CAN EXPLODE OR CAUSE BURNS IF OVERCHARGED, DISASSEMBLED OR EXPOSED TO FIRE. DO NOT MIX WITH USED OR OTHER BATTERY CHEMISTRIES (ALKALINE, LITHIUM)." As an added precaution, the battery holder has been placed inside a small, metal box (not visible) strapped to the breadboard with a rubber band.
Results
The charging station was placed with the solar cell facing the sun for 4 hours. After facing the sun for 4 hours, the (previously discharged) battery registered a charge on the mp3 player's charge indicator and provided over an hour of playing power to the mp3 player.
Refinement
With the prototype returning positive results, the charging station is refined by removing the breadboard. The positive wire from the solar cell is connected to the BAT85 diode positive. The BAT85 diode negative is connected to the positive wire on the battery holder. The negative wire from the solar cell is connected to the negative wire on the battery holder.

With the circuit complete, double-sided tape and electrical tape is used to attach the circuit to a box. The solar cell is attached to the outside while the diode and battery holder is attached to the inside of the box.
Inside the Box

Completed
The solar-powered battery charging station is pictured with the mp3 player.

Conclusion
The level of effort to build the solar-powered AAA battery charging station is very low.
History
- 5th November, 2014: Initial version
- 6th December, 2014: Added updates
