Abstract
.NET is the new distributed computing platform developed by Microsoft and ASP.NET is its programming model for web development. I'm creating a Web Form with a DataGrid for data entry using C#. How can I make a DataGrid cell display a textbox for showing a list of products in all the rows. This solution will teach you how to use a MySQL database with ASP.NET. I have developed this sample with ASP.NET 1.1 using C# as the code-behind using MySQL 4.1. I think this will be a more useful article for beginners studying .NET. In this sample, I have taken the DataGrid control for demonstration. All the basic operations of the DataGrid are explained in this article.
Overview of the Solution
MySQL:
MySQL Server 4.0 laid the foundation for the new features implemented in MySQL 4.1, such as subqueries and Unicode support, which were desired by many of our customers. The server is available as a separate program for use in a client/server networked environment. It is also available as a library that can be embedded (linked) into standalone applications. Such applications can be used in isolation or in environments where no network is available. Clients can connect to a MySQL server using TCP/IP sockets on any platform. On Windows systems belonging the NT family (NT, 2000, XP, or 2003), clients can connect using named pipes. On UNIX systems, clients can connect using UNIX domain socket files.
In MySQL 4.1, we cannot write stored procedures, functions, or views. The following are sample SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE queries in MySQL.
SELECT column_names from table_name [WHERE ...conditions];
UPDATE table_name SET column_names = ‘’ WHERE ...conditions;
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE ...conditions;
ODBC:
The Microsoft Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) interface is a C programming language interface that makes it possible for applications to access data from a variety of database management systems. The ODBC interface permits maximum interoperability — an application can access data in diverse DBMSs through a single interface. Furthermore, that application will be independent of any DBMS from which it accesses data. Users of the application can add software components called drivers, which interface between an application and a specific DBMS. Applications that use ODBC are responsible for any cross-database functionality. For example, ODBC is not a heterogeneous join engine, nor is it a distributed transaction processor. However, because it is DBMS-independent, it can be used to build such cross-database tools.
The following will explain to you the architecture of ODBC:
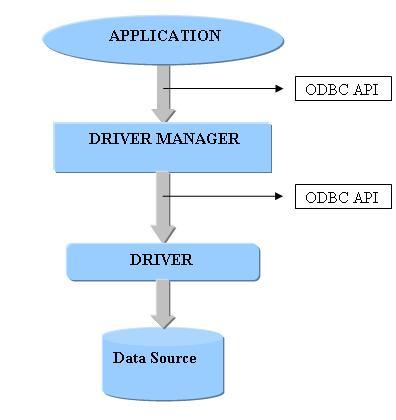
Namespace used for ODBC:
using System.Data.Odbc;
The System.Data.Odbc namespace is the .NET Framework Data Provider for ODBC.
The .NET Framework Data Provider for ODBC describes a collection of classes used to access an ODBC data source in the managed space. Using the OdbcDataAdapter class, you can fill a memory-resident DataSet, which you can use to query and update a data source.
Solution with Code
First, let us see how to connect ASP.NET with a MySQL database. The following code will explain how to connect with a MySQL 4.1 database:
private const string ConnStr =
"Driver={MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver};Server=localhost;" +
"Database=test;uid=root;pwd=;option=3";
private void BindDataGrid()
{
using(OdbcConnection con = new OdbcConnection(ConnStr))
using(OdbcCommand cmd =
new OdbcCommand("SELECT * FROM Sample", con))
{
con.Open();
DataGrid1.DataSource = cmd.ExecuteReader(
CommandBehavior.CloseConnection |
CommandBehavior.SingleResult);
DataGrid1.DataBind();
}
}
This snippet shows the code to bind data from a MySQL database to a DataGrid control. Each and every basic operation is written as a separate function. The following are the functions for the basic operations to be performed in the DataGrid:
private void InsertInfo()
{
if(CheckIsAddNameValid())
{
HtmlTable2.Visible = false;
using(OdbcConnection con = new OdbcConnection(ConnStr))
using(OdbcCommand cmd = new OdbcCommand("INSERT INTO sample" +
"(name, address) VALUES (?,?)", con))
{
cmd.Parameters.Add("@name", OdbcType.VarChar,
255).Value = TextBox3.Text.Trim();
cmd. Parameters.Add("@address", OdbcType.VarChar,
255).Value = TextBox4.Text.Trim();
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
BindDataGrid();
}
}
}
private void UpdateInfo(int id, string name, string address)
{
using(OdbcConnection con = new OdbcConnection(ConnStr))
using(OdbcCommand cmd = new OdbcCommand("UPDATE sample " +
"SET name = ?, address = ? WHERE ID = ?", con))
{
cmd.Parameters.Add("@name", OdbcType.VarChar, 255).Value = name;
cmd.Parameters.Add("@address",
OdbcType.VarChar, 255).Value = address;
cmd.Parameters.Add("@ID", OdbcType.Int).Value = id;
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
private void DeleteInfo(int id)
{
using(OdbcConnection con = new OdbcConnection(ConnStr))
using(OdbcCommand cmd = new OdbcCommand("DELETE " +
"FROM sample WHERE ID = ?", con))
{
cmd.Parameters.Add("@ID", OdbcType.Int).Value = id;
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
The table design for this sample:
CREATE TABLE sample (
id int AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL,
name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
address varchar(45) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
)
GO
Details about the DataGrid:
The DataGrid control displays tabular data and optionally supports selecting, sorting, paging, and editing of data. By default, a DataGrid generates a BoundColumn for each field in the data source (AutoGenerateColumns=true). Each field in the data is rendered in a separate column, in the order it occurs in the data. Field names appear in the grid's column headers, and values are rendered in text labels. A default format is applied to non-string values.
private void DataGrid1_UpdateCommand(object source,
System.Web.UI.WebControls.DataGridCommandEventArgs e)
{
try
{
int cUsrID ;
string strName;
string strAddress;
Literal ltID;
TextBox txtTempName;
TextBox txtTempAddress;
ltID = (System.Web.UI.WebControls.Literal )
e.Item.Cells[0].FindControl("Label");
cUsrID = Convert.ToInt32 (ltID.Text);
txtTempName = (System.Web.UI.WebControls.TextBox)
e.Item.Cells[1].FindControl("TextBox1");
strName = txtTempName.Text;
txtTempAddress = (System.Web.UI.WebControls.TextBox)
e.Item.Cells[2].FindControl("Textbox2");
strAddress = txtTempAddress.Text;
UpdateInfo(cUsrID, strName, strAddress);
DataGrid1.EditItemIndex = -1;
BindDataGrid();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
}
}
Conclusion
After reading this article, you will have a basic knowledge about ODBC connections, DataGrids and most importantly about MySQL. I hope this article will be more useful for budding programmers.

Reference
