In this article, the following words are mentioned to refer to a specific meaning unless mentioned otherwise.
- Control: The control you wish to print.
- Component: The
PrintControl component this article is talking about.
Note:
This component requires .NET Framework 2.0 or later.
Well, I think the title is clear. It’s all about printing. While I was developing some enterprise applications before, I used many lists in my application, and I needed to print them all, but they were on different forms, so in each form, I had to make a PrintDocument component and add a PrintPage event handler to draw its contents manually each time, spending hours to calculate each table’s height and width, then fitting this into the size of the page. Well, I actually didn’t do it. Instead, I thought of a component that will do this for me automatically, and here we are. The ControlPrint component will do the job.
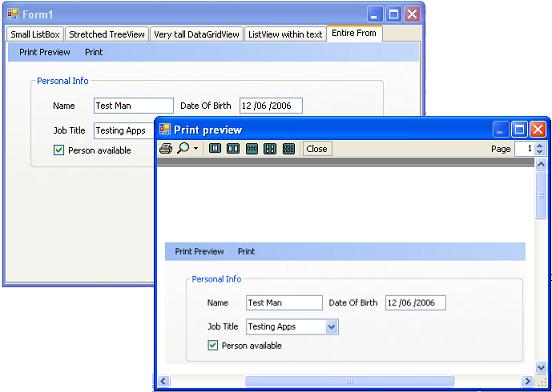
Also, I had some information input forms for inputting name, age, gender, address, etc. I wanted to print these information too, but I had to customize another printing form by drawing it in printing!! The ControlPrint component will also get it on paper. See the picture on top of this article.
I inherited my component from the PrintDocument component, and did all the printing work in the PrintPage event handler. So to use it, follow these steps:
- Make an instance of the component.
- Supply it with your control, you will know how shortly.
- Call the
Print() method, or use it with a PrintPreviewDialog.
You can deal with it just like any PrintDocument component, using this code:
PrintControl m_print = new PrintControl();
m_print.SetControl(MyControl);
prinPreviewDialog1.Document = (PrintDocument)m_print;
The component’s main idea is drawing the control you wish to print, whether it is a ListView, ListBox, TreeView, or whatever, to the printer as it’s drawn on the screen. Something like WYSIWYG, or What You See Is What You Get! So, the main steps here are:
- Obtaining the control.
- Calculating the best size to display all the elements inside the control. There is no scrolling on the paper, is there?
- Drawing the control on the page as it would on the screen.
Of course, it’s not that simple, but we will walk through it.
The ControlPrint component supports any control, including User Controls, that are inherited from the Control class. It actually calls the GetPreferredSize() method of the control to obtain the best size of the control to display all its elements. Some controls don’t support that method and return wrong values of the preferred size. That’s why I added the CalculateSize() and ApplyBestSize() methods in my component to add more special support to these controls. Currently, the specially supported controls are:
ListViews
TreeViews
- Forms and other controls that contain more controls in them, like
TabPages, GroupBoxes, etc…
Other controls should work fine using the ordinary GetPreferredSize() method, including DataGridViews, ListBoxes, etc. Also, forms usually work fine with GetPreferredSize(), and seldom need to use the CalculateSize() method
The component prints it to a bitmap using the Control.DrawToBitmap() method, and prints it.
You can also get that bitmap using the PrintControl.GetBitmap() method, and use it the way you like, like save it to a file, or print it inside other text, etc.
So after all that, the steps for printing are:
- Get the old values of the control’s size, dock status, and parent.
- Set the docking to
none, and all the parents' sizes to larger than the desired size, you will know why shortly.
- Change the control’s size to the preferred size that will remove the need to scroll.
- Draw it to a bitmap.
- Restore the control’s status, including the parents' statuses.
- Print it, or return the bitmap, according to your choice.
I had to remove the docking status because it forbids resizing the control. Also, the parents had to be resized to fit the control’s new size. Only then drawing it to a bitmap would be successful. Refer to the interesting points for details.
- If you make your own control, and would like to print it with
PrintControl component, override the GetPreferredSize() method, and return the best size that fits your control according to its content, if the Control.GetPreferredSize() method returns wrong values for your control.
- You can print the control in the size you specify, by calling the appropriate size specifying methods in my component (see below). This may help when there are errors in calculating the controls size for some reason or the other, or if you prefer this for your own reasons.
- When printing a
TreeView, only the expanded nodes will be printed, those that can be visible by scrolling to them. Other nodes that are hidden will not be printed. So if you want to make sure that you print all nodes in the TreeView, use the TreeView.ExpandAll() method.
- When you change the visual style of your control, it will also be printed as it is on screen, nice, isn’t it?
- Visual styles may be beautiful, but they will consume more ink and time in printing. So think about it.
- When printing forms, you might want to remove the background colors or images to make the text more clear.
- You can stretch the printed bitmap to fit exactly in one page by setting the
StretchControl property to true. But be careful as this disrupts the width/height ratio and may distort the image.
I think now would be an appropriate time to talk about the component’s members.
Constructors
ControlPrint()
The default constructor that initializes the component with no actual values.
ControlPrint(Control print)
Initialize the component with the selected control.
ControlPrint(Control print, bool Str)
Initialize the component with the selected control, specifying whether to stretch or not.
ControlPrint(Control print, int Width, int Height)
Initialize the component with the selected control, specifying the specific width and height.
Properties
StretchControl
Set true to stretch the control to fill a single printed page.
PrintWidth
The width of the control to print. You can change this value if the automatically calculated width does not fit all the elements of the control.
PrintHeight
The height of the control to print. You can change this value if the automatically calculated height does not fit all the elements of the control.
ReapeatArea
The area to be reprinted between pages if there is more than one page to be printed, to prevent data loss.
Methods
void SetControl(Control print)
Set the control to be printed.
void SetControl(Control print, int Width, int Height)
Set the control with a specified height and width.
Bitmap GetBitmap()
Draw the control fully to a bitmap and return it.
Size CalculateSize()
Return the best size that fits the control.
void ApplyBestSize()
Apply the best size that fits the control.
These are some points that I saw interesting as it stood in front of me while developing the component.
- I had to resize the control in the first place because otherwise it would only print the visible part and it would print the scrollbars also. I think that won’t be much of a help.
- Trying to resize the control while it is docked was a failure so I had to undock it first.
- Also, the parents of the control had to be larger than it. Otherwise, the control would only draw the visible part. I first tried to make the parent to null and then restore it, but that didn’t work with forms that contained controls. The text fields’ values were lost, I don’t know why!! Any ideas? So I decided to resize the parents too and then restore them.
- When the control's length is longer than the page’s length, there will be more than one page to print. So I store the printed length in a private field, and when there will be more than one page, I put the area to be printed on the current page in another bitmap, then print the second one. Refer to the
PrintPage event handler in the code.
- Also, when printing long tables, lists or
DataGrids over more than one page, it’s quite likely that a row may be separated on two pages making its data unreadable. So as a simple solution, I added a RepeatArea property, which is an area to be reprinted on the next page. So if half of the row is printed on the end of a page, it will be reprinted fully on the next. The RepeatArea is modifiable. If you have brighter ideas to solve this problem, I’d be happy to add them to the component.
- If you revise the source code, you will notice that I used a recursive method to access all the nodes of a
TreeView. You call the method from a foreach loop, and apply another foreach loop inside the method to recall itself. My method is named EnumNodes.
- I used the
GetType().AssemblyQualifiedName to identify the control’s type. Also, this will identify controls inherited from it as it will also contain its base control name. For example:
if (m_ctrl.GetType().AssemblyQualifiedName.IndexOf("TreeView") >= 0)
The if statement will be true if the control is or inherited from the TreeView control.
- When trying to calculate the size of special controls, currently
TreeViews, ListViews, and Forms, I enumerate their elements, Nodes, Items, and Controls respectively, get their bounds, and get the maximum Bounds.Right and Bounds.Bottom as the desired width and height, after assigning a margin, of course.
I hope that I explained how to use the component well, and that it will help you. I wanted to go through the code in the article, but I believe it’s a bit large ad unnecessary. I added comments to the code, maybe it’ll help. If anybody has any ideas, suggestions, or has discovered any bugs, I’ll be eagerly waiting for your posts.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article.
