Introduction
When I ship a software product for the .NET environment, I would like to know the versions for all the files. From this information, I'll know what's happening if the application gets a crash. Besides that, the file version information can help me to update files properly if I would like to update the application. In this article, I'll show how to get file version information, using C#.
Getting Started
To get version information from a file, we can get it from its assembly. For example, I would like to get the file version from my console application.
Here is the console application code:
1 using System;
2 using System.Reflection;
3
4 namespace ConsoleVersionApp
5 {
6 class Program
7 {
8 static void Main(string[] args)
9 {
10 Assembly asm = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();
11 Console.WriteLine("File Version:");
12 Console.WriteLine(asm.FullName);
13
14 Console.WriteLine("References :");
15 AssemblyName[] asmNames = asm.GetReferencedAssemblies();
16 foreach (AssemblyName nm in asmNames)
17 {
18 Console.WriteLine(nm.FullName);
19 }
20
21 Console.ReadLine();
22 }
23 }
24 }
From this code, I run the console application that looks as in the picture below:

File Version Wrapper
Now, I would to wrap my file version code. Firstly, I create the AssembyInformation object to keep the file version information. The AssembyInformation class defines a value object. Look at the class diagram below:

The wrapper object I created to get the file version information is PeVersion. From the PeVersion object, we will get information about file version and the referenced file information. The PeVersion object has two public methods, GetVersion(string fileName) and GetVersion(Assembly asm).
77 public bool GetVersion(string fileName)
78 {
79 Assembly asm = null;
80 try
81 {
82 asm = Assembly.LoadFrom(fileName);
83 }
84 catch (Exception err)
85 {
86 this._errMsg = err.Message;
87 return false;
88 }
89 if (asm != null)
90 {
91 this._info = new AssemblyInformation();
92 this._info.Name = asm.GetName().Name;
93 this._info.Version = asm.GetName().Version.ToString();
94 this._info.FullName = asm.GetName().ToString();
95 }
96 else
97 {
98 this._errMsg = "Invalid assembly";
99 return false;
100 }
101
102 return GetReferenceAssembly(asm);
103 }
104 public bool GetVersion(Assembly asm)
105 {
106 if (asm != null)
107 {
108 this._info = new AssemblyInformation();
109 this._info.Name = asm.GetName().Name;
110 this._info.Version = asm.GetName().Version.ToString();
111 this._info.FullName = asm.GetName().ToString();
112 }
113 else
114 {
115 this._errMsg = "Invalid assembly";
116 return false;
117 }
118
119 return GetReferenceAssembly(asm);
120 }
GetReferenceAssembly() is a private method that is defined as below:
46 private bool GetReferenceAssembly(Assembly asm)
47 {
48 try
49 {
50 AssemblyName[] list = asm.GetReferencedAssemblies();
51 if (list.Length > 0)
52 {
53 AssemblyInformation info = null;
54 _lstReferences = new List<ASSEMBLYINFORMATION>();
55 for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++)
56 {
57 info = new AssemblyInformation();
58 info.Name = list[i].Name;
59 info.Version = list[i].Version.ToString();
60 info.FullName = list[i].ToString();
61
62 this._lstReferences.Add(info);
63 }
64 }
65 }
66 catch (Exception err)
67 {
68 this._errMsg = err.Message;
69 return false;
70 }
71
72 return true;
73 }
I has created the PeVersion and AssemblyInformation objects in a library project, i.e., Pe.Framework.Version. You can download the code from the link above.
Usage
After creating the wrapper class (PeVersion), I will show you how to use this wrapper object. As you know, the PeVersion object can receive input parameters, i.e., file name with full location and the assembly object. Here is a simple usage of the PeVersion object:
1 using System;
2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3
4 using Pe.Framework.Version;
5 namespace PeVersionTestingApp
6 {
7 class Program
8 {
9 static void Main(string[] args)
10 {
11 string file = @"c:\VersionTestApp.exe";
12 PeVersion ver = new PeVersion();
13 if (ver.GetVersion(file))
14 {
15 AssemblyInformation obj = ver.CurrentAssemblyInfo;
16 Console.WriteLine("File Info:");
17 Console.WriteLine("Name : {0}", obj.Name);
18 Console.WriteLine("Version : {0}", obj.Version);
19 Console.WriteLine("Full Name : {0}", obj.FullName);
20 Console.WriteLine("");
21
22 List<ASSEMBLYINFORMATION> list = ver.ReferenceAssembly;
23 if (list.Count > 0)
24 {
25 Console.WriteLine("References Info:");
26 for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
27 {
28 AssemblyInformation info = list[i];
29 Console.WriteLine("Name : {0}", info.Name);
30 Console.WriteLine("Version : {0}", info.Version);
31 Console.WriteLine("Full Name : {0}", info.FullName);
32 Console.WriteLine("-------------------------------");
33 }
34 }
35 }
36
37 Console.ReadLine();
38 }
39 }
40 }
If you want to get the version with the Assembly object as a passing parameter on the PeVersion object, you can use this code:
1 System.Reflection.Assembly asm =
System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();
2 PeVersion ver = new PeVersion();
3 if (ver.GetVersion(asm))
4 {
5
6
7
8 }
File Version Tester Application
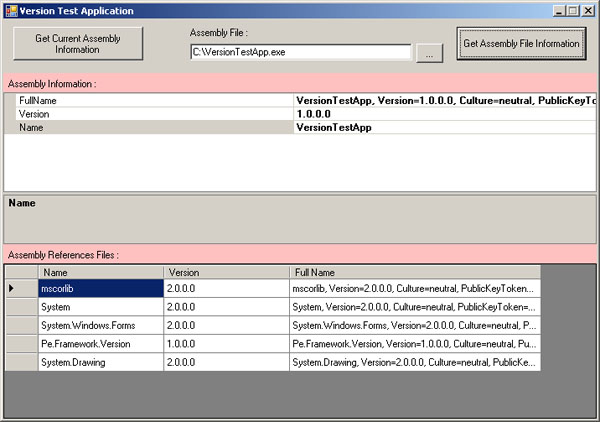
The file version tester application is a small application based on the desktop application to check the version and reference files from a file. Using this application, you just pass a file (DLL or EXE Managed) into the application, then the application will check the file version and the references files information. The GUI of this application can looks as below:

You can download this application with the source code above.
Running On Visual Studio
If you have download this source code and run it via Visual Studio, you will get a warning if you put the executable file (*.exe) as the passing parameter into the PeVersion object for checking version information. The warning message looks as below:

To suppress this message, you just uncheck "Warn if no user code on launch" on the debugging options of the IDE of Visual Studio. Look at this picture below:

This warning only shows if you run the application via Visual Studio.
