Introduction
As you all know Microsoft has launched .NET 3.0 with four very powerful foundations.
- WCF (Windows Communication Foundation)
- WPF (Windows Presentation Foundation)
- WF (Windows Workflow Foundation)
- Windows Cardspace
There is already a lot of material available on what is WCF, WPF, WF and cardspace. I am not going in details of these technologies. While exploring WCF, I came across many interesting things which are newly introduced. In my previous chat application using remoting, I was using an interface that is distributed across the client and server. There was an abstract class that was implemented at the client side. When the server wants to send a message to the client, the server should have the list of clients and something which is common in all clients. An interface implementation was the best way to achieve this. There was serialization, channels, protocols and much more in .NET remoting.
In WCF things are made pretty simple. The first and the most important thing is that you can have as many endpoints as you want depending upon the requirements of your application. If you want your application to be used by a .NET client, Java client then you can go for TCP binding and basic HTTP binding. What you need to do is add those many end points in the configuration file of the server and start the server. It is the responsibility of WCF to give you performance benefits of communication with different clients. The basic communication protocol for WCF is SOAP. But when you establish communication between WCF service and WCF client, the foundation uses binary over SOAP to give you optimum performance. I will say that you can have WCF service with everything under one roof. Currently I am also into the process of exploring more about WCF and specifically the bindings. There are some features that are required but I do not have any idea about how to get them from netPeerTcpBinding and PeerResolvers.
About the application
The simple WCF chat application I have written, uses netTcpPeerBinding. Using this binding, it is very easy to create a simple intranet chat application that can be used over intranet. You do not have to write much of the code and you do not even have to write
any special interfaces, classes at server side. Everything is encapsulated in:
- System.ServiceModel;
- System.ServiceModel.Channels;
- System.ServiceModel.PeerResolvers;
Chat Server
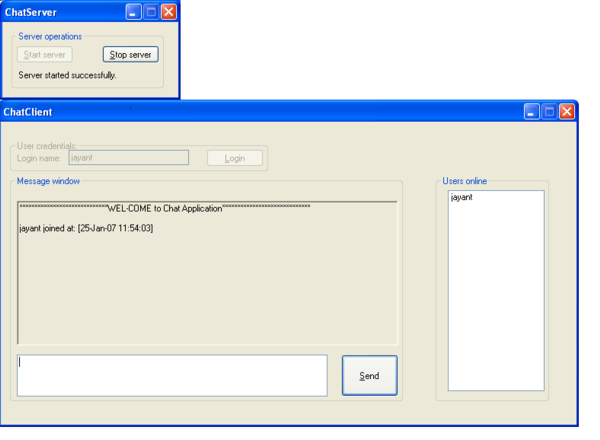
A very simple chat server with merely four lines of code. As said earlier, you do not need to write any special code. Hence the server application looks like this.
<CODE>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Channels;
using System.ServiceModel.PeerResolvers;
namespace ChatServer
{
public partial class ChatServer : Form
{
private CustomPeerResolverService cprs;
private ServiceHost host;
public ChatServer()
{
InitializeComponent();
btnStop.Enabled = false;
}
private void btnStart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
cprs = new CustomPeerResolverService();
cprs.RefreshInterval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5);
host = new ServiceHost(cprs);
cprs.ControlShape = true;
cprs.Open();
host.Open(TimeSpan.FromDays(1000000));
lblMessage.Text = "Server started successfully.";
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
}
finally
{
btnStart.Enabled = false;
btnStop.Enabled = true;
}
}
private void btnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
cprs.Close();
host.Close();
lblMessage.Text = "Server stopped successfully.";
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
}
finally
{
btnStart.Enabled = true;
btnStop.Enabled = false;
}
}
}
}
The code is self explanatory. You create an object of CustomPeerResolverService and pass that object as an input parameter to the ServiceHost class. Open peer resolver service and host and you are done. No new classes and no end points. Surprising right? But wait, I have to show you the config file. The config file plays the most important role of specifying the required details.
<CODE>
?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?
configuration
system.serviceModel
services
service name="System.ServiceModel.PeerResolvers.
CustomPeerResolverService"
host
baseAddresses
add baseAddress="net.tcp://10.34.34.241/ChatServer"/
baseAddresses
host
endpoint address="net.tcp://10.34.34.241/ChatServer"
binding="netTcpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="TcpConfig"
contract="System.ServiceModel.PeerResolvers.
IPeerResolverContract"
endpoint
service
services
bindings
netTcpBinding
binding name="TcpConfig"
security mode="None"/security
binding
netTcpBinding
bindings
system.serviceModel
configuration
I have removed '<' and '>' because I was not able to show config files directly. If you know how to show then please let me know. Config file is very simple. We are using .NET predefined service in this case System.ServiceModel.PeerResolvers.CustomPeerResolverService. Give the base address for hosting the resolver service as shown. The important thing about the end point is that it uses System.ServiceModel.PeerResolvers.IPeerResolverContract contract which is already available in the foundation. As said earlier, we are using TCP end point for the communication. Hence we specify the endpoint with TCP binding and we configure it with security mode as none. That's it and you are done. Just start the server and you are ready for your chat client.
Chat Client
As compared to the Chat server, the client becomes little bit complicated. It does everything on its own. As said earlier, we need something common that the server will use to communicate with clients and that can be established using interfaces.
Same concepts apply here also and we have client code that looks like this:
<CODE>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Channels;
namespace ChatClient
{
[ServiceContract(CallbackContract = typeof(IChatService))]
public interface IChatService
{
[OperationContract(IsOneWay = true)]
void Join(string memberName);
[OperationContract(IsOneWay = true)]
void Leave(string memberName);
[OperationContract(IsOneWay = true)]
void SendMessage(string memberName, string message);
}
public interface IChatChannel : IChatService, IClientChannel
{
}
public partial class ChatClient : Form, IChatService
{
private delegate void UserJoined(string name);
private delegate void UserSendMessage(string name, string message);
private delegate void UserLeft(string name);
private static event UserJoined NewJoin;
private static event UserSendMessage MessageSent;
private static event UserLeft RemoveUser;
private string userName;
private IChatChannel channel;
private DuplexChannelFactory<ichatchannel /> factory;
public ChatClient()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.AcceptButton = btnLogin;
}
public ChatClient(string userName)
{
this.userName = userName;
}
private void btnLogin_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtUserName.Text.Trim()))
{
try
{
NewJoin += new UserJoined(ChatClient_NewJoin);
MessageSent += new UserSendMessage
(ChatClient_MessageSent);
RemoveUser += new UserLeft(ChatClient_RemoveUser);
channel = null;
this.userName = txtUserName.Text.Trim();
InstanceContext context = new InstanceContext(
new ChatClient(txtUserName.Text.Trim()));
factory =
new DuplexChannelFactory<ichatchannel />(context, "ChatEndPoint");
channel = factory.CreateChannel();
channel.Open();
channel.Join(this.userName);
grpMessageWindow.Enabled = true;
grpUserList.Enabled = true;
grpUserCredentials.Enabled = false;
this.AcceptButton = btnSend;
rtbMessages.AppendText
("****WEL-COME to Chat Application*****\r\n");
txtSendMessage.Select();
txtSendMessage.Focus();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
}
}
}
void ChatClient_RemoveUser(string name)
{
try
{
rtbMessages.AppendText("\r\n");
rtbMessages.AppendText(name + " left at " +
DateTime.Now.ToString());
lstUsers.Items.Remove(name);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
}
void ChatClient_MessageSent(string name, string message)
{
if (!lstUsers.Items.Contains(name))
{
lstUsers.Items.Add(name);
}
rtbMessages.AppendText("\r\n");
rtbMessages.AppendText(name + " says: " + message);
}
void ChatClient_NewJoin(string name)
{
rtbMessages.AppendText("\r\n");
rtbMessages.AppendText(name + " joined at:
[" + DateTime.Now.ToString() + "]");
lstUsers.Items.Add(name);
}
#region IChatService Members
public void Join(string memberName)
{
if (NewJoin != null)
{
NewJoin(memberName);
}
}
public new void Leave(string memberName)
{
if (RemoveUser != null)
{
RemoveUser(memberName);
}
}
public void SendMessage(string memberName, string message)
{
if (MessageSent != null)
{
MessageSent(memberName, message);
}
}
#endregion
private void btnSend_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
channel.SendMessage(this.userName, txtSendMessage.Text.Trim());
txtSendMessage.Clear();
txtSendMessage.Select();
txtSendMessage.Focus();
}
private void ChatClient_FormClosing(object sender,
FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (channel != null)
{
channel.Leave(this.userName);
channel.Close();
}
if (factory != null)
{
factory.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
}
}
}
}
Again the client is also very simple. The important thing is the config file. We will see the details.
<CODE>
?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?
configuration
system.serviceModel
client
endpoint name="ChatEndPoint" address="net.p2p://chatMesh/ChatServer"
binding="netPeerTcpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="PeerTcpConfig"
contract="ChatClient.IChatService"endpoint
client
bindings
netPeerTcpBinding
binding name="PeerTcpConfig" port="0"
security mode="None"security
resolver mode="Custom"
custom address="net.tcp://10.34.34.241/ChatServer"
binding="netTcpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="TcpConfig"custom
resolver
binding
netPeerTcpBinding
netTcpBinding
binding name="TcpConfig"
security mode="None"security
binding
netTcpBinding
bindings
system.serviceModel
configuration
Here in the config file we have endpoint names "ChatEndpoint", which point to a chat mesh and use netPeerTcpBinding. When we configure the binding, we use the custom resolver mode and give the custom TCP address where our actual server is running.
Giving port number as zero will automatically detect the free port for communication. We use security mode as none. Thus using this configuration we can start the clients and send a message across the intranet.
Limitations
I did not find a way to send back a list of online users to the new joined user. I'll appreciate the solution. Also let me know if you find anything more interesting. I am also into WCF exploring stage and this might not be the perfect chat application.
Any suggestions, corrections are welcome.
Reference
I have referred to the Microsoft Technology Samples for getting familiar with WCF and working of different bindings.
Conclusion
We can conclude that WCF provides us a very simple but very powerful way of establishing communication between diverse systems, maintaining the performance benefits with similar OS.
