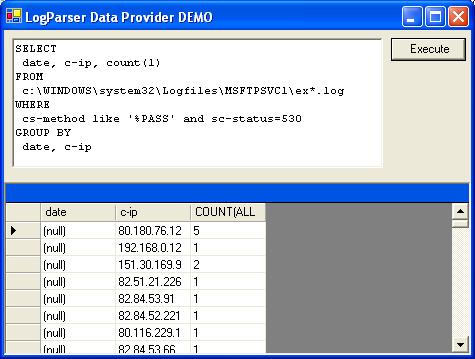
Introduction
LogParser DataProvider is an ADO.NET data provider that wraps the SQL functionality of the LogParser Microsoft tool. So, you can use parsed log data with dataset and datatable using binding features of the .NET Framework.
Background
Log parser is a powerful, versatile tool that provides universal query access to text-based data such as log files, XML files and CSV files, as well as key data sources on the Windows® operating system such as the Event Log, the Registry, the file system, and Active Directory®. You can download it from the official Microsoft site here.
Using the Code
To use LogParser DataProvider, first you must install Microsoft LogParser tool. The project is a simple custom DataProvider implementation that uses LogParser COM interfaces. I have followed the instructions I found in the MSDN article written by Bob Beauchemin "ADO.NET: Building a Custom Data Provider for Use with the .NET Data Access Framework". The project consist of the implementation of four classes:
ConnectionCommandDataReaderDataAdapter
This article is shipped with a demo project that use LogParser DataProvider. In the demo form, the user can write and execute a SQL statement and view the results in a dataGrid.
Points of Interest
Making a custom Data Provider, the "Connection" is a required class even if you don't actually connect to a data source. Other classes, such as the Command class, require a Connection class for basic functionality. DataAdapters will call the Open and Close methods on the Connection class in the process of filling a DataTable in the DataSet. In my implementation, this class is empty; it's only a strongly typed class to use with the others.
- The "
Command" class serves at least two purposes. Commands, in the command language of your choice, are supported to directly effect the data store. For LogParser, only "SQL SELECT" command is supported. - The "
DataAdapter" class fills the DataSet with results from the Command class. - The "
DataReader" class is the main class where I've made the most customization. It's used for processing results from a Command. Its methods allow the consumer to iterate, in a forward-only manner, through rows of one or more sets of results. It also provides methods to get the data in the columns of those rows into variables of .NET types. The execute method of the LogParserDataReader class executes the SQL statement using ILogQuery interface of the LogParser COM wrapper, and initializes some internal array with name, type and size of the columns returned by the query.
internal void Execute(String command)
{
_lp = new LogQueryClassClass();
rs = _lp.Execute(command, null);
_RecordsAffected = -1;
_fieldCount = rs.getColumnCount();
_cols.Clear();
_names.Clear();
_types.Clear();
_sizes.Clear();
for (int i=0;i<_fieldCount;i++)
{
_cols.Add(null);
_names.Add(rs.getColumnName(i));
Type t = null;
Int32 s = 0;
switch (rs.getColumnType(i))
{
case 1:
t = typeof(int);
break;
case 2:
t = typeof(double);
break;
case 3:
t = typeof(string);
s = 1024;
break;
case 4:
t = typeof(DateTime);
break;
}
_types.Add(t);
_sizes.Add(s);
}
_CurrentRow = -1;
_ie = new LogRecordsetEnumerator(rs);
_isClosed = false;
}
The method GetSchemaTable() is used to retrieve information about the columns of the result DataTable. The most significant attributes are ColumnName, DataType, ColumnSize and ColumnOrdinal.
public DataTable GetSchemaTable()
{
Debug.WriteLine("LogParserDataReader.GetSchemaTable", "LogParserDataReader");
DataTable tab = new DataTable();
tab.Columns.Add("ColumnName", typeof(System.String));
tab.Columns.Add("ColumnSize", typeof(Int32));
tab.Columns.Add("ColumnOrdinal", typeof(Int32));
tab.Columns.Add("NumericPrecision", typeof(Int16));
tab.Columns.Add("NumericScale", typeof(Int16));
tab.Columns.Add("DataType", typeof(System.Type));
tab.Columns.Add("AllowDBNull", typeof(bool));
tab.Columns.Add("IsReadOnly", typeof(bool));
tab.Columns.Add("IsUnique", typeof(bool));
tab.Columns.Add("IsRowVersion", typeof(bool));
tab.Columns.Add("IsKey", typeof(bool));
tab.Columns.Add("IsAutoIncrement", typeof(bool));
tab.Columns.Add("IsLong", typeof(bool));
for (int i=0;i < _fieldCount;i++)
{
DataRow r = tab.NewRow();
r["ColumnName"] = _names[i];
r["ColumnSize"] = _sizes[i];
r["ColumnOrdinal"] = i;
r["NumericPrecision"] = 0;
r["NumericScale"] = 0;
r["DataType"] = _types[i];
r["AllowDBNull"] = false;
r["IsReadOnly"] = true;
r["IsUnique"] = false;
r["IsRowVersion"] = false;
r["IsKey"] = false;
r["IsAutoIncrement"] = false;
r["IsLong"] = false;
tab.Rows.Add(r);
}
return tab;
}
The other interesting method is the Read() function of the LogParserProvDataReader class. It is used to read the current row of the reader but it is also called internally by base class DBDataAdapter to fill a Dataset or a DataTable.
public bool Read()
{
Debug.WriteLine("LogParserDataReader.Read", "LogParserDataReader");
if (_ie != null)
{
bool notEOF = _ie.MoveNext();
if (notEOF == true)
{
_CurrentRow++;
ILogRecord lr = (ILogRecord)_ie.Current;
for (int i=0;i<_fieldCount;i++)
{
_cols[i] = lr.getValue(i);
}
}
return notEOF;
}
return false;
}
About the Demo Project
The demo project is a Windows Form written in VB.NET with a DataGrid binded runtime to an ADO.NET Dataset.
Imports Data.LogParser
Public Class Form1
Inherits System.Windows.Forms.Form
Private c As LogParserConnection
Public Sub New()
MyBase.New()
InitializeComponent()
Initialize()
End Sub
#Region " Windows Form Designer generated code "...
Private Sub Initialize()
c = New LogParserConnection
c.Open()
End Sub
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim sql As String = Me.TextBox1.Text
If sql <> "" Then
Try
Dim da As LogParserDataAdapter = New LogParserDataAdapter(sql, c)
Dim dt As DataTable
dt = New DataTable
da.Fill(dt)
Me.DataGrid1.DataSource = dt
Me.DataGrid1.Refresh()
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message & vbCrLf & ex.StackTrace)
End Try
End If
End Sub
End Class
Below there's a useful query to check users access failure (from Microsoft sample query):
SELECT
COUNT(EventID) AS TotalLogonFailures,
TO_LOWERCASE(EXTRACT_TOKEN(Strings,0,'|')) AS User,
TO_LOWERCASE(EXTRACT_TOKEN(Strings,1,'|')) AS Domain,
TO_LOWERCASE(EXTRACT_TOKEN(Strings,5,'|')) AS WorkStation,
CASE TO_INT(EXTRACT_TOKEN(Strings,2,'|'))
WHEN 2 THEN 'Interactive -
Intended for users who will be interactively using the machine,
such as a user being logged on by a terminal server,
remote shell, or similar process.'
WHEN 3 THEN 'Network - Intended for high performance servers
to authenticate clear text passwords.
LogonUser does not cache credentials for this logon type.'
WHEN 4 THEN 'Batch - Intended for batch servers,
where processes may be executing on behalf
of a user without their direct intervention;
or for higher performance servers that process many
clear-text authentication attempts at a time,
such as mail or web servers. LogonUser does not cache
credentials for this logon type.'
WHEN 5 THEN 'Service - Indicates a service-type logon.
The account provided must have the
service privilege enabled.'
WHEN 6 THEN 'Proxy - Indicates a proxy-type logon.'
WHEN 7 THEN 'Unlock - This logon type is intended for GINA DLLs
logging on users who will be interactively using the machine.
This logon type allows a unique audit record to be generated that
shows when the workstation was unlocked.'
WHEN 8 THEN 'NetworkCleartext - Windows 2000; Windows XP and
Windows Server 2003 family:
Preserves the name and password in the authentication packages,
allowing the server to make connections to
other network servers while impersonating the client.
This allows a server to accept
clear text credentials from a client, call LogonUser,
verify that the user can access the system
across the network, and still communicate with other servers.'
WHEN 9 THEN 'NewCredentials - Windows 2000;
Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 family:
Allows the caller to clone its current token and
specify new credentials for outbound connections.
The new logon session has the same local identity,
but uses different credentials for other
network connections.'
WHEN 10 THEN 'RemoteInteractive -
Terminal Server session that is both remote and interactive.'
WHEN 11 THEN 'CachedInteractive -
Attempt cached credentials without accessing the network.'
WHEN 12 THEN 'CachedRemoteInteractive -
Same as RemoteInteractive. This is used for internal auditing.'
WHEN 13 THEN 'CachedUnlock - Workstation logon'
ELSE EXTRACT_TOKEN(Strings,2,'|')
END AS Type
INTO DATAGRID
FROM \\%machine%\security
WHERE EventID IN (529)
GROUP BY User,Domain,WorkStation,Type
ORDER BY TotalLogonFailures DESC
Enhancement
Using a data provider to extract programmatically security audit data can be useful to create automatic audit process and in conjunction with ADSI functions can become a powerful risk managing tool.
History
- 11th May, 2007: Initial post
