Introduction
AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) is not a technology, but a technique that uses a number of technologies:
- HTML and CSS for marking up and styling information.
- The Document Object Model that is accessed with client–side scripting, mainly ECMA script implementation such as JavaScript and JScript, to show and interact with the information presented.
- The XML is generally used as a format of transferring data between client and server. However, it is not obligatory; even plain text can be used as data format. In certain situations, preformatted HTML, JSON, plain text and even EBML may be used.
- The
XMLhttpRequest object is used to asynchronously exchange data with the server. In some AJAX frameworks and in certain situations, the IFrame object is used to exchange data with the server, in others dynamically added "script" tag may be used.
As stated above, AJAX is not a technology in itself. It is like DHTML that refers to a number of technologies (markup language (such as HTML), a client-side scripting language (such as JavaScript), a presentation definition language (Cascading Style Sheets, CSS), and a Document Object Model.). The main element of AJAX is XMLhttpRequest that allows browsers to make dynamic and asynchronous requests to the server without having to reload the page. The XmlHttpRequest can eliminate the need for page refreshes and the other technologies get more prominently used and highlighted with this development approach. When the XMLHttpRequest object is used, the extensive use of JavasSript, CSS and DOM get more important and are used in conjunction to provide a more advanced "single-page" experience. The other technologies are lumped in this term because of their relationship to user experience when they are combined with XMLHttpRequest.
The reason for using AJAX
The most obvious reason for using AJAX is improved user experience. Pages that use AJAX behave more like a standalone application than typical web pages. Clicking on links that cause the entire page to reload looks like a heavy operation. With AJAX, the page often can be updated dynamically, allowing faster response to user interaction. Some people believe that it will prove to be an important technology and will make the web much better than it currently is.
The AJAX implementation
In the current sample of the project, I used the AJAX development approach to dynamically display and interact with the information presented. I decided to couple the JavaScript Grid and Web Service from my previous articles. This article shows how it's simple to use my JavaScript Grid along with AJAX on client side. Since the client and server code were done, all that I needed to do is to couple it into one application. It is pretty simple to introduce the Grid into a web application. I needed a proxy class on client side that would deal with the web service. I created three classes ProxyHelper, CustomerProxy and OrderProxy. The ProxyHelper class is a utility class, both CustomerProxy and OrderProxy classes use this class to send a SOAP request to web service.
function ProxyHelper()
{
var httpObj = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
httpObj.onreadystatechange = onReadyStateChange;
var thisRef = this;
this.onDataLoaded;
this.send = function(strRequest , soapAction, servicePath)
{
httpObj.open("POST", servicePath, true);
httpObj.setRequestHeader("SOAPAction",soapAction );
httpObj.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "text/xml; charset=utf-8");
httpObj.send(strRequest);
}
function onReadyStateChange()
{
if(httpObj.readyState == 4)
{
if(httpObj.status == 200)
{
if(thisRef.onDataLoaded!=null)
{
httpObj.responseXml.setProperty("SelectionLanguage", "XPath");
thisRef.onDataLoaded(httpObj.responseXml);
}
}
else
{
alert("Status: "+httpObj.statusText+".\nResponseText:
"+httpObj.responseText);
}
}
}
}
Both customerProxy and orderProxy classes have two events: onDeserialized, onXmlDataLoaded that are fired on receiving the data from web service. These classes also have the corresponding methods to call the web service methods such as "CreateCustomer, CreateOrder, UpdateOrder, GetCustomers and so on". The methods have the same signatures as the web service methods.
The onXmlDataLoaded event fires when the XML data has been loaded, while onDeserialized event fires when the XML data has been loaded and deserialized into an object. The onXmlDataLoaded has an argument XMLDocument and onDeserialized has a deserialized XML into an object as an argument.
function CustomerProxy()
{
var path = "../Server/Customer.asmx";
var proxyHelper = new ProxyHelper();
proxyHelper.onDataLoaded = onDeserialize;
var thisRef = this;
this.onDeserialized;
this.onXmlDataLoaded;
function onDeserialize(responseXml)
{
if(thisRef.onXmlDataLoaded!=null)
thisRef.onXmlDataLoaded(responseXml);
if(thisRef.onDeserialized==null)
return;
thisRef.onDeserialized(deserializeXML(responseXml));
}
this.getCustomers = function()
{
var soapRequest = "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"utf-8\"?>";
soapRequest += "<soap:Envelope
xmlns:xsi=\"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance\" ";
soapRequest += " xmlns:xsd=\http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema\
xmlns:soap=\"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/\"> ";
soapRequest += " <soap:Body><GetCustomers
xmlns=\"http://tempuri.org/\" /></soap:Body></soap:Envelope>";
proxyHelper.send(soapRequest,"http://tempuri.org/GetCustomers",path);
}
...
}
I wrote the simple utility function called "deserializeXML" on the client side that converted the XML into a js object.
function deserializeXML(responseXml)
{
var result = responseXml.documentElement.selectSingleNode
("./child::*/child::*/child::*");
if(result.firstChild==null)
return emptyResponse;
if(result.firstChild.nodeType==1)
{
var resultArray = new Array();
for(var index = 0; index < result.childNodes.length; index++)
{
resultItem = result.childNodes[index];
var customer = new Object();
for(var index1 = 0; index1 < resultItem.childNodes.length;
index1++)
{
customer[resultItem.childNodes[index1].nodeName] =
resultItem.childNodes[index1].text;
}
resultArray.push(customer);
}
return resultArray;
}
else
return result.firstChild.nodeValue;
}
I used a similar approach when working on the server side, especially on XMLRepository dataSource. I needed to save a transfer object into XML. I wrote the utility class that had two static methods.
public class Serialization
{
public static T FillObjectFromXMLDoc<T>(XmlDocument xmlDoc)
{
using (MemoryStream memoryStream = new MemoryStream())
{
StreamWriter streamWriter = new StreamWriter(memoryStream);
streamWriter.Write(xmlDoc.OuterXml);
streamWriter.Flush();
XmlSerializer serilazer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(T));
memoryStream.Position = 0;
T obj = (T)serilazer.Deserialize(memoryStream);
return obj;
}
}
public static XmlDocument FillXmlDocFromObject<T>(T obj)
{
using (MemoryStream memoryStream = new MemoryStream())
{
StreamReader streamReader = new StreamReader(memoryStream);
XmlSerializer serilazer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(T));
serilazer.Serialize(memoryStream,obj);
memoryStream.Position = 0;
XmlDocument xmlDoc = new XmlDocument();
xmlDoc.LoadXml(streamReader.ReadToEnd());
return xmlDoc;
}
}
}
Using the proxy classes
function onGridCustomerUpdated(rowItem)
{
var customerProxy = new CustomerProxy();
customerProxy.onDeserialized = onServerCustomerUpdated;
customerProxy.onXmlDataLoaded = onShowResponseXml;
customerProxy.updateCustomer(rowItem.id,rowItem["Company Name"],
rowItem["Contact Name"], rowItem["Contact Title"],
rowItem["Address"] , rowItem["City"],rowItem["Region"],
rowItem["Postal Code"], rowItem["Country"] ,
rowItem["Phone"] , rowItem["Fax"]);
}
function onServerCustomerUpdated(result)
{
if(result!="true")
alert("Failure to save the data.");
}
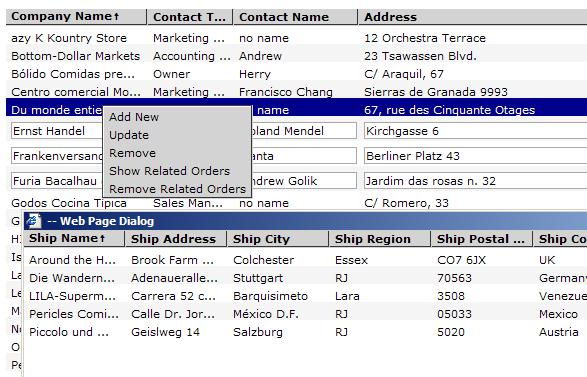
The onGridCustomerUpdated is the event handler of grid.onRowUpdated event. You can find all information regarding the Grid event model in Grid's article.
Links
Note
Please don't use this code AS IS in your projects. It's just a demo version that deals with data and needs to be tested well.
If you find this article interesting, please vote for me.
