Author's Note
This three-part article is an adaptation of one of the tutorials found in MSDN library for creating a sequential workflow ( http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms734794.aspx). The main purpose of re-producing the same sample here is to give readers more clarity and explanation in performing the steps to create a workflow. Most of my friends and community peers have expressed a deep sense of dissatisfaction in understanding the steps defined in the workflow creation process. They have cited certain sample pages which are thoroughly imprecise and not clear enough to follow through the steps.
The MSDN tutorial consists of three exercises featured in these URLs:
In this article, keeping the major exercises intact, I have explained the steps, tasks, and coding parts in detail, and included a few diagrams so that it would be easier for anyone to start with creating a sequential workflow.
Introduction
This sample application is a Simple Expense Report that consists of a text field to enter an amount and a button to submit the expense report. The workflow uses rules to evaluate the amount and to require approval from a lead if the amount is less than 1000, or approval from a manager if the amount is greater than or equal to 1000. If approval is needed, the workflow communicates back to the application and displays a drop-down panel that contains Approve and Reject buttons. When one of these buttons is clicked, the application notifies the workflow of the response, and the workflow continues to process the event.
This walk-through contains three major steps and sub-tasks under each step:
- Create Expense Report Project.
- Create a Windows Application
- Create the Sequential Workflow
- Host the Sequential Workflow
- Create Expense Report Service.
- Define the Workflow Parameters
- Define the IExpenseReportService Interface
- Create Expense Report Sequential Workflow Class Library
- Create the CallExternalMethod Activities
- Create the HandleExternalEvent Activities
1. Create Expense Report Project
Create a Windows Application
In Visual Studio 2005, select New Project; under C# project types, select Windows Application.
Change the name of the default form to "MainForm" that appears in the project, drag and drop the controls as required, and design the layout as in the figure below.
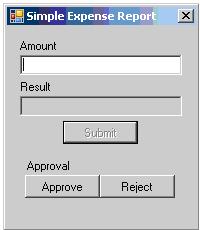
Here is a table of controls and their properties defined in the form.
Control
| Property
| Value
|
Form
| Name
| MainForm
|
| Text
| Simple Expense Report
|
Label
| Name
| Label1
|
| Text
| Amount
|
Label
| Name
| Label2
|
| Text
| Result
|
TextBox
| Name
| amount
|
| Text
| |
TextBox
| Name
| result
|
| Text
| |
Label
| Name
| ApprovalState
|
| Text
| Approval
|
Button
| Name
| submitButton
|
| Text
| Submit
|
| | |
Button
| Name
| approveButton
|
| Text
| Approve
|
| | |
Button
| Name
| rejectButton
|
| Text
| Reject
|
Panel
| Name
| Panel1
|
Add approveButton and rejectButton inside panel1.
Add two event handler methods for the KeyPress and TextChanged events of the amount textbox.
private void amount_KeyPress(object sender, KeyPressEventArgs e)
{
if (!Char.IsControl(e.KeyChar) && (!Char.IsDigit(e.KeyChar)))
e.KeyChar = Char.MinValue;
}
private void amount_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
submitButton.Enabled = amount.Text.Length > 0;
}
Ensure that you have replaced the code in Program.cs that runs the application's default form.
Application.Run(new MainForm());
And finally, to complete this first step, add references to the following assemblies.
- System.Workflow.Activities
- System.Workflow.ComponentModel
- System.Workflow.Runtime
Build the application.
Create a Sequential Workflow
In Visual Studio 2005, select New Project from menu; under C# project types, select Workflow, and on the right-side panel of templates, choose Sequential Workflow Library.
Name the project ExpenseReportWorkflow.
In the Workflow designer file (Workflow1.designer.cs) created by default, modify the code in the IntializeComponent method as below:
this.Name = "ExpenseReportWorkflow";
this.CanModifyActivities = false;
Build the project.
Host the Sequential Workflow
To execute a workflow, you must create an instance of the WorkflowRuntime class. Then, create a host class and pass in the type specification of your workflow by using the CreateWorkflow method. You can then call the Start method from the returned WorkflowInstance object to start executing your workflow. Because a sequential workflow does not rely on an external event to execute, it will begin immediately.
To host the Windows Workflow runtime engine
Go back to your Windows application, and add a reference to the class library (ExpenseReportWorkflow.dll) you have just created in the previous task.
In the MainForm class, declare the fields as below:
private WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime = null;
private WorkflowInstance workflowInstance = null;
In the constructor method, after the call to the InitializeComponent method, add the following code. This would start the runtime but does not execute any workflows until the application notifies it to start a workflow.
this.workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime();
workflowRuntime.StartRuntime();
Create a generic event handler for the WorkflowCompleted event of the workflowRuntime object.
workflowRuntime.WorkflowCompleted +=
new EventHandler<WorkflowCompletedEventArgs>
(workflowRuntime_WorkflowCompleted);
And, also add the corresponding event handler method.
void workflowRuntime_WorkflowCompleted(object sender,
WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e)
{
}
In the submitButton_Click method, create a local Type object equal to the type of the workflow that you created in the previous task. Create the workflow object for that type and start it.
Type type = typeof(ExpenseReportWorkflow);
workflowInstance = workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow(type);
workflowInstance.Start();
Now, build the project again.
2. Create Expense Report Service
To enable communication between your Windows Forms application and your sequential workflow, define an interface marked with ExternalDataExchangeAttribute and implement that interface in your form class. To make communication between the form and the workflow easier, you will use ExternalDataExchangeService by adding the Windows form class as a service that your workflow can access.
Define the Workflow Parameters
The first task in this exercise is to create two properties in the workflow. These properties enable you to pass parameters from the Windows Forms application or to receive parameters from the workflow.
The host application can set that property before the workflow executes by passing in a parameters collection during the CreateWorkflow method call. To return parameters back to the host application after it finishes executing, you can define a get method for the property. The host application can then access the WorkflowCompletedEventArgs object that is passed to the WorkflowCompleted event. The WorkflowCompletedEventArgs object contains all the properties defined in the workflow that contain get methods.
In the workflow class in your ExpenseReportWorkflow class library project, include a property named "amount" with a set accessor.
private int reportAmount = 0;
public int Amount
{
set
{
this.reportAmount = value;
}
}
Include another property named Result with a get accessor.
private string reportResult = "";
public string Result
{
get
{
return this.reportResult;
}
}
Back to your Windows application, SimpleExpenseReport; in submitButton_Click, modify the code as below.
Type type = typeof(ExpenseReportWorkflow.ExpenseReportWorkflow);
Dictionary<string, object> properties =
new Dictionary<string, object>();
properties.Add("Amount", Int32.Parse(this.amount.Text));
workflowInstance = workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow(type, properties);
workflowInstance.Start();
The new code would create a workflow instance for the ExpenseReportWorkflow type and the amount property added in the Dictionary object.
In the workflowRuntime_WorkflowCompleted method in the MainForm class, display the result returned by the workflow and clear the amount text field.
if (this.result.InvokeRequired)
{
this.result.Invoke(new EventHandler<WorkflowCompletedEventArgs>
(this.workflowRuntime_WorkflowCompleted), sender, e);
}
else
{
this.result.Text = e.OutputParameters["Result"].ToString();
this.amount.Text = string.Empty;
}
Build the project once again to check for errors, if any.
Define the IExpenseReportService Interface
In this second task, define the service interface mentioned earlier and implement the methods that the workflow uses to call a method that is defined in the Windows Form class. Additionally, two events are defined for the host application to notify the workflow when certain events occur. This would enable the host application and workflow to communicate each other.
Add a new interface file in the ExpenseReportWorkflow project by selecting Project -> Add New Item -> Interface.
To decorate the interface with the ExternalDataExchange attribute, import the namespace as below.
using System.Workflow.Activities;
[ExternalDataExchange]
public interface IExpenseReportService
{
void GetLeadApproval(string message);
void GetManagerApproval(string message);
event EventHandler<ExternalDataEventArgs> ExpenseReportApproved;
event EventHandler<ExternalDataEventArgs> ExpenseReportRejected;
}
Modify the MainForm class so that it implements the IExpenseReportService interface.
public class MainForm : Form, IExpenseReportService
Add the following delegate declaration and declare the events that occur during the running of the form. Remember that we have two buttons "accept" and "reject" in the form to raise the appropriate events.
private delegate void GetApprovalDelegate(string message);
private event EventHandler<ExternalDataEventArgs> reportApproved;
private event EventHandler<ExternalDataEventArgs> reportRejected;
Also, add the event handlers for both the events.
public event EventHandler<ExternalDataEventArgs> ExpenseReportApproved
{
add
{
reportApproved += value;
}
remove
{
reportApproved -= value;
}
}
public event EventHandler<ExternalDataEventArgs> ExpenseReportRejected
{
add
{
reportRejected += value;
}
remove
{
reportRejected -= value;
}
}
The next thing you do is very important. Since the form is an implementation of the service IExpenseReportService, it should be added to the ExternalDataExchangeService class.
To do so, create an instance for ExternalDataExchangeService in the MainForm class.
private ExternalDataExchangeService exchangeService = null;
Modify the code in the constructor method as below.
this.workflowRuntime = new WorkflowRuntime();
this.exchangeService = new ExternalDataExchangeService();
workflowRuntime.AddService(exchangeService);
exchangeService.AddService(this);
workflowRuntime.StartRuntime();
Implement the two methods defined in the IExpenseReportService in the MainForm class.
public void GetLeadApproval(string message)
{
}
public void GetManagerApproval(string message)
{
}
Build the project and check for errors.
Create Expense Report Sequential Workflow ClassLibrary
The workflow starts with "IfElseActivity" to determine whether a manager or a lead person must approve the value specified in the Amount property that was set when the workflow began executing.
After it determines this, the workflow calls a method defined in the host application to request user input for approval or rejection of the amount. When the Approve or Reject button is clicked, the host application raises the corresponding event, which is handled by one of the HandleExternalEventActivity activities that the workflow is waiting for. As soon as one of the events is raised and handled by the workflow, the workflow sets the Result property and completes its processing.
Create the CallExternalMethod Activities
Open the workflow designer in the ExpenseReportWorkflow project, and drag the "IfElseActivity" control from the toolbox.
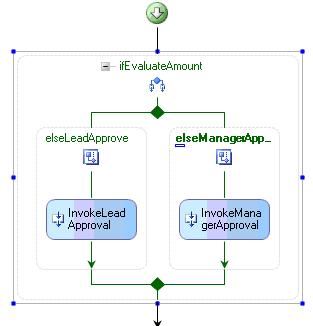
Drag the CallExternalMethodActivity from the toolbox and drop it in the if branch of IfElseActivity. Drag another CallExternalMethodActivity from the toolbox and drop it in the else branch of IfElseActivity.
Name the Activities appropriately as given below.
Type
| Name
|
IfElseActivity
| ifEvaluateAmount
|
IfElseBranchActivity
| elseLeadApprove
|
IfElseBranchActivity
| elseManagerApprove
|
CallExternalMethodActivity
| invokeLeadApproval
|
CallExternalMethodActivity
| invokeManagerApproval
|
Select the elseLeadApprove rectangular box and press F4 to open the properties window. Set the "Condition" property to "Code Condition". Expand the "Condition" property.
Set the value of the Condition as DetermineApprovalContact.
Write a helper method in the same name as below.
void DetermineApprovalContact(object sender, ConditionalEventArgs e)
{
if (this.reportAmount < 1000)
{
e.Result = true;
}
else
{
e.Result = false;
}
}
Now, set the properties for the CallExternalMethodActivity boxes as well.
Select the invokeLeadApproval box, and set the following properties:
Property
| Value
|
Interface
| SimpleExpenseReport.IExpenseReportService (to do this, click the ellipse button at the corner of the property, select the type in the dialog shown)
|
message
| "Lead Approval needed"
|
MethodName
| GetLeadApproval (click the drop-down list and select this method)
|
Select the invokeManagerApproval box, and set the following properties:
Property
| Value
|
Interface
| SimpleExpenseReport.IExpenseReportService (to do this, click the ellipse button at the corner of the property, select the type in the dialog shown)
|
message
| "Manager Approval needed"
|
MethodName
| GetManagerApproval (click the drop-down list and select this method)
|
Add the code to the two methods defined in the IExpenseReportService in the MainForm class as below:
public void GetLeadApproval(string message)
{
if (this.approvalState.InvokeRequired)
this.approvalState.Invoke(new GetApprovalDelegate
(this.GetLeadApproval), message);
else
{
this.approvalState.Text = message;
this.approveButton.Enabled = true;
this.rejectButton.Enabled = true;
this.Height = this.MinimumSize.Height + this.panel1.Height;
this.submitButton.Enabled = false;
}
}
public void GetManagerApproval(string message)
{
if (this.approvalState.InvokeRequired)
this.approvalState.Invoke(new GetApprovalDelegate
(this.GetManagerApproval), message);
else
{
this.approvalState.Text = message;
this.approveButton.Enabled = true;
this.rejectButton.Enabled = true;
this.Height = this.MinimumSize.Height + this.panel1.Height;
this.submitButton.Enabled = false;
}
}
Build the project and run the application. You should get the form displayed with the Approve and Reject buttons not working at this time.
Create the HandleExternalEvent Activities
In this task, you create a ListenActivity activity that contains two HandleExternalEventActivity activities to capture an approval or rejection event that is raised by the host application. When an approval or rejection event is raised, the workflow continues, sets the result, and then finishes.
Modify the ExpenseReportWorkflow class so that it can listen for specific events that the host application raises.
Create a new method that accepts an object named sender and an ExternalDataEventArgs named e as parameters.
void approveEvent_Invoked(object sender, ExternalDataEventArgs e)
{
this.reportResult = "Report Approved";
}
private void rejectEvent_Invoked(object sender,ExternalDataEventArgs e)
{
this.reportResult = "Report Rejected";
}
In the workflow designer, place the ListenActivity diagram by dragging it from the toolbox.
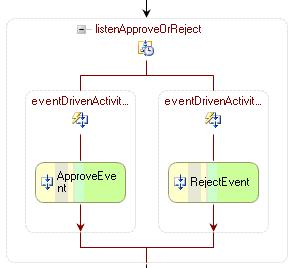
Drag the HandleExternalEvent Activity from the toolbox and drop it in both the EventDrivenActivitys.
Name the activities appropriately as below:
Type
| Name
|
ListenActivity
| listenApproveOrReject
|
EventDrivenActivity
| eventDriven1
|
EventDrivenActivity
| eventDriven2
|
HandleExternalEventActivity
| ApproveEvent
|
HandleExternalEventActivity
| RejectEvent
|
Select the ApproveEvent activity box, and press F4 to display the Properties window.
Property
| Value
|
InterfaceType
| SimpleExpenseReport.IExpenseReportService (to do this, click the ellipse button at the corner of the property, select the type in the dialog shown)
|
EventName
| ExpenseReportApproved
|
Invoked
| approveEvent_Invoked (click the drop-down list and select this method)
|
Select the RejectEvent Activity box, and press F4 to display the Properties window.
Property
| Value
|
InterfaceType
| SimpleExpenseReport.IExpenseReportService (to do this, click the ellipse button at the corner of the property, select the type in the dialog shown)
|
EventName
| ExpenseReportRejected
|
Invoked
| rejectEvent_Invoked (click the drop-down list and select this method)
|
The next step is to raise the event from the host application. To do so, add code to the approvebutton_Click handler.
(this.workflowInstance.InstanceId));
this.Height = this.MinimumSize.Height;
this.submitButton.Enabled = true;
Similarly, add code to the rejectbutton_Click handler.
reportRejected(null, new ExternalDataEventArgs (
this.workflowInstance.InstanceId));
this.Height = this.MinimumSize.Height;
this.submitButton.Enabled = true;
Build and run the application.
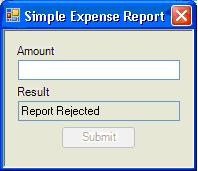
When you submit an expense report amount, the form expands to show the Approve and Reject buttons and a message that is received from the workflow. Clicking one of the buttons does the following:
- Collapses the form.
- Raises an event back to the workflow.
- Retrieves the
Results property from the workflow. - Displays it on the form.
This is the end of the walk-through for creating a sequential workflow.
