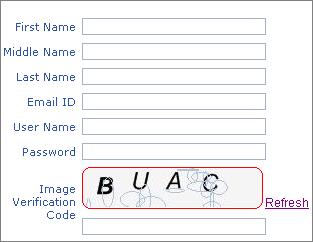
Introduction
This article describes how to create a custom control in ASP.NET for implementing image verification functionality. What is image verification? You might have
seen this implemented in many websites like microsoft.com, google.com, yahoo.com, etc., during the signup process. It's simply used for verifying the user's input,
by validating the code which the user enters against a random code displayed as image in the form. This helps the application to identify automated submission of forms
and reject such requests which could even crash the web site by inputting bulk data to the site.
Background
I saw this functionality implemented in various sites and thought of implementing it while creating a personal website. When I started implementing
the functionality in my site, I faced a few issues. Some of them generated random text, persisting the text so that it can be verified against the user input
code during post backs, avoid storing the generated code in viewstate or URLs etc. Gradually I found solutions to these issues. I will be explaining those solutions in the sections below.
Key Points
Explaining every piece of code used in the sample application is difficult to do in this article. Hence I will explain the following key steps involved
in the development of this custom control.
- Create a custom control capable of rendering
<img> tags. - Generate a random text, persist it, and render it as image.
- Verify the user input against the persisted random text.
Create a custom control to render <Img> tags
First of all, we need to create a custom control which can render the standard HTML <img> tags. It should also generate a dynamic URL and attach
it to the src attribute of the <img> tag generated.
This is done in the example by deriving a class named ImageVerifier from WebControl, as shown below.
namespace NatsNet.Web.UI.Controls
{
[DefaultProperty("Text")] [ToolboxData(
"<{0}:ImageVerifier runat="server">")]
public class ImageVerifier : WebControl, IHttpHandler
{
private string m_UniqueID = string.Empty;
public ImageVerifier(): base(HtmlTextWriterTag.Img) { }
private string MyUniqueID { ... }
public string Text { ... }
private string GetRandomText() { ... }
protected override void OnInit(EventArgs e) { ... }
protected override void LoadControlState(object savedState) { ... }
protected override object SaveControlState() { ... }
protected override void Render(HtmlTextWriter output) { ... }
public void ProcessRequest(HtmlTextContext context) { ... }
public bool IsReusable { ... }
}
}
In addition to deriving the control from WebControl, I have implemented IHttpHandler too in that class. This is for making the control
render the image itself in addition to the normal <img> tag rendering.
The rendering of the control happens inside the Render method.
protected override void Render(HtmlTextWriter output)
{
output.AddAttribute(HtmlTextWriterAttribute.Src,
"ImageVerifier.axd?uid=" + this.MyUniqueID);
base.Render(output);
output.Write("<script language="'javascript'">");
output.Write("function RefreshImageVerifier(id,srcname)");
output.Write("{ var elm = document.getElementById(id);");
output.Write(" var dt = new Date();");
output.Write(" elm.src=srcname + '&ts=' + dt;");
output.Write(" return false;");
output.Write("}</script>");
output.Write(" <a href='#' onclick=\"return RefreshImageVerifier('"
+ this.ClientID + "','ImageVerifier.axd?&uid="
+ this.MyUniqueID + "');\">Refresh</a>");
}
The first line in the Render method assigns the src attribute for the rendered <img> tag. It generates the URL
in the format "ImageVerifier.axd?uid=" + this.MyUniqueID. The control has a property MyUniqueID which will be a unique GUID generated
for each control instance. The last line of the Render method outputs a hyperlink to refresh the image without postback.
Generate a random text, persist it, and render it as image
For rendering a dynamic text as the image of this control, we will be using the same class ImageVerifier through the implementation of the IHttpHandler method
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context). This method will be called when the browser requests the URL specified in the src attribute
of the <img> tag rendered. In order to make this happen, we need to configure our ImageVerifier class as an HTTPHandler for URLs
like ImageVerifier.axd in the web.config file of the consuming application.
<httpHandlers>
<add
verb="GET"
path="ImageVerifier.axd"
type="NatsNet.Web.UI.Controls.ImageVerifier, NatsNet.Web.UI.Controls"
/>
</httpHandlers>
Shown below is the implementation of the ProcessRequest() method:
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
Bitmap bmp = new Bitmap(180, 40);
Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(bmp);
string randString = GetRandomText();
string myUID = context.Request["uid"].ToString();
if (context.Cache[myUID] == null)
context.Cache.Add( myUID,
randString,
null,
Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration,
TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5),
System.Web.Caching.CacheItemPriority.Normal,
null
);
else
context.Cache[myUID] = randString;
g.FillRectangle(Brushes.WhiteSmoke,0, 0, 180, 40);
g.SmoothingMode = System.Drawing.Drawing2D.SmoothingMode.Default;
g.TextRenderingHint = System.Drawing.Text.TextRenderingHint.AntiAlias;
Random rand = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < randString.Length; i++)
{
Font drawFont = new Font("Arial", 18,
FontStyle.Italic | (rand.Next() % 2 == 0 ?
FontStyle.Bold : FontStyle.Regular));
g.DrawString(randString.Substring(i,1), drawFont,
Brushes.Black, i * 35 + 10, rand.Next()% 12);
Point[] pt = new Point[15];
for (inti = 0; i < 15; i++)
{
pt[i] = newPoint(rand.Next() % 180, rand.Next() % 35);
g.DrawEllipse(Pens.LightSteelBlue,pt[i].X, pt[i].Y,
rand.Next() % 30 + 1, rand.Next() % 30 + 1);
}
context.Response.Clear();
context.Response.ClearHeaders();
context.Response.ContentType = "image/jpeg";
bmp.Save(context.Response.OutputStream, System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Jpeg);
context.Response.End();
}
}
In the ProcessRequest() method, a random text is generated using the private method GetRandomText() and is persisted using the Cache object
as shown above. The value of the query string uid will be used as the key for persisting the random text in the Cache object.
For generating random text of a specific length, we can write custom logic. Here in the sample, I have used the Random class to generate
random numbers and convert them to the corresponding characters. The same logic can be implemented in different ways as you wish.
private string GetRandomText()
{
string uniqueID = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
string randString = "";
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < uniqueID.Length && j < 5; i++)
{
char l_ch = uniqueID.ToCharArray()[i];
if ((l_ch >= 'A' && l_ch <= 'Z') || (l_ch >= 'a' &&
l_ch <= 'z') || (l_ch >= '0' && l_ch <= '9'))
{
randString += l_ch;
j++;
}
}
return randString;
}
Verify user input against the persisted random text
Finally, we need to validate the user input against the random text which is displayed as the image. For this, I have added a Text property for our user control.
This property retrieves the random text stored in the Cache and returns it. We can use this value to verify the user input.
public string Text
{
get
{
return string.Format("{0}",
HttpContext.Current.Cache[this.MyUniqueID]);
}
}
The code below shows an example of the code to be implemented in the consuming application for verifying the user input.
protected void btnSubmit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (txtImgVerifyText.Text == ImageVerifier1.Text)
{
}
else
{
}
}
Points of interest
In this article, I explained how to use the concept of image verification to help applications in identifying automated submission of forms. The implementation
of this image verification used a few coding concepts such as HTTPHandlers, Random class, Cache object, etc.
