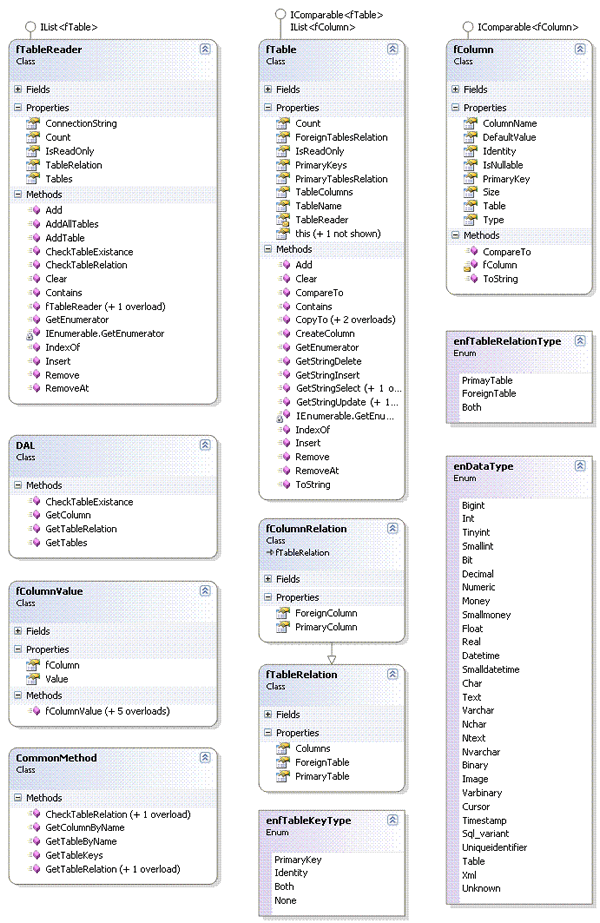
Introduction
Having the need to map database tables at runtime, columns, and relations, the basic is to know four properties about tables:
- Check if a table exists
- Get objects that represent which tables are in the database
- Know, for each table, which columns are Identity and/or Primary Keys, nullable, the datatype, the default value, and the size (depending on the datatype)
- The relationship between two or more tables
This article explains how the Class Library TableReader reads a database and returns its data map.
In the first version, it was only possible to read Tables, Columns, and Relations. In the second version, some Interfaces and methods were implemented to improve the usability and integration with other classes.
How it reads tables
This Class Library uses a SQL statement to read all the columns of a table, uses some native Stored Procedures to check if a table exists in the database, and reads all the tables and all the relations between the tables.
- Checking if a table exists in the database:
sp_tables @table_type = "'TABLE'", @table_name='The name of the Table to be checked'
To read more about "sp_tables", follow this link to MSDN: http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms186250.aspx.
Reading all the columns of a table:
SELECT c.COLUMN_NAME, c.IS_NULLABLE, c.DATA_TYPE, c.CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH,
tc.CONSTRAINT_TYPE, COLUMNPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID(c.TABLE_NAME),
c.COLUMN_NAME, 'IsIdentity') AS IS_AUTOINCREMENT, COLUMN_DEFAULT
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS c
LEFT JOIN INFORMATION_SCHEMA.KEY_COLUMN_USAGE kcu on
c.COLUMN_NAME = kcu.COLUMN_NAME AND c.TABLE_NAME = kcu.TABLE_NAME
LEFT JOIN INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_CONSTRAINTS
tc on kcu.CONSTRAINT_NAME = tc.CONSTRAINT_NAME
WHERE c.TABLE_NAME = 'The name of the Table to be read' BY c.ORDINAL_POSITION
Reading all the tables:
sp_tables @table_type = "'TABLE'"
Reading all the tables and all the relations between tables:
sp_fkeys @pktable_name = 'Primary Table', @fktable_name = 'Foreign Table'
To read more about "sp_fkeys", follow this link to MSDN: http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa933402(SQL.80).aspx.
Improvements
The classes are now Serializable
The fTableReader object can be serialized, added to ViewState, etc.
Added method to get the SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE SQL clauses for a table, based on a column-value pair
The fColumnValue class is used to relate columns with a string value.
A List<fColumn> is sent to these methods in order to filter a clause or attribute values.
List<fcolumnvalue> lstFcv = new List<fcolumnvalue>();
lstFcv.Add(new fColumnValue(MyfTableReader["myTableName"]["myColumnName1"],
"Value for Column 1"));
lstFcv.Add(new fColumnValue(MyfTableReader["myTableName"]["myColumnName2"],
"Value for Column 2"));
lstFcv.Add(new fColumnValue(MyfTableReader["myTableName"]["myColumnName3"]));
lstFcv.Add(new fColumnValue(MyfTableReader["myTableName2"]["myColumnName10"]));
string strSelect = "SELECT: " +
MyfTableReader["myTableName"].GetStringSelect(lstFcv);
string strUpdate = "UPDATE: " +
MyfTableReader["myTableName"].GetStringUpdate(lstFcv);
string strDelete = "DELETE: " +
MyfTableReader["myTableName"].GetStringDelete(lstFcv, true);
string strInsert = "INSERT: " +
MyfTableReader["myTableName"].GetStringInsert(lstFcv, false);
Added the IComparable<T> interface to fTable and fColumn so that they could be ordered by table name and column name, respectively
In order to alphabetically order the tables or columns by table name or column name, respectively, without having the need to use a delegate with a List of table or column names, the IComparable<T> interface was implemented to be able to sort with the Sort() method directly.
MyfTableReader.Tables.Sort();
MyfTable.TableColumns.Sort();
Added the IList<T> interface to fTableReader and fColumn so that they could be used as DataSource
In order to populate DropDownLists, RadioButtonLists, and others easily, the IList<T> interface was implemented.
ddlMyDropDownListTables.DataSource = MyTableReader;
ddlMyDropDownListTables.DataBind();
ddlMyDropDownListColumns = MyTableReader["MyTable"];
ddlMyDropDownListColumns.DataBind();
Using the Code
In order to use the TableReader, your project must be .NET 2.0 and needs a reference to the project source or the DLL.
This project is only compatible with SQL Server 2000/2005.
Using Generics to get the objects is very simple. Here is a sample code of how to use the TableReader to read the database and its tables.
The second version requires less code to get the objects and its properties. There is an example of the use of TableReader below:
fTableReader tr = new TableReader("server=Your SQL Server;Integrated " +
"Security=false;User Id=User Name;Password=Your Password;" +
"database=Your DataBase;Pooling=false;");
fTable newfTable1 = new fTable();
if (tr.CheckTableExistance("myTable"))
newfTable1 = tr.AddTable("myTable");
tr.AddAllTables();
fTable newfTable2 = tr["myTable"];
List<ftablerelation> lstTableRelation = newfTable1.ForeignTablesRelation;
List<fcolumn> lstFcolumn = newfTable1.PrimaryKeys;
Points of Interest
To know more, follow these links to MSDN:
History
v2.0 (18/10/2007)
- Added methods to get the
SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE SQL clauses for a table, based on a column-value pair. - Added the
IComparable<T> interface to fTable and fColumn so that they could be ordered by table name and column name, respectively. - Added the
IList<T> interface to fTableReader and fColumn so that it could be used as DataSource. - The classes are now
Serializable. - Added new properties and methods to classes.
- Bug fixes.
v1.0 (08/10/2007)
